Your Examples of plant tissues images are ready. Examples of plant tissues are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Examples of plant tissues files here. Get all royalty-free photos.
If you’re looking for examples of plant tissues images information connected with to the examples of plant tissues interest, you have pay a visit to the right site. Our website always provides you with suggestions for seeking the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video content and graphics that fit your interests.
Examples Of Plant Tissues. Xylem tissue transports water and nutrients from the roots to different parts of the plant, and includes three different cell types: Parenchyma is the main tissue of apples, pears, plums, and tomatoes. This classification is on the basis of parts of the plants they are present. The three fundamental tissue patterns seen in roots and stems that serve to distinguish between woody dicot, herbaceous dicot, and monocot plants are an excellent illustration of this.
 Plant and Animal Tissues MeitY OLabs YouTube From youtube.com
Plant and Animal Tissues MeitY OLabs YouTube From youtube.com
Transparent, one cell thick and is usually covered with cuticle usually has guard cells with stomata • found on the outermost layer of the plant body such as leaves, flowers, stem & roots • function is to protect the plant from dessication and infection. So, the correct answer is � all of these�. Dermal tissues, vascular tissues, and ground tissues. Xylem tissue transports water and nutrients from the roots to different parts of the plant, and includes three different cell types: Functions of connective tissue include shaping and supporting organs and the body, allowing body movement, and providing oxygen diffusion. It will especially be a help to those students who intend to take up biology as a career later on as getting the fundamentals right at an early stage will always come to one’s rescue when he/ she faces.
