Your General plant morphology images are available in this site. General plant morphology are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the General plant morphology files here. Find and Download all free images.
If you’re looking for general plant morphology images information connected with to the general plant morphology interest, you have visit the right blog. Our site always gives you hints for downloading the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
General Plant Morphology. The term anatomy also refers to the study of biological structure but usually. The study of various external features of the plant is known as plant morphology. Plant habit refers to the overall shape of a plant, and it describes a number of components such as stem length and development, branching pattern, and texture. Morphology, in biology, the study of the size, shape, and structure of animals, plants, and microorganisms and of the relationships of their constituent parts.
 Free Morphology of Flowering Plants PowerPoint Template From myfreeslides.com
Free Morphology of Flowering Plants PowerPoint Template From myfreeslides.com
Generally, dicotyledonous plants have tap roots while monocotyledonous plants have fibrous roots. Morphology is the study of the form of a plant or plant part. And (2) branches of different orders (e.g. No matter which plant you take, the morphology of a flowering plant includes the roots, stem, leaves, flowers, and fruits. The general principles of plant morphology, including evolutionary tendencies, phylogenetic lines and the life cycles of the principal groups of vascular plants. The general principles of plant morphology, including evolutionary tendencies, phylogenetic lines and the life cycles of the principal groups of vascular plants.
The main characteristics of angiosperm are:
While it occasionally uses the anatomical level of organization as morphological. The main characteristics of angiosperm are: General plant morp hology of musa 5 passage thr ough the ps eudostem, with the right ha lf rolled upon itself a nd the left half rolled over the right and the midrib. Plant morphology is a field of botanic biology, researching the form and structure of plants according either to: Morphology is the name given to the science that deals with the study of the form and structure of things. 1general plant morphology of musa deborah karamura, eldad karamura, and guy blomme 1.1 introduction in this chapter, musa stands for the genus.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Plant morphology (or phytomorphology) is the general term for the study of the morphology (physical form and external structure) of plants. Morphology, in biology, the study of the size, shape, and structure of animals, plants, and microorganisms and of the relationships of their constituent parts. The term refers to the general aspects of biological form and arrangement of the parts of a plant or an animal. Thirdly, plant morphology studies plant structure at a range of scales. Figure 4.1 morphological features of typical plant parasitic nematodes (female and male) synonyms:
 Source: myfreeslides.com
Source: myfreeslides.com
Morphology, in biology, the study of the size, shape, and structure of animals, plants, and microorganisms and of the relationships of their constituent parts. Plant habit refers to the overall shape of a plant, and it describes a number of components such as stem length and development, branching pattern, and texture. While many plants fit neatly into some main categories, such as grasses, vines, shrubs, or trees, others can be more difficult to categorise. Morphology is the name given to the science that deals with the study of the form and structure of things. It deals with the study of forms and featuresof different plant organs like roots, stems, leaves, flowers, seeds, fruits etc.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Morphology is the study of the form of a plant or plant part. At this scale, plant morphology overlaps with plant anatomy as a It deals with the study of forms and featuresof different plant organs like roots, stems, leaves, flowers, seeds, fruits etc. The general principles of plant morphology, including evolutionary tendencies, phylogenetic lines and the life cycles of the principal groups of vascular plants. The shoot system is differentiated into stem, leaves, flowers and fruits.
