Your Define senescence in plants images are available. Define senescence in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Define senescence in plants files here. Find and Download all free photos.
If you’re looking for define senescence in plants images information linked to the define senescence in plants topic, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our site always provides you with hints for seeking the highest quality video and image content, please kindly search and locate more informative video content and graphics that match your interests.
Define Senescence In Plants. Senescence is not confined only to whole plant. Senescence is widely recognized to occur among plants with a single reproductive event, but the extent to which. Introduction proteases were some of the first enzymes to be purified and their substrate specificity and kinetics studied. Some examples of this are:
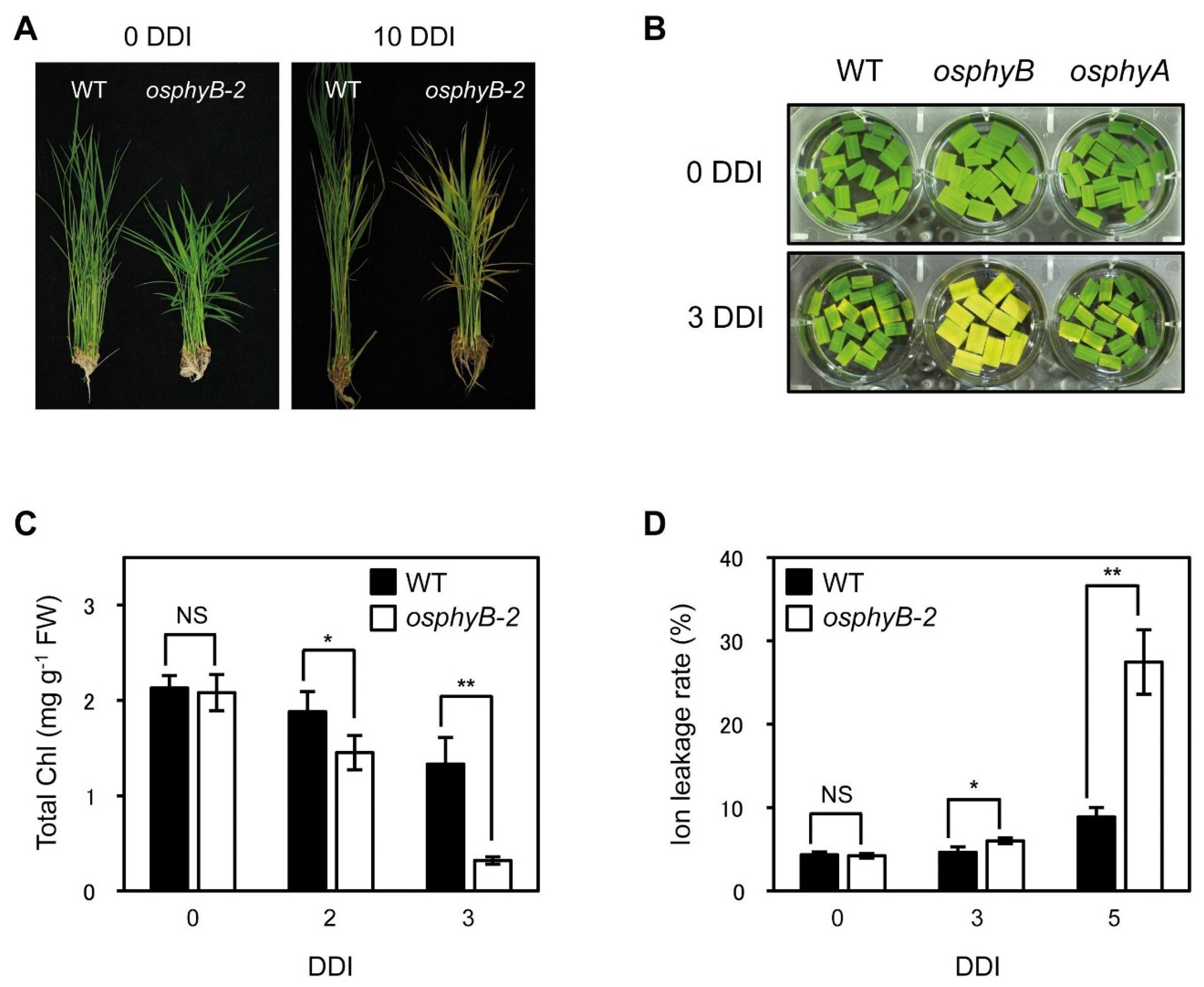 Plants Free FullText Rice Phytochrome B (OsPhyB From mdpi.com
Plants Free FullText Rice Phytochrome B (OsPhyB From mdpi.com
Senescence is the latter part of the development of flower, fruits and seeds in plants which leads from maturity to the ultimate complete loss of organisation and function. Plant senescence is a natural phenomenon known for the appearance of beautiful autumn colors and the ripening of cereals in the field. Environmental stress and plant senescence 5.3. Senescence and crop yield acknowledgements glossary bibliography biographical sketch summary senescence is a terminal stage of plant development. Similar to human beings, senescence in plants is the second last stage of their development. The growth of the vascular plant depends upon the activity of meristems, which are, in a sense, always embryonic.