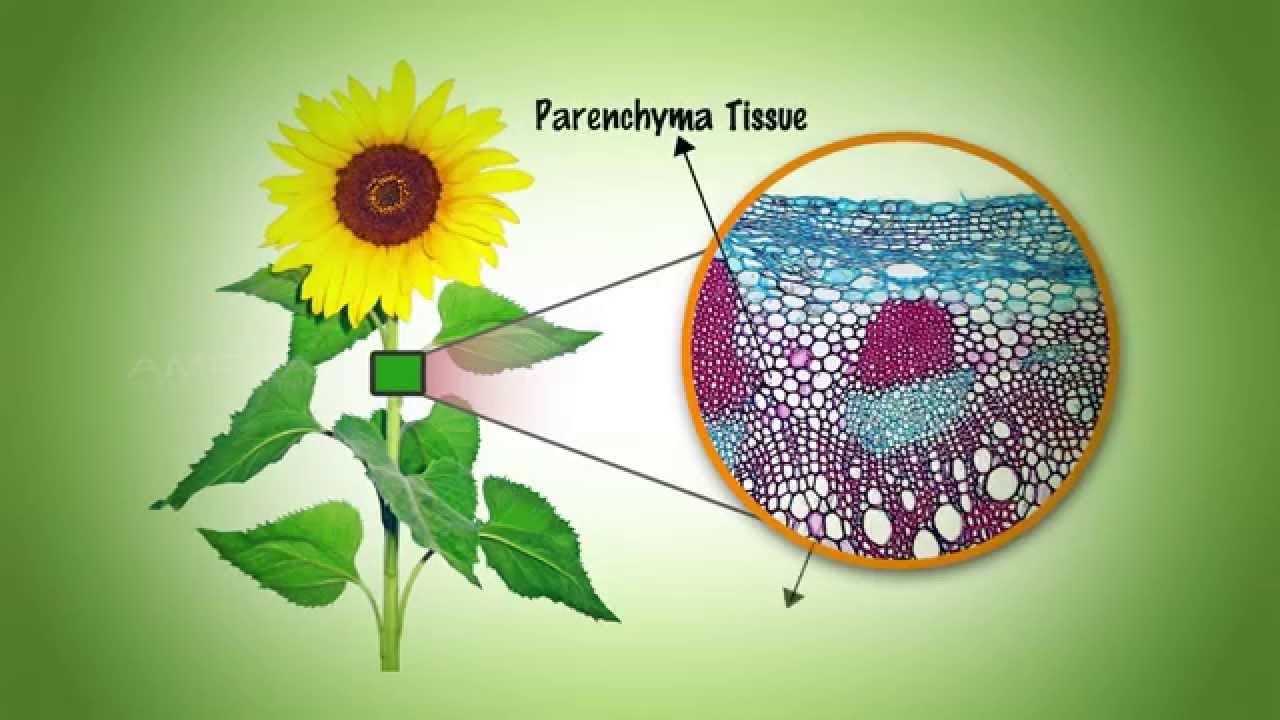
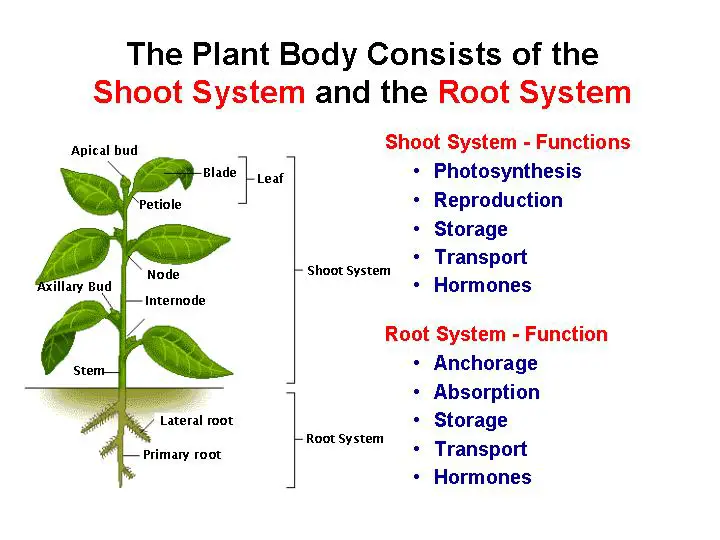
A plant body is made up of different kinds of tissue.
Plant leaves are adapted for photosynthesis, and the exchange of gases required for the process. It will especially be a help to those students who intend to take up biology as a career later on as getting the fundamentals right at an early stage will always come to one’s rescue when he/ she faces. Although it is very difficult to survive in the arctic, many low growing plants can be found there. Xylem tissue transports water and nutrients from the roots to different parts of the plant, and includes three different cell types: This plant tissue is commonly found in stems, bark, and in the hard shells of some fruits and nuts, such as pears. Plant leaves are adapted for photosynthesis, and the exchange of gases required for the process.
 Source: pmfias.com
Source: pmfias.com
Dermal tissues, vascular tissues, and ground tissues. Xylem and phloem are the two tissues of plants list two examples of tissues found in plants. Xylem is the tissue which is responsible for the transport of water in plants while the phloem is responsible for. This plant tissue is commonly found in stems, bark, and in the hard shells of some fruits and nuts, such as pears. Plant tissues are either simple (composed of similar cell types) or complex (composed of different cell types).
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
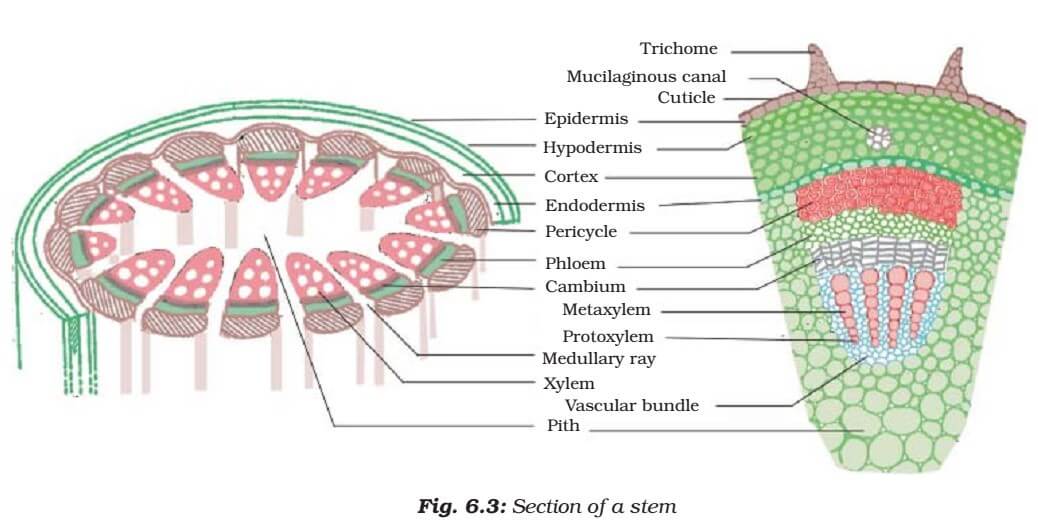
Class 9 cbse notes plant tissues. (1) pith, (2) protoxylem, (3) xylem, (4) phloem, (5) sclerenchyma, (6) cortex, and (7) epidermis are the different plant tissues. This classification is on the basis of parts of the plants they are present. Vascular tissue is an example of a complex tissue, and is made of two specialized conducting tissues: This is because the dividing tissue, also known as meristematic tissue, is located only at these points.