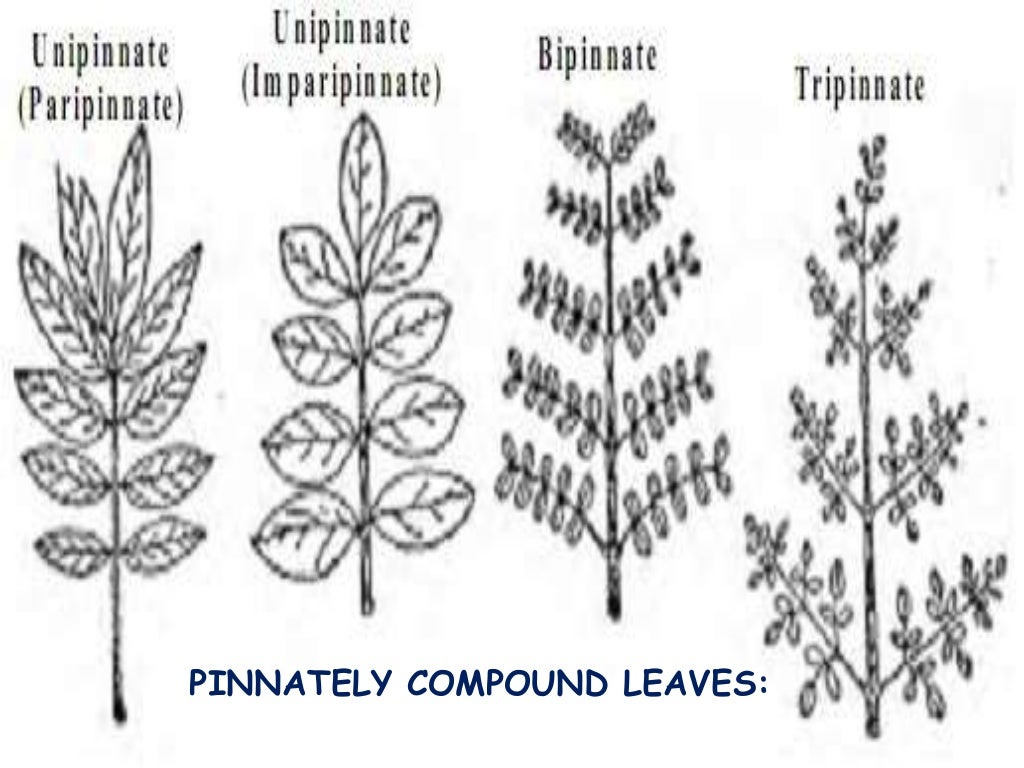 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Obviously, all facets of the morphology and anatomy of vascular plants cannot be covered in this brief summary. And (2) branches of different orders (e.g. I illustrate some of these general principles and their application by evaluating them in a phyletically heterogeneous plant. Plant morphology (or phytomorphology) is the general term for the study of the morphology (physical form and external structure) of plants. This led to an attempt to formulate a general scheme, though it is quite open to critics to show
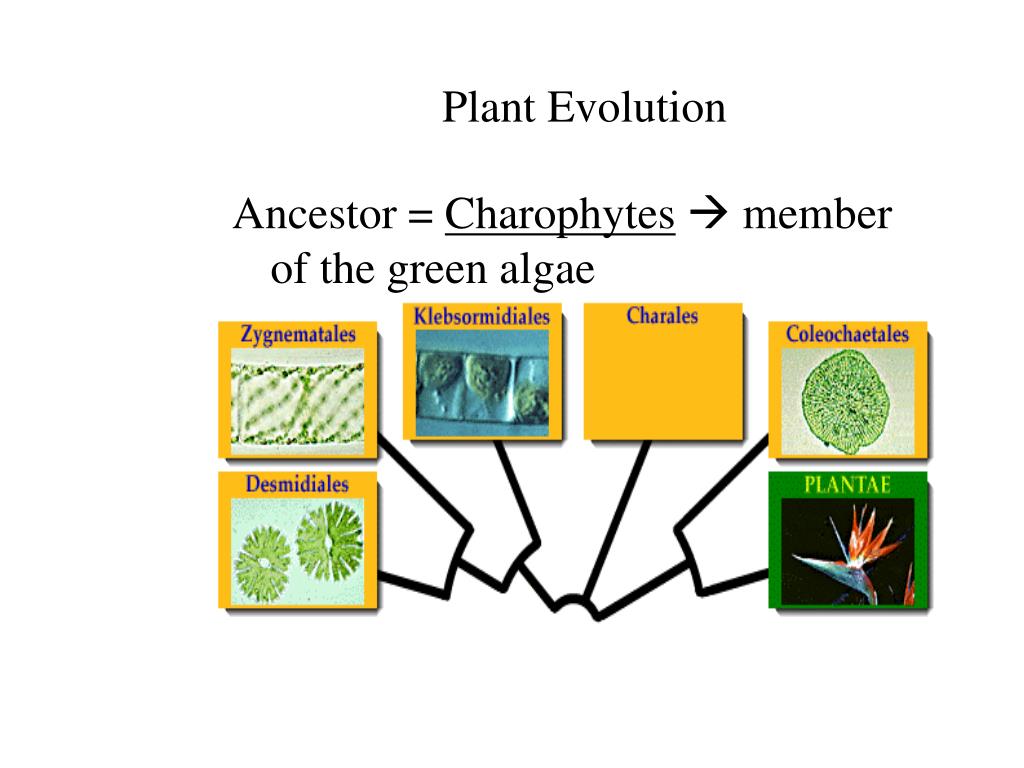 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Let us have a look at the flowering plants and morphology of flowering plants notes in detail. Figure 4.1 morphological features of typical plant parasitic nematodes (female and male) synonyms: Nematodes are generally vermiform having a cylindrical body tapering towards both anterior as well as posterior ends and having maximum diameter near mid body. The angiosperm is characterized by the presence of roots, stems, leaves, flowers and fruits. Morphology is the name given to the science that deals with the study of the form and structure of things.
