Your Epidermal cells in plants images are ready. Epidermal cells in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Epidermal cells in plants files here. Get all royalty-free photos.
If you’re looking for epidermal cells in plants pictures information linked to the epidermal cells in plants keyword, you have come to the right site. Our site always provides you with suggestions for viewing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video articles and images that match your interests.
Epidermal Cells In Plants. The cuticle, however, is located on the upper epidermis for the most part. Also question is, where is epidermal tissue found in plants? Various modified epidermal cells regulate transpiration, increase water absorption, and secrete substances. This range of function is performed by a number of different types of specialized cells, which differentiate from the early undifferentiated epidermis in adaptively significant patterns and frequencies.
 Stomata On Epidermis Of Rose Leaf Photograph by Power And From pixels.com
Stomata On Epidermis Of Rose Leaf Photograph by Power And From pixels.com
J, budding cells, like those of the yeast plant; 6, guard cells inclosing a breathing hole, or stomate^ on the. The plants were then transferred to a chloral hydrate solution for destaining. (in plants) the thin tissue, usually one cell thick, that surrounds young roots, stems and leaves. Following successful epidermal invasion, the invading hyphae extend in the intercellular space of the root cortex toward the vascular tissues. The plant epidermal cell is the primary stronghold that combats environmental pathogens;
In stems and leaves the epidermal cells secrete a cuticle (1), in roots they do not.
In plants leaves, epidermal cells are located on the upper and lower part of the leaf where they form the upper and lower epidermis. (in animals) the outer layer of the skin derived from embryonic ectoderm. A stoma is an opening (pore) which is bounded by two bean shaped cells called guard cells and two to four subsidiary cells that lack chloroplasts. They contain a thick covering of cutin, which reduces the water loss from plants. They provide a barrier which is almost totally impermeable to water, and yet can allow water to leave (and gas to enter) as effectively as if there were no epidermis at all. These three cell types, along with the function of the epidermis, will be.

The plants were then transferred to a chloral hydrate solution for destaining. They provide a barrier which is almost totally impermeable to water, and yet can allow water to leave (and gas to enter) as effectively as if there were no epidermis at all. The epidermis may be a single layer, as found in plants, or it may consist of many different layers as is the case of vertebrate animals. Analyzed, based on a new physical model, the functions of cellulose nanofibrils and matrix polysaccharides during elongation growth. 4, swimming spores of a water mold ;
 Source: sitn.hms.harvard.edu
Source: sitn.hms.harvard.edu
Epidermal cells are living cells covering the outside surface of the herbaceous plants. In plants, we call this specialized skin the epidermis.the epidermal cells that make up this skin. 3, moving ciliated cells, like those of typhoid bacilli; In leaves, the epidermal cell walls appear as sinuous in dicots and in monocots they appear as straight or sinuous in surface view. In plants leaves, epidermal cells are located on the upper and lower part of the leaf where they form the upper and lower epidermis.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
What is the function of epidermal tissue in plants? (in plants) the thin tissue, usually one cell thick, that surrounds young roots, stems and leaves. The plant epidermal cell is the primary stronghold that combats environmental pathogens; The cuticle, however, is located on the upper epidermis for the most part. Plant epidermal cells, such as trichomes, root hairs, salt glands, and stomata, play pivotal roles in the growth, development, and environmental adaptation of terrestrial plants.
 Source: scitechdaily.com
Source: scitechdaily.com
They provide a barrier which is almost totally impermeable to water, and yet can allow water to leave (and gas to enter) as effectively as if there were no epidermis at all. Made up of epidermal cells, the epidermis in plants also serves as a protective layer that not only prevents various microorganisms from gaining entrance into the underlying tissue of leaves and stems, but also prevents excess water loss among a few other functions. Certain epidermal cells protect the plant The cuticle, however, is located on the upper epidermis for the most part. They provide a barrier which is almost totally impermeable to water, and yet can allow water to leave (and gas to enter) as effectively as if there were no epidermis at all.
 Source: flickr.com
Source: flickr.com
The plastids are normally small and colourless. Their results indicate that stiff, ca. But the frequency of epidermal cells is higher in xerophytic plants (figure 8, figure 9, and figure 10) as shown above. The epidermal cells are more or less tabular (=horizontally flattened) in cross sectional view. This range of function is performed by a number of different types of specialized cells, which differentiate from the early undifferentiated epidermis in adaptively significant patterns and frequencies.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In plants, this is the outermost part that is secreted by the epidermis. The epidermal cells are living with lining layer of protoplast around large central vacuole. Certain epidermal cells protect the plant from herbivores while others attract the predators of those herbivores and still others are involved in attracting pollinating animals. What is the function of epidermal tissue in plants? The guard cells differ from normal epidermal cells in that they have chloroplasts and the cell walls are thickening unevenly;
 Source: carolina.com
Source: carolina.com
The epidermal cells are more or less tabular (=horizontally flattened) in cross sectional view. The epidermis and its waxy cuticle provide a protective barrier against mechanical injury, water loss, and infection. The inoculated cotyledons were mounted on a slide in 50% glycerol and observed under a light microscope (eclipse e100, nikon). The guard cells differ from normal epidermal cells in that they have chloroplasts and the cell walls are thickening unevenly; 3 nm wide cellulose fibrils, which form.