 Source: hortsciences.com
Source: hortsciences.com
In humans, cranial bones derive from the ectoderm, but the other connective tissues come from the mesoderm. They help in providing the elasticity and flexibility to the organs. This is because the dividing tissue, also known as meristematic tissue, is located only at these points. These tissues have the capability to develop by swift division. Xylem is the tissue which is responsible for the transport of water in plants while the phloem is responsible for.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Plants like liverworts and hornworts are not vascular plants due to a lack of vascular tissue. A plant body is made up of different kinds of tissue. Parenchyma is the main tissue of apples, pears, plums, and tomatoes. Different types of plant tissues include permanent and meristematic tissues. The cells of this tissue are dead.
 Source: biologyjunction.com
Source: biologyjunction.com
In humans, cranial bones derive from the ectoderm, but the other connective tissues come from the mesoderm. This is because the dividing tissue, also known as meristematic tissue, is located only at these points. Xylem and phloem are the two tissues of plants list two examples of tissues found in plants. Plant tissue is divided into two types. In potatoes and fruits, the parenchyma cells store starch.
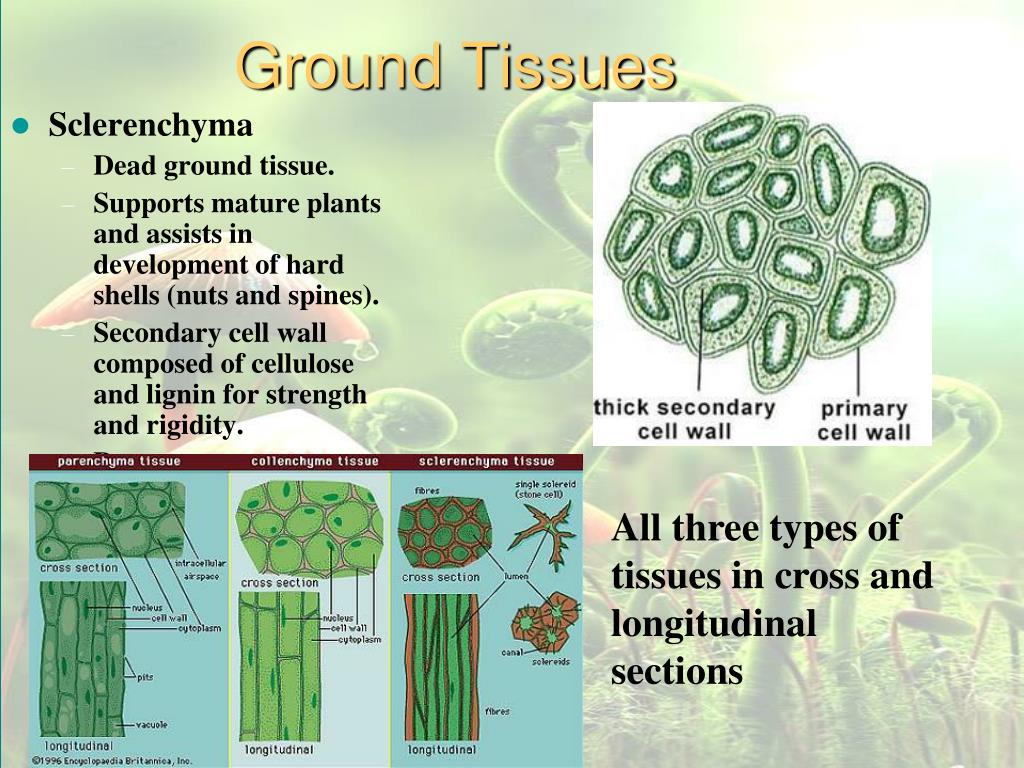 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Examples of connective tissue include blood, bone, adipose, tendons, and ligaments. Xylem is the tissue which is responsible for the transport of water in plants while the phloem is responsible for. Vascular tissue is an example of a complex tissue, and is made of two specialized conducting tissues: The apical side contains protein. Often, collenchyma plant tissue is seen in young plants, with a.