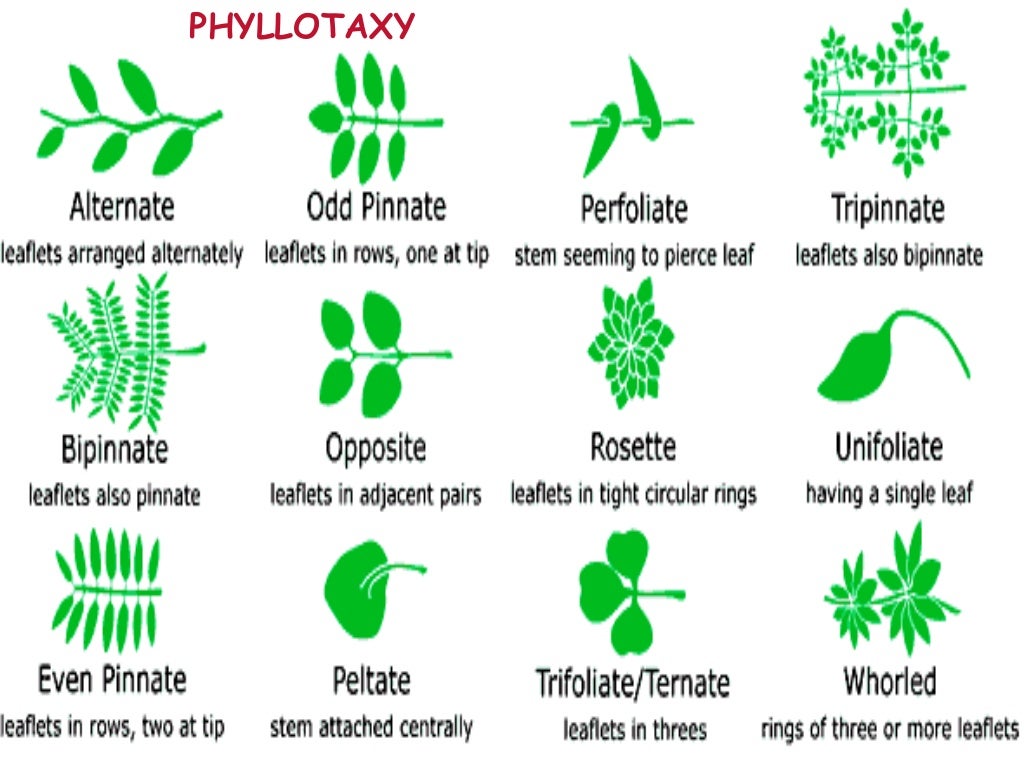 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
It can be applied to any species and involves a detailed study of vegetative and reproductive characters in order to form a profile of a plant, which can be used to make general comparisons of plant species displaying a similar structure or detailed comparisons within a species to identify varieties (cultivars). It can be applied to any species and involves a detailed study of vegetative and reproductive characters in order to form a profile of a plant, which can be used to make general comparisons of plant species displaying a similar structure or detailed comparisons within a species to identify varieties (cultivars). Obviously, all facets of the morphology and anatomy of vascular plants cannot be covered in this brief summary. Truncatula plant is made up of (1) a main axis that can organize either in a rosette (i.e. The term refers to the general aspects of biological form and arrangement of the parts of a plant or an animal.