Senescence may be defined as the period between reproductive maturity and death of a plant or a part of it.
Senescence ( / sɪˈnɛsəns /) or biological aging is the gradual deterioration of functional characteristics in living organisms. Example sentences learn more about senescence Senescence ( / sɪˈnɛsəns /) or biological aging is the gradual deterioration of functional characteristics in living organisms. Some examples of this are: Continued indefinitely, this mode of growth could mean immortality; Diseases and plant senescence 5.4.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Senescence is the latter part of the development of flower, fruits and seeds in plants which leads from maturity to the ultimate complete loss of organisation and function. Plants, just like other forms of organisms, seem to have both unintended and programmed aging. Senescence is a normal energy dependent developmental process which is controlled by plants own genetic programme and the death of the plant or plant part consequent to senescence is called as programmed cell death (pcd). Senescence defined as metaplasia clearly satisfies this requirement. Proteases, proteolytic activity, protein degradation, plant senescence, protein turnover.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
Senescence is a controlled process that plants utilize to. Senescence ( / sɪˈnɛsəns /) or biological aging is the gradual deterioration of functional characteristics in living organisms. The growth of the vascular plant depends upon the activity of meristems, which are, in a sense, always embryonic. Senescence and crop yield acknowledgements glossary bibliography biographical sketch summary senescence is a terminal stage of plant development. The optimal timing of the initiation and progression of senescence are thus prerequisites for.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Concepts and types of senescence in plants concepts, classification, and the relationship between different types of senescence are discussed in this chapter. It is characterized by a collective, progressive and deteriorative developmental process which ultimately leads to completeloss of organization and function of the plant or parts of it. Types of senescence leopold (1961) has proposed types of senescence patterns in plants which are as follows. Seasonal influences on plant senescence 5.2. Senescence is not confined only to whole plant.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Effects on the construction of transgenic plants for future research accomplishments and agricultural use. How much of what happens in terminal processes is transcription‐dependent? Senescence is not confined only to whole plant. Diseases and plant senescence 5.4. These cytological features define a form of pcd termed vacuolar cell death and share some characteristics of autophagy.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
The word senescence can refer to either cellular senescence or to senescence of the whole organism. Senescence is not confined only to whole plant. The growth phase in a plant or plant part (such as a leaf) from full maturity to death other words from senescence did you know? It is a heavily studied subject just as it is in the other kingdoms of life. Verified by toppr correct option is c) when a plant part undergoes senescence, nutrient resources (minerals and carbohydrates) shift away or are translocated from the senescened part to other parts.