 Source: csus.edu
Their main role is in the transportation of food, minerals, and water. Vascular tissue is an example of a complex tissue, and is made of two specialized conducting tissues: They are epithelial tissues, muscle tissues, nervous tissues and connective tissues. Plants like liverworts and hornworts are not vascular plants due to a lack of vascular tissue. It is produced by the ground meristem.
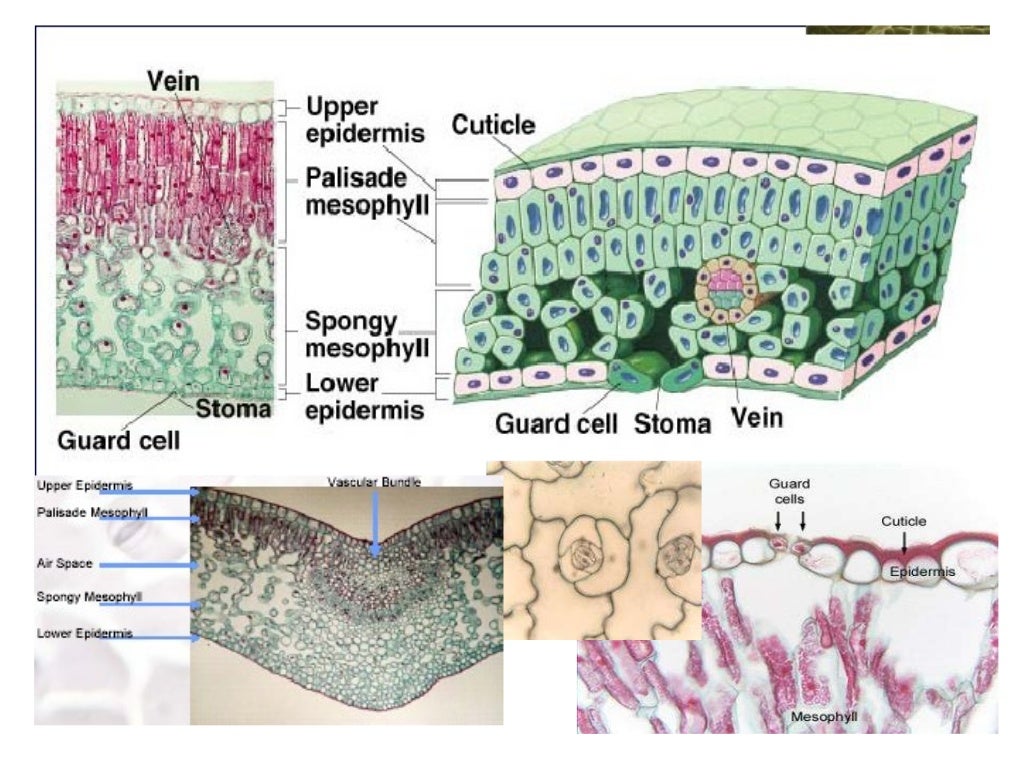 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Dermal tissue, for example, is a simple tissue that covers the outer surface of the plant and controls gas exchange. Vessel elements and tracheids (both of which conduct water), and xylem parenchyma. Examples are sedges, lichens, and heaths list two examples of. One of the most significant features of parenchyma is that it retains living protoplasts at maturity. Vascular tissue is an example of a complex tissue.
 Source: pmfias.com
Source: pmfias.com
Plant tissue is divided into two types. Parenchyma tissue found in cells responsible for storage. The three fundamental tissue patterns seen in roots and stems that serve to distinguish between woody dicot, herbaceous dicot, and monocot plants are an excellent illustration of this. Vascular tissue is an example of a complex tissue. Transports dissolved sugars from the leaves to growth.