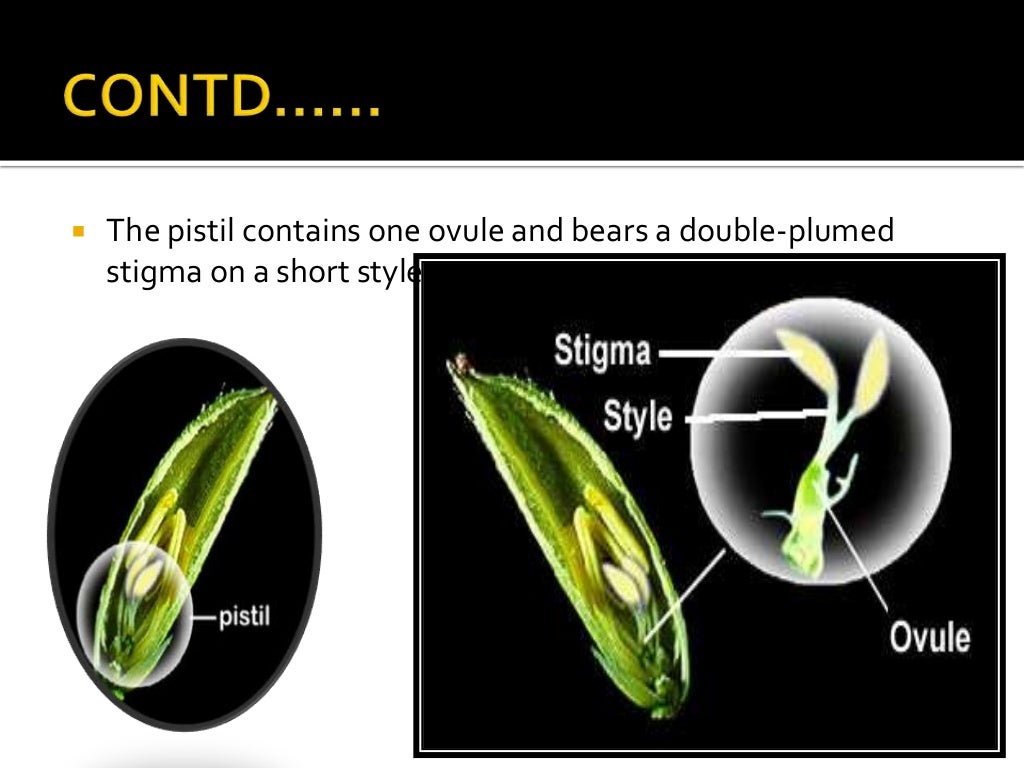 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Let us have a look at the flowering plants and morphology of flowering plants notes in detail. Let us have a look at the flowering plants and morphology of flowering plants notes in detail. Plant morphology (or phytomorphology) is the general term for the study of the morphology (physical form and external structure) of plants. A comprehensive general botany textbook is a good source for more information about the structure and diversity of vascular plants (mauseth, 2003; The xerophytic plants and plants belonging to the crassulaceae family have thick and succulent leaves that store water in their tissues.