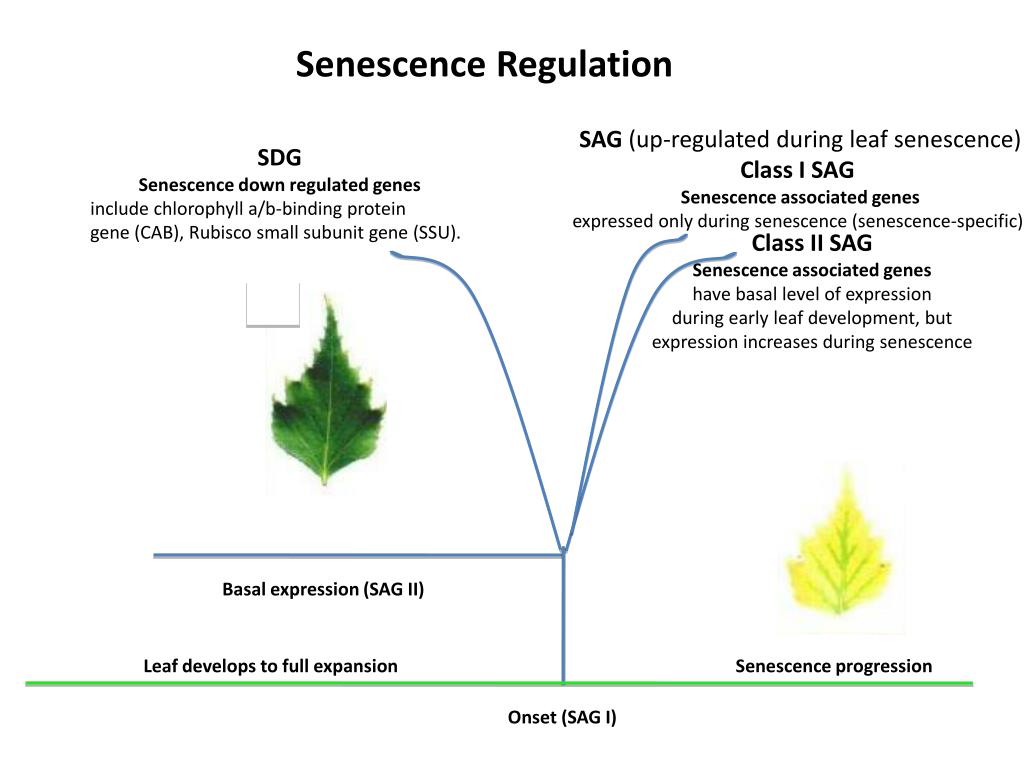 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
In a seminal article, leopold (1961) defined senescence in plant cells, along the lines previously proposed by medawar (1957), as ‘the deteriorative processes that are natural causes of death’. The optimal timing of the initiation and progression of senescence are thus prerequisites for. Some examples of this are: Moreover, senescence is essential for the fitness and survival of plants. Plant senescence is the study of aging in plants.
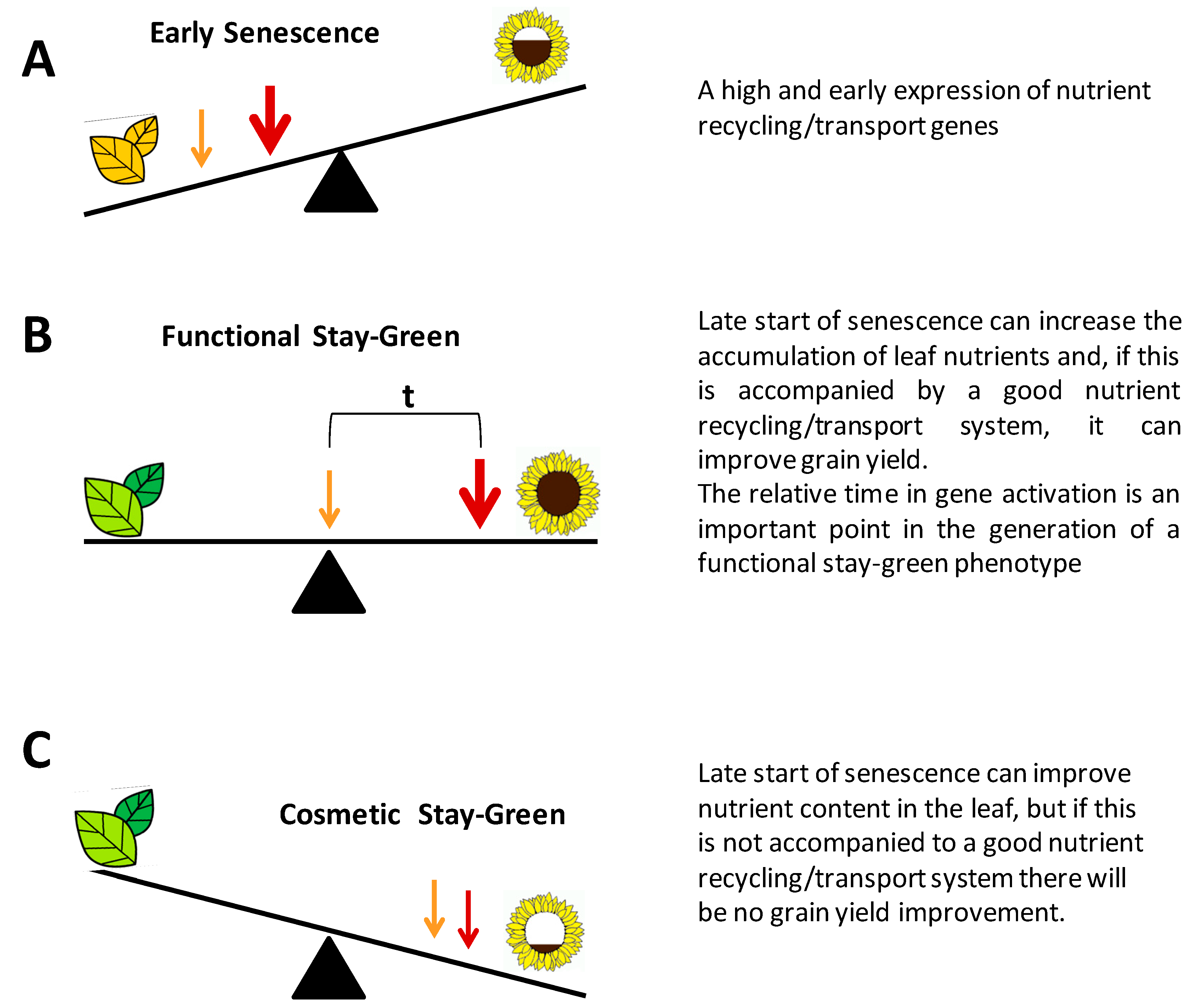 Source: kovodym.blogspot.com
Source: kovodym.blogspot.com
Plants, just like other forms of organisms, seem to have both unintended and programmed aging. Plant senescence is a natural phenomenon known for the appearance of beautiful autumn colors and the ripening of cereals in the field. Seasonal influences on plant senescence 5.2. Senescence is a phase of the aging process. It may be limited to a particular plant organ such as leaf and flowers or cells or cell, organelles.