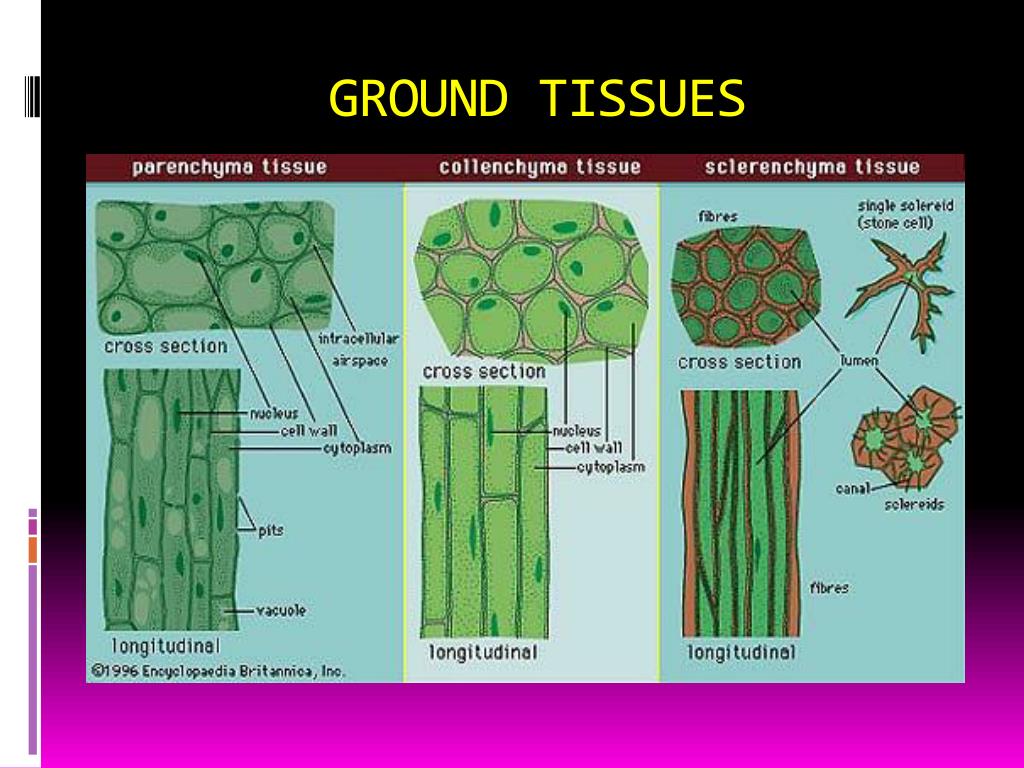 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Parenchyma tissue found in cells responsible for storage. (1) pith, (2) protoxylem, (3) xylem, (4) phloem, (5) sclerenchyma, (6) cortex, and (7) epidermis are the different plant tissues. The three fundamental tissue patterns seen in roots and stems that serve to distinguish between woody dicot, herbaceous dicot, and monocot plants are an excellent illustration of this. Collenchyma plant tissue is similar to sclerenchyma, in that it provides support. 7 rows phloem (vascular tissue) plant:
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
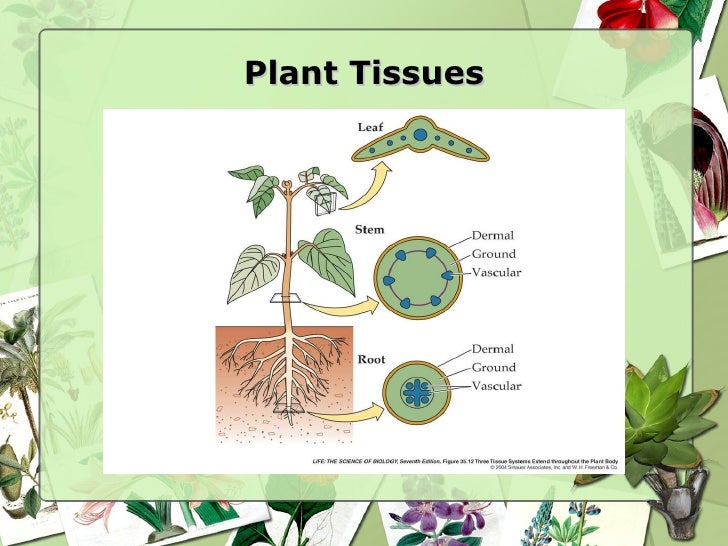
There are three fundamental types of specialised (differentiated) tissues in vascular plants: So, the correct answer is � all of these�. Dermal tissue, for example, is a simple tissue that covers the outer surface of the plant and controls gas exchange. This classification is on the basis of parts of the plants they are present. Although it is very difficult to survive in the arctic, many low growing plants can be found there.