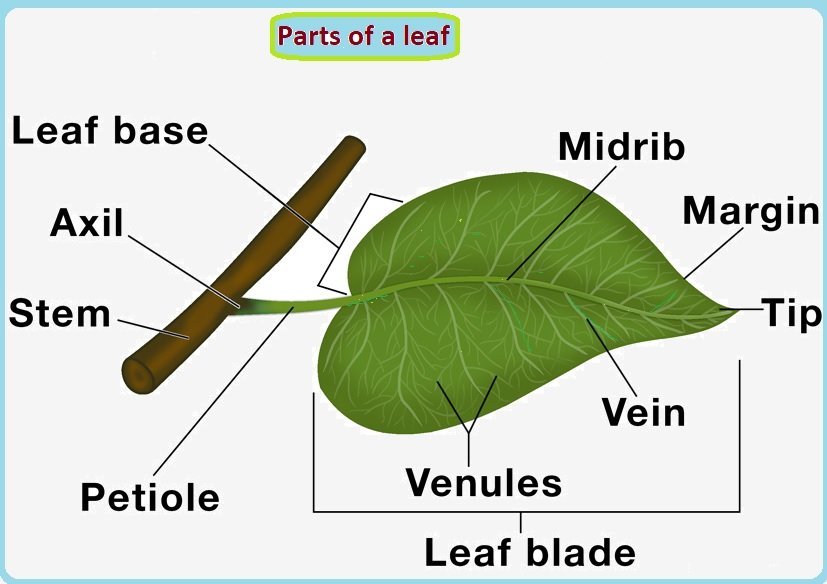 Source: pcsstudies.com
Source: pcsstudies.com
The term anatomy also refers to the study of biological structure but usually. General plant morp hology of musa 5 passage thr ough the ps eudostem, with the right ha lf rolled upon itself a nd the left half rolled over the right and the midrib. This is usually considered distinct from plant anatomy, which is the study of the internal structure of plants, especially at the microscopic level. Morphology, in biology, the study of the size, shape, and structure of animals, plants, and microorganisms and of the relationships of their constituent parts. The general principles of plant morphology, including evolutionary tendencies, phylogenetic lines and the life cycles of the principal groups of vascular plants.
Source: researchgate.net
The journal of general plant pathology presents papers dealing with plant diseases or their control, including pathogen characterization, identification of pathogens, disease physiology and biochemistry, molecular biology, morphology and ultrastructure, genetics, disease transmission, ecology and epidemiology, chemical and biological control, disease assessment,. This modification helps the plant to resist desiccation. The term anatomy also refers to the study of biological structure but usually. The parenchymatous cells of these leaves have large vacuoles filled with hydrophilic colloid. 1general plant morphology of musa deborah karamura, eldad karamura, and guy blomme 1.1 introduction in this chapter, musa stands for the genus.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
While many plants fit neatly into some main categories, such as grasses, vines, shrubs, or trees, others can be more difficult to categorise. The terminology of morphological description of plants was introduced principally in the 17th century, at which time the first theoretical generalizations were made by the italian scientists a. The general principles of plant morphology, including evolutionary tendencies, phylogenetic lines and the life cycles of the principal groups of vascular plants. A comprehensive general botany textbook is a good source for more information about the structure and diversity of vascular plants (mauseth, 2003; Threadworms, eelworms (serpentile eel like body), round worms, nemas, paudh/padap krimi etc.