 Source: jcs.biologists.org
Source: jcs.biologists.org
There is a confusion between ageing and senescence which should be clear. Proteases, proteolytic activity, protein degradation, plant senescence, protein turnover. Continued indefinitely, this mode of growth could mean immortality; Environmental stress and plant senescence 5.3. Concepts and types of senescence in plants concepts, classification, and the relationship between different types of senescence are discussed in this chapter.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Types of senescence leopold (1961) has proposed types of senescence patterns in plants which are as follows. ‘senescence […] refers to those changes that provide for the endogenous regulation of death. The word senescence can refer to either cellular senescence or to senescence of the whole organism. Senescence is a controlled process that plants utilize to. Example sentences learn more about senescence
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Aging, stress, and senescence in plants are interconnected processes that determine longevity. Example sentences learn more about senescence Senescence is a normal energy dependent developmental process which is controlled by plants own genetic programme and the death of the plant or plant part consequent to senescence is called as programmed cell death (pcd). Leaf senescence represents a key developmental process through which resources trapped in the photosynthetic organ are degraded in an organized manner and transported away to sustain the growth of other organs including newly forming leaves, roots, seeds, and fruits. Diseases and plant senescence 5.4.
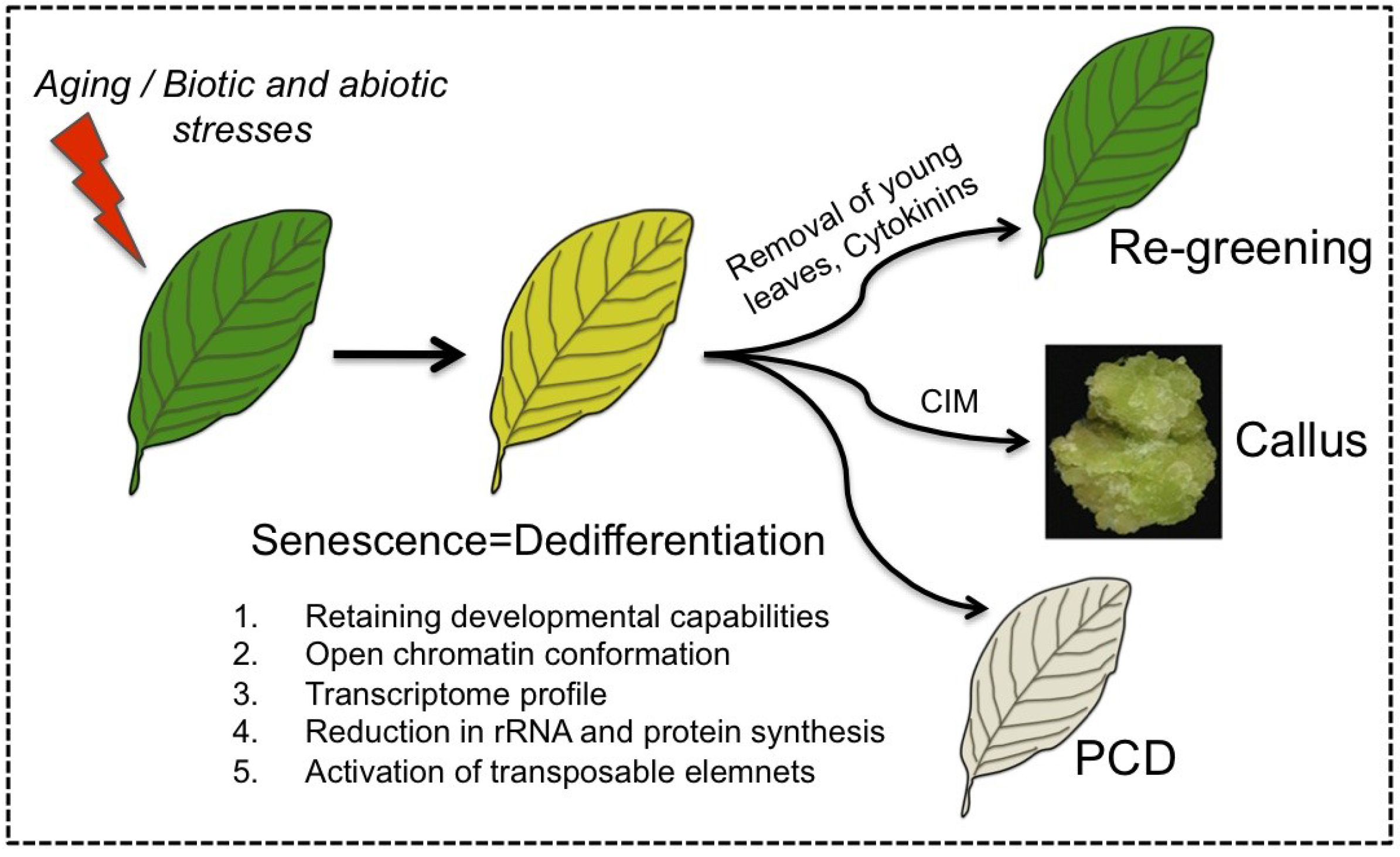 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Senescence is a phase of the aging process. ‘senescence […] refers to those changes that provide for the endogenous regulation of death. How much of what happens in terminal processes is transcription‐dependent? It