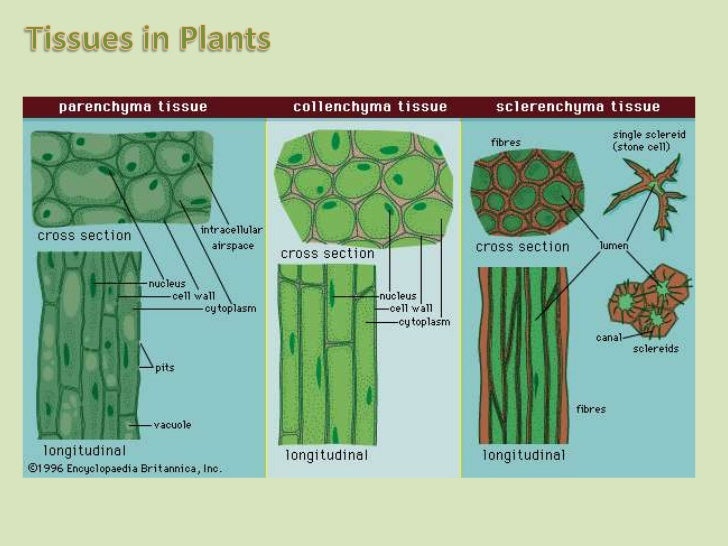 Source: jangmuk.blogspot.com
Source: jangmuk.blogspot.com
Xylem is the tissue which is responsible for the transport of water in plants while the phloem is responsible for. This classification is on the basis of parts of the plants they are present. Growth in length and growth in diameter of the plant is carried about by these cells. Examples are sedges, lichens, and heaths list two examples of. These tissues have the capability to develop by swift division.
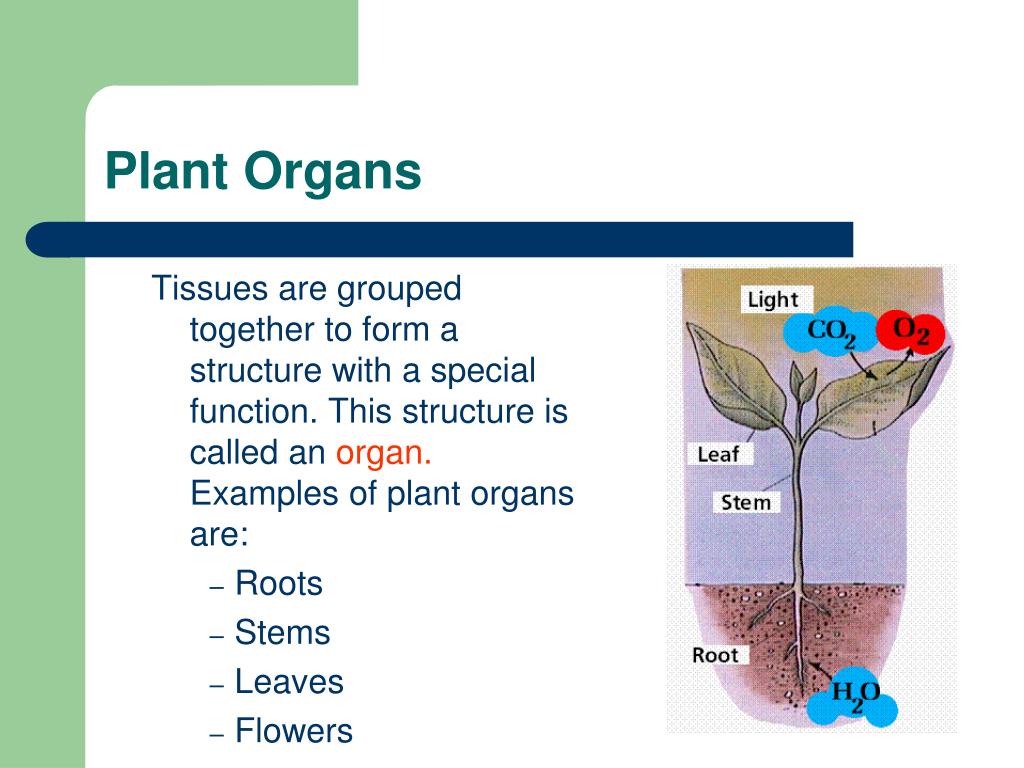 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Dermal tissues, vascular tissues, and ground tissues. They help in providing the elasticity and flexibility to the organs. Plant tissues have different functions depending upon their structure and location help provide mechanical strength to organs. Transparent, one cell thick and is usually covered with cuticle usually has guard cells with stomata • found on the outermost layer of the plant body such as leaves, flowers, stem & roots • function is to protect the plant from dessication and infection. A plant body is made up of different kinds of tissue.