The plant epidermal cell is the primary stronghold that combats environmental pathogens; The inoculated cotyledons were mounted on a slide in 50% glycerol and observed under a light microscope (eclipse e100, nikon). Ad discover how you can evaluate the integrity and permeability of ali cultures in this video. (in animals) the outer layer of the skin derived from embryonic ectoderm. Epidermal cells in roots are specialized for water and ion absorption.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Humans and animals have specialized skin that covers and protects their bodies. Analyzed, based on a new physical model, the functions of cellulose nanofibrils and matrix polysaccharides during elongation growth. The plastids are normally small and colourless. The interlocking epidermal cells of a plant provide mechanical strength while still allowing growth and flex ibility. 4, swimming spores of a water mold ;
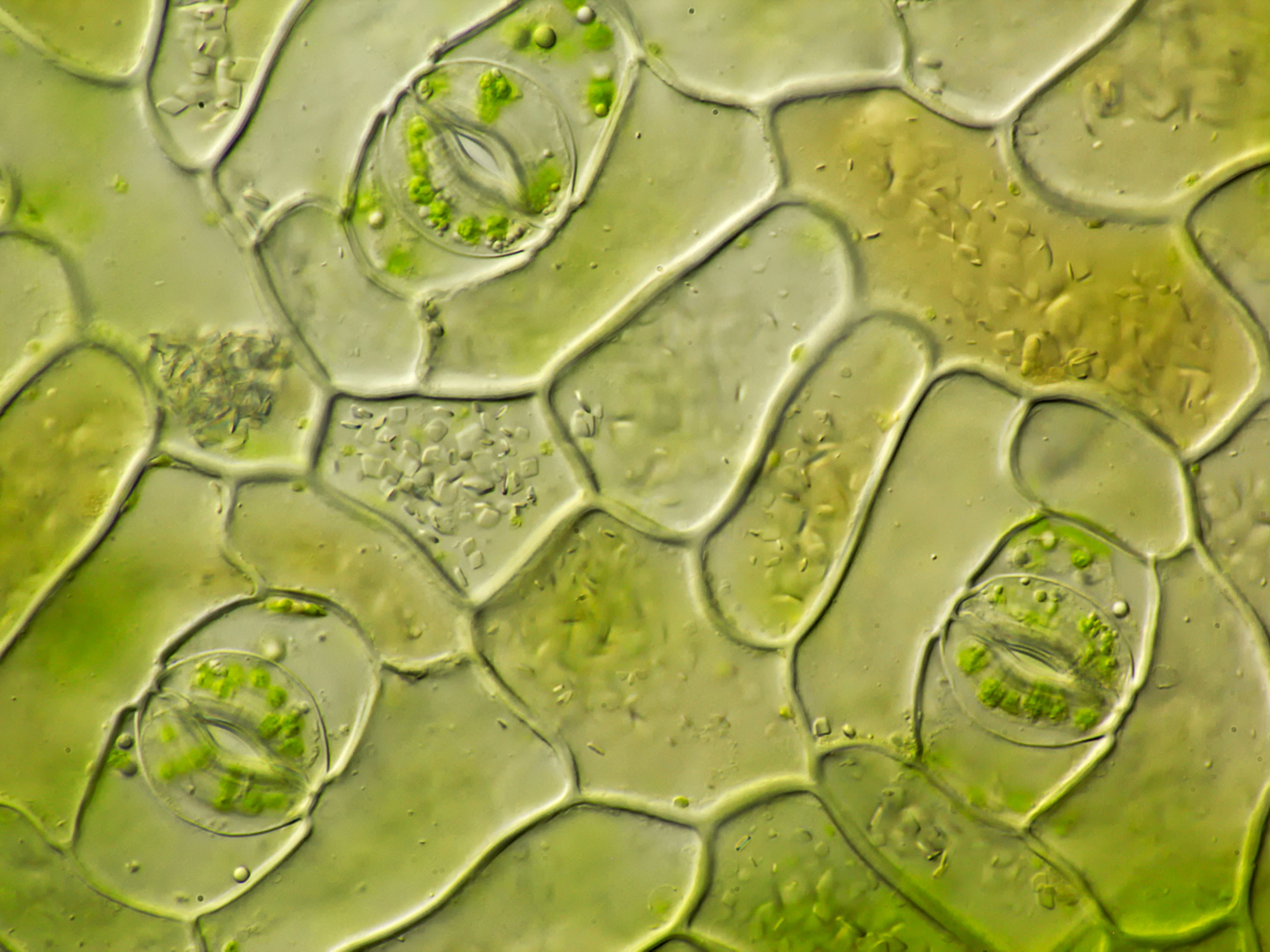 Source: microscopyofnature.com
Source: microscopyofnature.com
But the frequency of epidermal cells is higher in xerophytic plants (figure 8, figure 9, and figure 10) as shown above. In plants, this is the outermost part that is secreted by the epidermis. J, budding cells, like those of the yeast plant; The plant epidermis is a multifunctional tissue playing important roles in water relations, defence and pollinator attraction. They provide a barrier which is almost totally impermeable to water, and yet can allow water to leave (and gas to enter) as effectively as if there were no epidermis at all.