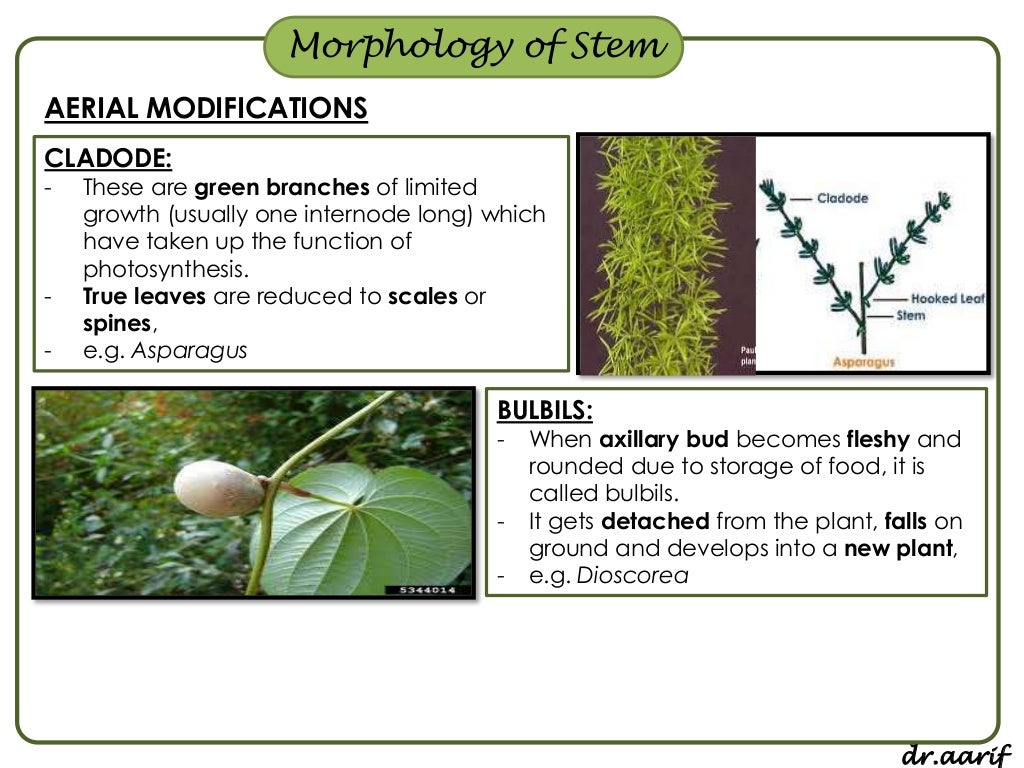 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Not only can plant morphology be delimited horizontally from other biological disciplines but it also can be vertically delimited from other levels of biological organization. Morphology, in biology, the study of the size, shape, and structure of animals, plants, and microorganisms and of the relationships of their constituent parts. Morphology is an important subject for herbalists to know, especially if you ever find yourself writing an herbal monograph, hosting a plant walk, writing an article on plant identification, or engaged in any other activity where morphology and descriptive language is needed. This chapter describes the morphology of the musa plant and discusses the potential benefits of morphological diversity. The discipline of plant morphology encompasses the whole plant down to the organ level of organization.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
At the smallest scales are ultrastructure, the general structural features of cells visible only with the aid of an electron microscope, and cytology, the study of cells using optical microscopy. Morphology is the study of the form of a plant or plant part. The body of a typical angiospermic plant is differentiated into : Figure 4.1 morphological features of typical plant parasitic nematodes (female and male) synonyms: Leaf tendrils exist in plants with weak stems.