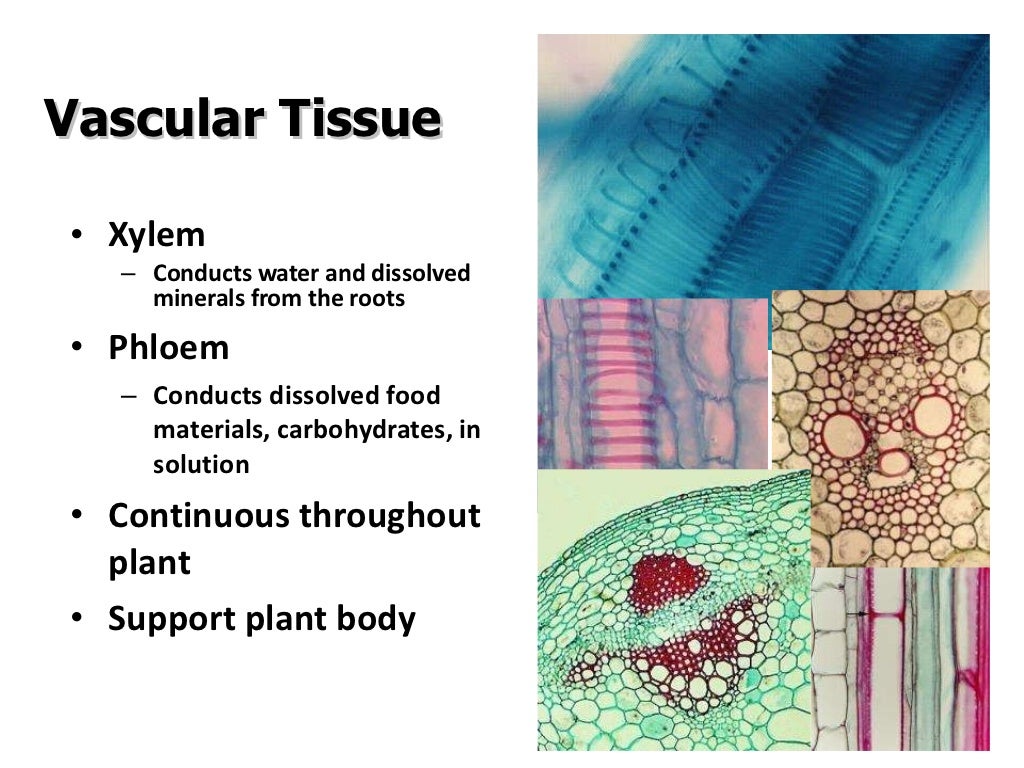 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
It is produced by the ground meristem. Collenchyma plant tissue is similar to sclerenchyma, in that it provides support. Some of the most important types of plant tissues we can observe in different layers of a plant are pith, protoxylem, xylem, phloem, parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma, cortex, and the epidermis. Meristematic tissues may be defined as a group or collection of living cells which ar located specific locations and divide continuously to add new cells to the plant body. Their main role is in the transportation of food, minerals, and water.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The apical side contains protein. This plant tissue is commonly found in stems, bark, and in the hard shells of some fruits and nuts, such as pears. In humans, cranial bones derive from the ectoderm, but the other connective tissues come from the mesoderm. Plant tissues are either simple (composed of similar cell types) or complex (composed of different cell types). The growth of plants occurs only in certain specific regions.