is a heavily studied subject just as it is in the other kingdoms of life. It may be limited to a particular plant organ such as leaf and flowers or cells or cell, organelles.
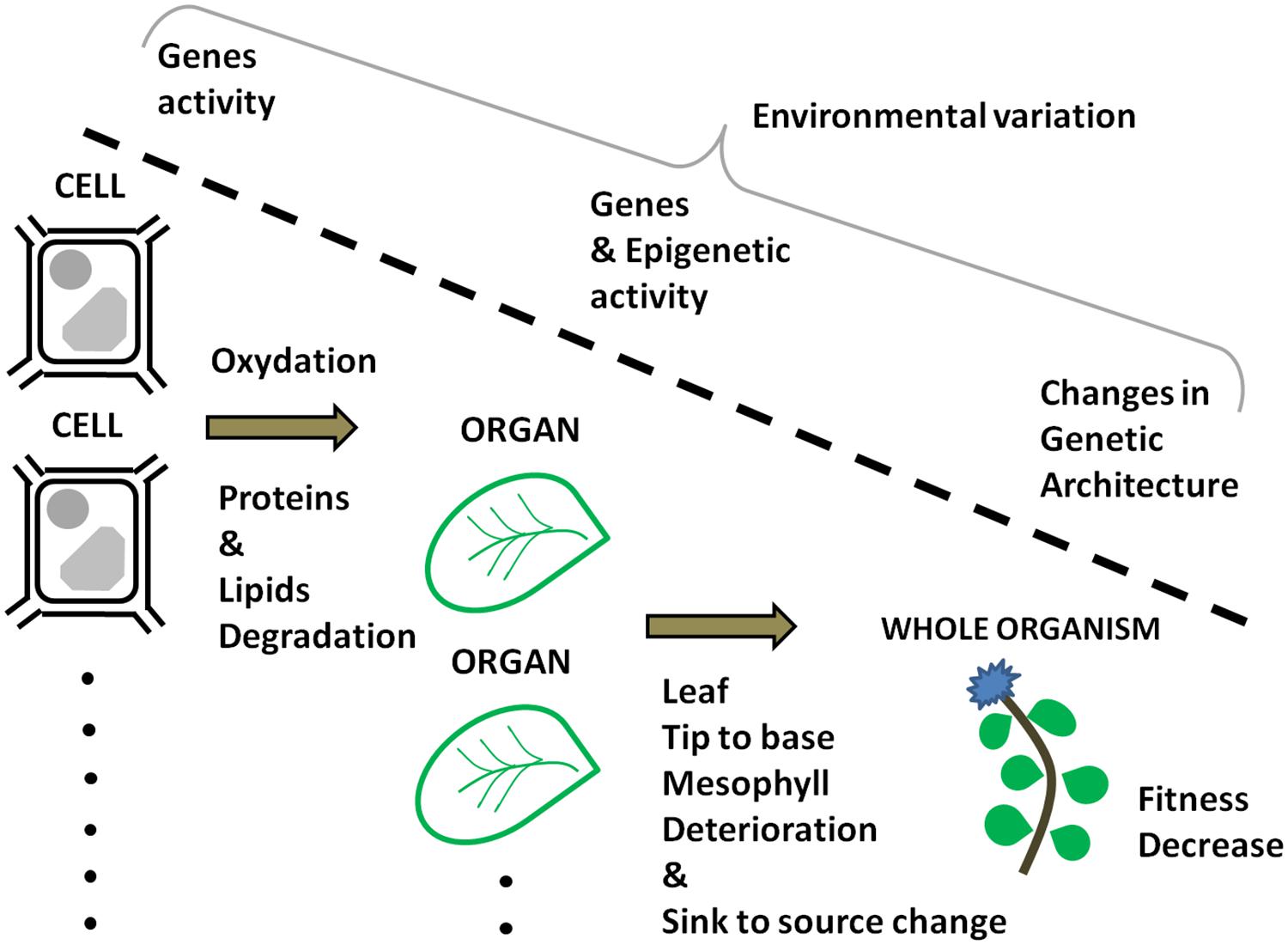 Source: journal.frontiersin.org
Source: journal.frontiersin.org
The growth phase in a plant or plant part (such as a leaf) from full maturity to death other words from senescence did you know? Senescence is not confined only to whole plant. Leaf senescence is the cause of autumn leaf color in deciduous trees. The optimal timing of the initiation and progression of senescence are thus prerequisites for. Plant senescence is the study of aging in plants.
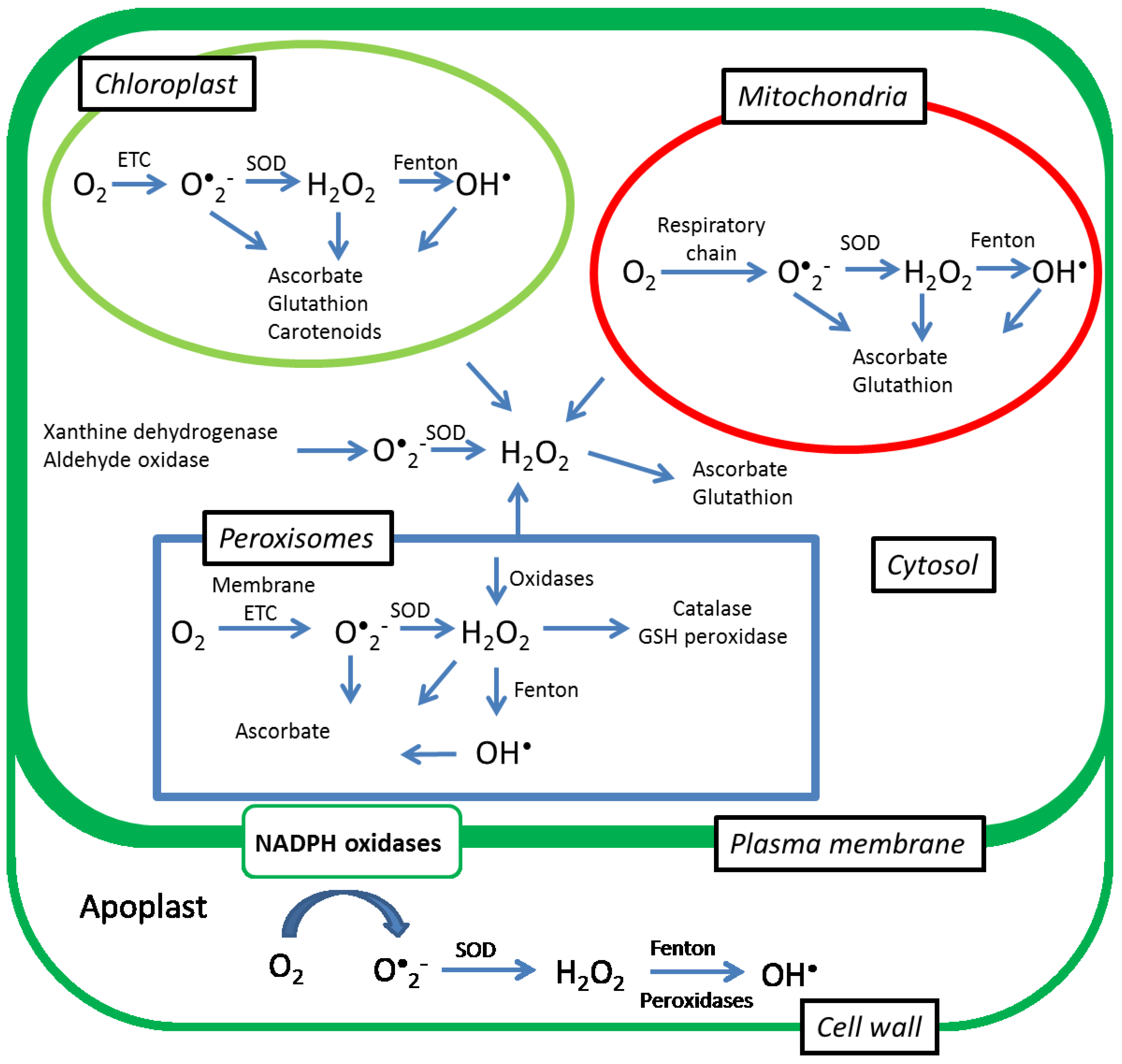 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
The growth of the vascular plant depends upon the activity of meristems, which are, in a sense, always embryonic. Example sentences learn more about senescence Types of senescence leopold (1961) has proposed types of senescence patterns