 Source: dreamstime.com
Source: dreamstime.com
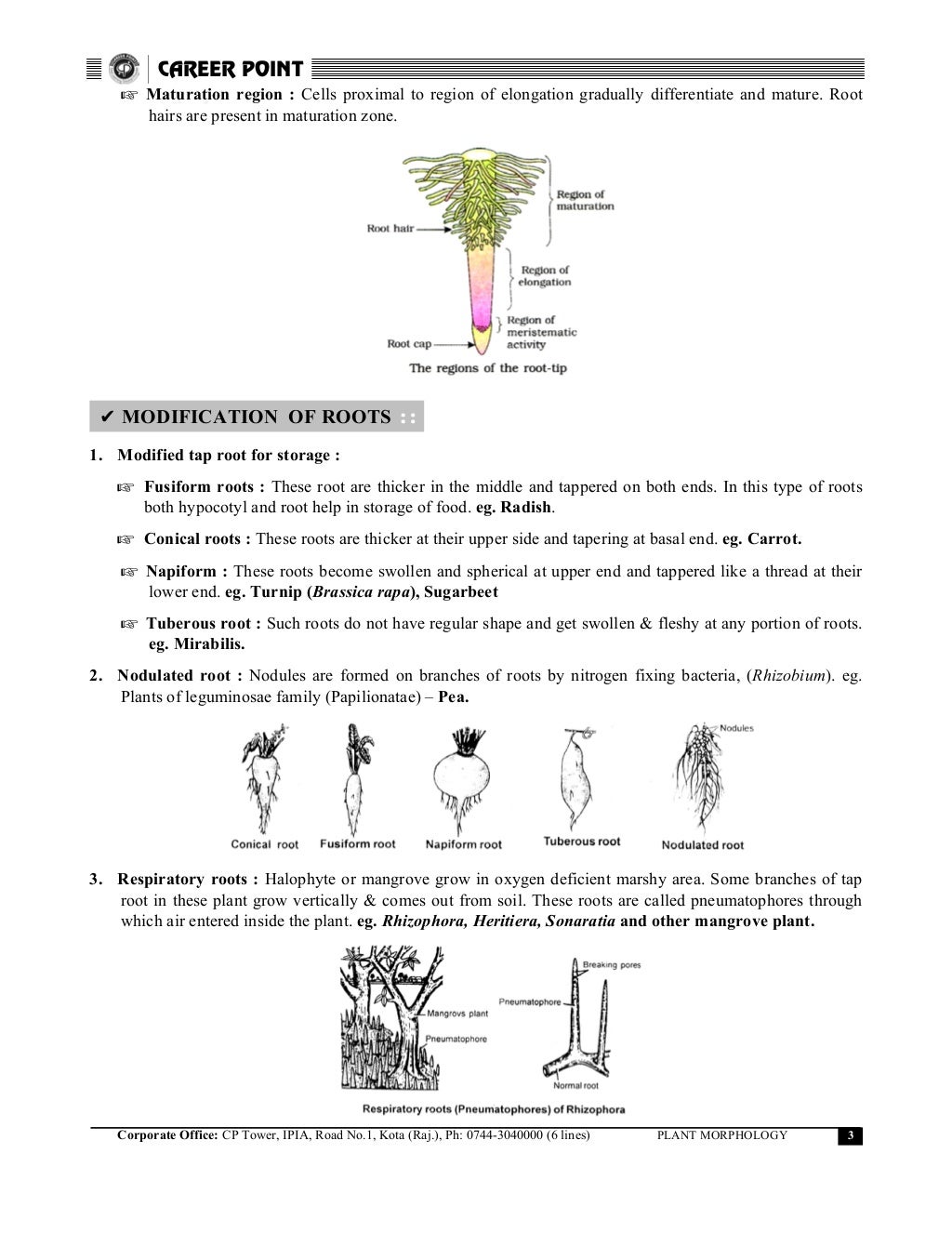
The roots in some plants get modified for storage of food, mechanical support and respiration. The xerophytic plants and plants belonging to the crassulaceae family have thick and succulent leaves that store water in their tissues. This led to an attempt to formulate a general scheme, though it is quite open to critics to show Plant habit refers to the overall shape of a plant, and it describes a number of components such as stem length and development, branching pattern, and texture. The leaves are at the level of the neck with very short internodes) or as an elongated axis;
Source: researchgate.net
An underground root system an aerial shoot system. Thirdly, plant morphology studies plant structure at a range of scales. General plant morphology and architecture a m. This modification helps the plant to resist desiccation. The xerophytic plants and plants belonging to the crassulaceae family have thick and succulent leaves that store water in their tissues.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Morphology is the study of the form of a plant or plant part. The journal of general plant pathology presents papers dealing with plant diseases or their control, including pathogen characterization, identification of pathogens, disease physiology and biochemistry, molecular biology, morphology and ultrastructure, genetics, disease transmission, ecology and epidemiology, chemical and biological control, disease assessment,. While many plants fit neatly into some main categories, such as grasses, vines, shrubs, or trees, others can be more difficult to categorise. This chapter describes the morphology of the musa plant and discusses the potential benefits of morphological diversity. Morphology is an important subject for herbalists to know, especially if you ever find yourself writing an herbal monograph, hosting a plant walk, writing an article on plant identification, or engaged in any other activity where morphology and descriptive language is needed.