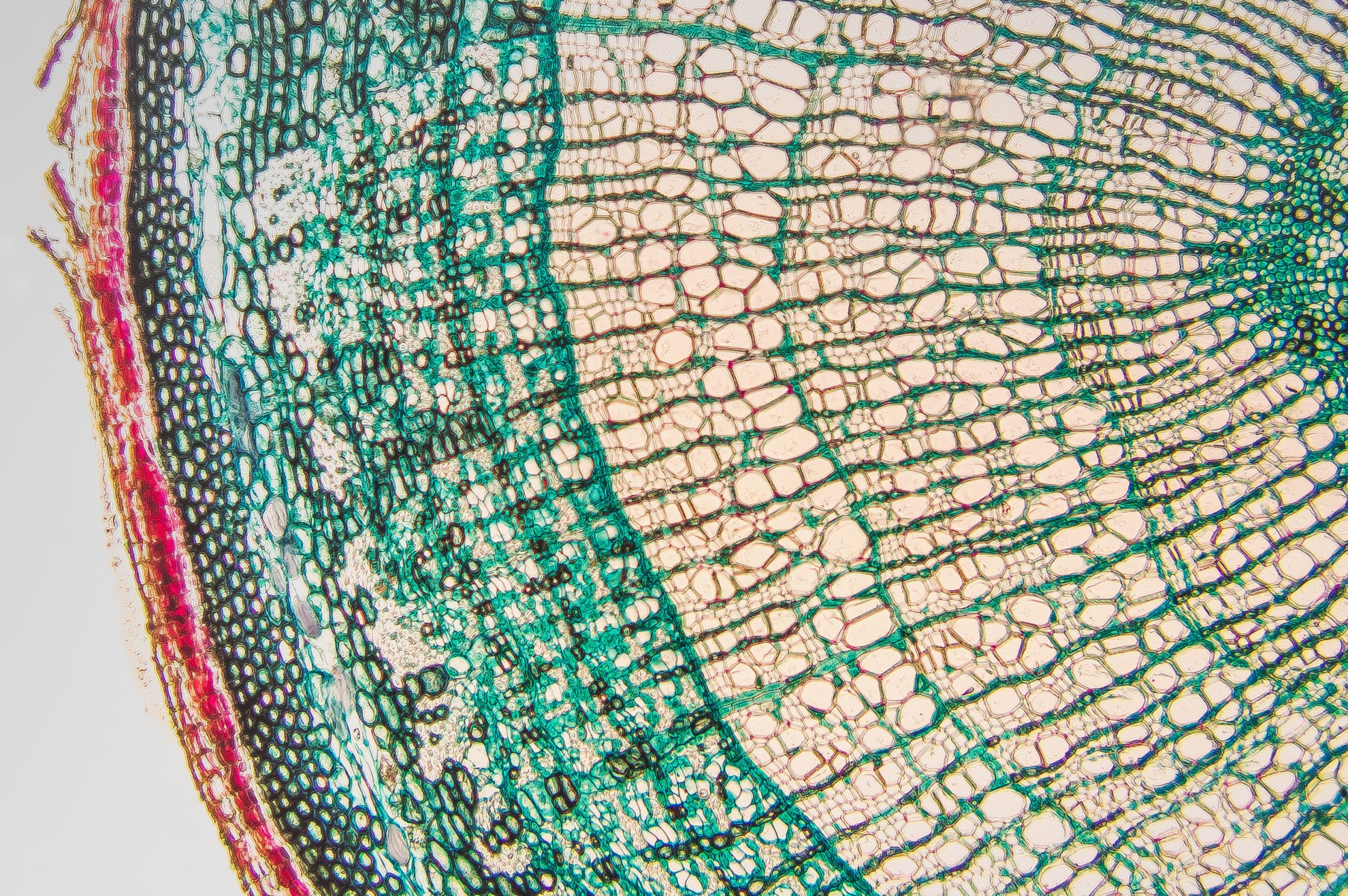 Source: biologyonline.com
Source: biologyonline.com
In potatoes and fruits, the parenchyma cells store starch. Different types of plant tissues include permanent and meristematic tissues. Examples of connective tissue include blood, bone, adipose, tendons, and ligaments. The epidermis are the tissue cells that form. Examples are sedges, lichens, and heaths list two examples of.
Source: sonuacademy.in
The cells cut off by the meristematic tissue based on the location and function get modified to respective tissues like secondary cortex, secondary xylem and secondary phloem in roots, monocot stem, cork cells etc. Xylem and phloem are the conducting tissues of the vascular strands. Functions of connective tissue include shaping and supporting organs and the body, allowing body movement, and providing oxygen diffusion. Vascular tissue is an example of a complex tissue, and is made of two specialized conducting tissues: Classification of plant tissues :
 Source: pinterest.com.au
Source: pinterest.com.au
It is produced by the ground meristem. Xylem is the tissue which is responsible for the transport of water in plants while the phloem is responsible for. Although it is very difficult to survive in the arctic, many low growing plants can be found there. One of the most significant features of parenchyma is that it retains living protoplasts at maturity. Different types of plant tissues include permanent and meristematic tissues.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title examples of plant tissues by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