 Source: botanyprofessor.blogspot.com.au
Source: botanyprofessor.blogspot.com.au
The plastids are normally small and colourless. To detect the cell death of both epidermal and mesophyll cells, stained plants were incubated in chloral hydrate solution for 45 min. Also question is, where is epidermal tissue found in plants? Made up of epidermal cells, the epidermis in plants also serves as a protective layer that not only prevents various microorganisms from gaining entrance into the underlying tissue of leaves and stems, but also prevents excess water loss among a few other functions. They provide a barrier which is almost totally impermeable to water, and yet can allow water to leave (and gas to enter) as effectively as if there were no epidermis at all.
 Source: lookfordiagnosis.com
Source: lookfordiagnosis.com
In plants, this is the outermost part that is secreted by the epidermis. The epidermis and its waxy cuticle provide a protective barrier against mechanical injury, water loss, and infection. The plant epidermal cell is the primary stronghold that combats environmental pathogens; Various modified epidermal cells regulate transpiration, increase water absorption, and secrete substances. Pavement cells, guard cells, and their subsidiary cells.
 Source: pixels.com
Source: pixels.com
In plants leaves, epidermal cells are located on the upper and lower part of the leaf where they form the upper and lower epidermis. 3 nm wide cellulose fibrils, which form. The cuticle, however, is located on the upper epidermis for the most part. The inoculated cotyledons were mounted on a slide in 50% glycerol and observed under a light microscope (eclipse e100, nikon). They contain a thick covering of cutin, which reduces the water loss from plants.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In plants, we call this specialized skin the epidermis.the epidermal cells that make up this skin. In plants leaves, epidermal cells are located on the upper and lower part of the leaf where they form the upper and lower epidermis. A stoma is an opening (pore) which is bounded by two bean shaped cells called guard cells and two to four subsidiary cells that lack chloroplasts. The epidermis usually has a single layer. In stems and leaves the epidermal cells secrete a cuticle (1), in roots they do not.
 Source: sitn.hms.harvard.edu
Source: sitn.hms.harvard.edu
The epidermis usually has a single layer. Following successful epidermal invasion, the invading hyphae extend in the intercellular space of the root cortex toward the vascular tissues. Pavement cells, guard cells, and their subsidiary cells. The epidermal cell frequency differed a lot within the same surface and also on both the surfaces of the same leaf of the species. Humans and animals have specialized skin that covers and protects their bodies.

In many organs these different functions are fulfilled simultaneously by the activities of different specialized cells, and for those cells to function effectively they must be distributed in a. Epidermal cells in roots are specialized for water and ion absorption. Also question is, where is epidermal tissue found in plants? 4, swimming spores of a water mold ; Highest frequency is dominated at middle zone on both surface.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Various modified epidermal cells regulate transpiration, increase water absorption, and secrete substances. Epidermal cells in roots are specialized for water and ion absorption. Various kinds of plant cells /, epidermal, or skin, cells of a leaf, showing the outer wall greatly thickened, and the cuticle; In plants, this is the outermost part that is secreted by the epidermis. The 4d image series demonstrated that the apex of invading hyphae becomes tapered and directly invades the intercellular space of root epidermal cells at the initial infection.
 Source: luc.edu
Source: luc.edu
Certain epidermal cells protect the plant from herbivores while others attract the predators of those herbivores and still others are involved in attracting pollinating animals. The cuticle, however, is located on the upper epidermis for the most part. The cuticle, however, is located on the upper epidermis for the most part. Pavement cells, guard cells, and their subsidiary cells. The epidermis and its waxy cuticle provide a protective barrier against mechanical injury, water loss, and infection.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title epidermal cells in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