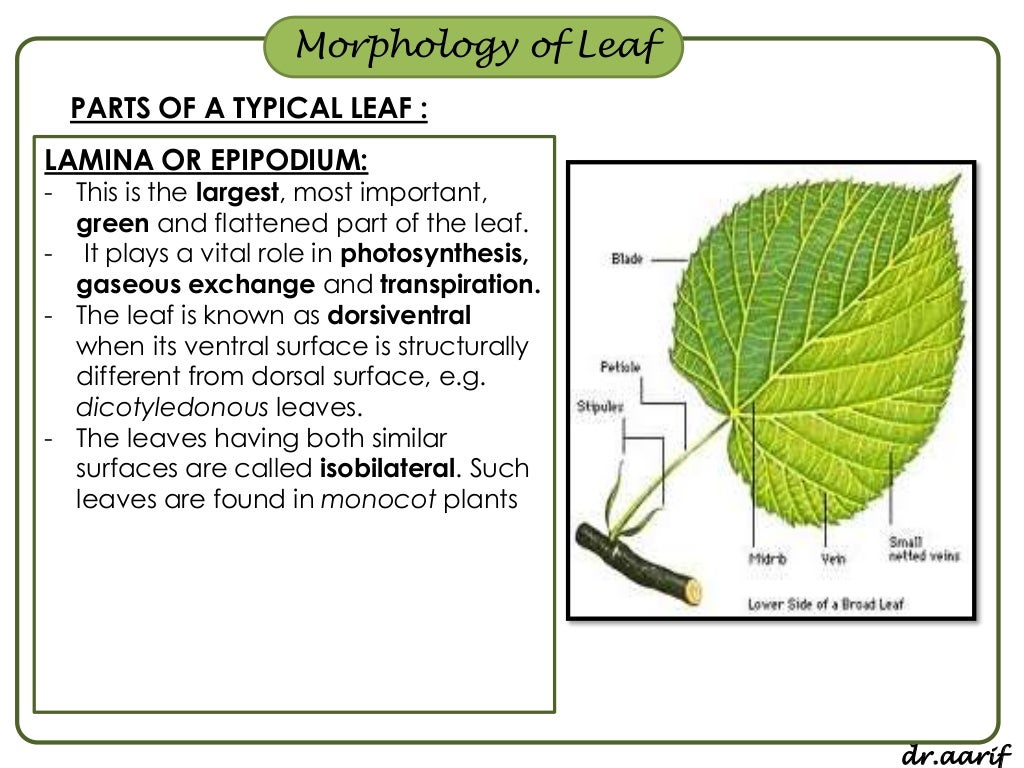 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
No matter which plant you take, the morphology of a flowering plant includes the roots, stem, leaves, flowers, and fruits. The definition of plant morphology is the physical appearance of a plant. At the smallest scales are ultrastructure, the general structural features of cells visible only with the aid of an electron microscope, and cytology, the study of cells using optical microscopy. Brief historical survey the beginnings of plant morphology, and of botany in general, go back to early antiquity. The general principles of plant morphology, including evolutionary tendencies, phylogenetic lines and the life cycles of the principal groups of vascular plants.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Plant morphology is a field of botanic biology, researching the form and structure of plants according either to: This modification helps the plant to resist desiccation. The xerophytic plants and plants belonging to the crassulaceae family have thick and succulent leaves that store water in their tissues. Not only can plant morphology be delimited horizontally from other biological disciplines but it also can be vertically delimited from other levels of biological organization. While many plants fit neatly into some main categories, such as grasses, vines, shrubs, or trees, others can be more difficult to categorise.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title general plant morphology by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