in plants which are as follows. Senescence is a phase of the aging process. Similar to human beings, senescence in plants is the second last stage of their development.
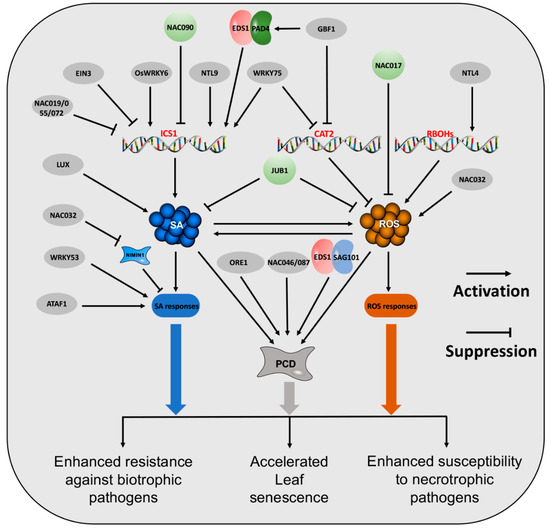 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Indeed, the longest lived individual organisms ever to have existed on earth have been certain species of trees. It is characterized by a collective, progressive and deteriorative developmental process which ultimately leads to completeloss of organization and function of the plant or parts of it. Effects on the construction of transgenic plants for future research accomplishments and agricultural use. Indeed, the longest lived individual organisms ever to have existed on earth have been certain species of trees. Senescence is a normal energy dependent developmental process which is controlled by plants own genetic programme and the death of the plant or plant part consequent to senescence is called as programmed cell death (pcd).
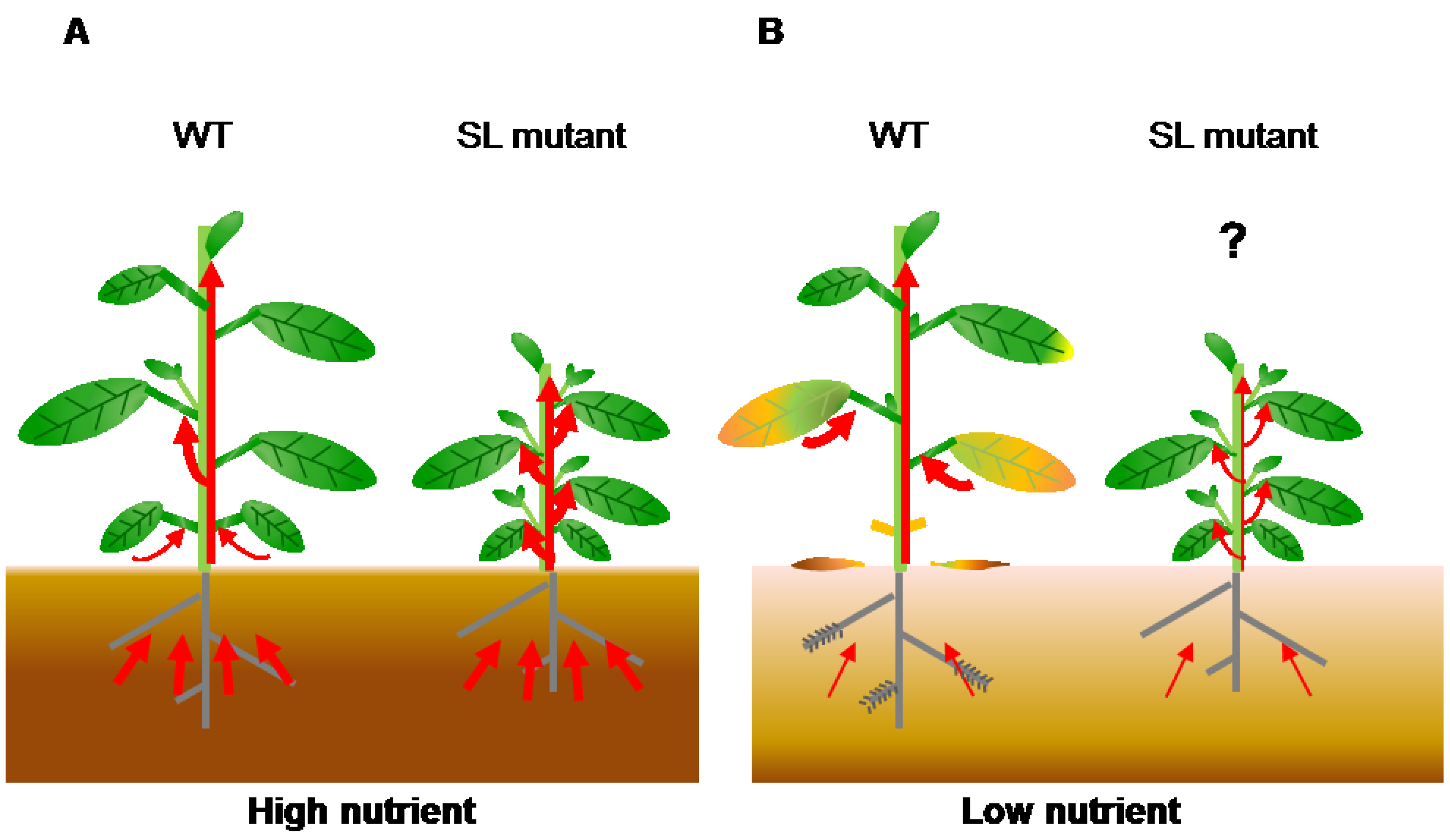 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
There is a confusion between ageing and senescence which should be clear. Effects on the construction of transgenic plants for future research accomplishments and agricultural use. Senescence is a normal energy dependent developmental process which is controlled by plants own genetic programme and the death of the plant or plant part consequent to senescence is called as programmed cell death (pcd). Senescence is a controlled process that plants utilize to. The major characteristic of senescence is that the metabolic processes are catabolic and eventually become irreversible and terminate to death.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Effects on the construction of transgenic plants for future research accomplishments and agricultural use. Proteases, proteolytic activity, protein degradation, plant senescence, protein turnover. It may be limited to a particular plant organ such as leaf and flowers or cells or cell, organelles. Seasonal influences on plant senescence 5.2. Senescence is a phase of the aging process.
 Source: nature.com
Source: nature.com
The major characteristic of senescence is that the metabolic processes are catabolic and eventually become irreversible and terminate to death. Senescence is a controlled process that plants utilize to. Medium open in app solution verified by toppr it is the process of aging in plants in which cells reach permanent growth arrest without the death of cells as the whole cell division process comes to a termination. These cytological features define a form of pcd termed vacuolar cell death and share some characteristics of autophagy. Senescence is widely recognized to occur among plants with a single reproductive event, but the extent to which.
 Source: plantphysiol.org
Source: plantphysiol.org
Senescence defined as metaplasia clearly satisfies this requirement. It may be limited to a particular plant organ such as leaf and flowers or cells or cell, organelles. Similar to human beings, senescence in plants is the second last stage of their development. Senescence is the latter part of the development of flower, fruits and seeds in plants which leads from maturity to the ultimate complete loss of organisation and function. Medium open in app solution verified by toppr it is the process of aging in plants in which cells reach permanent growth arrest without the death of cells as the whole cell division process comes to a termination.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title define senescence in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






