Your Genome editing in plants images are available in this site. Genome editing in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Genome editing in plants files here. Find and Download all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re searching for genome editing in plants images information related to the genome editing in plants topic, you have come to the ideal blog. Our site always gives you hints for viewing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video content and images that fit your interests.
Genome Editing In Plants. The delivery of gene editing reagents into the plant cells has been dominated by plasmid vectors. Recently, genome editing technologies have shown great potential in plants. The novel genome editing systems help to introduce stably inherited point modifications into the plant genome, and transgenic region can be easily removed after editing a target gene. New genome editing techniques are still being developed and improved for new plant species.
 Frontiers Advances in Genome Editing With CRISPR Systems From frontiersin.org
Frontiers Advances in Genome Editing With CRISPR Systems From frontiersin.org
Principles and applications addresses the information of genome editing starting from principles and historical aspects to the latest advancements in the field. Scientists use different technologies to do this. Genome editing in plants with crispr/cas9 1. Instead, cas10d is the functional nuclease in vivo. Biotech 2021, 10, 14 9 of 17 table 7. Commission is expected to publish a.
This project has been formulated based on leads obtained in 12th fyp project and expertise developed by the group.
The emergence of genome editing methods promises a real revolution in genetic engineering. Recently, genome editing technologies have shown great potential in plants. New genome editing techniques are still being developed and improved for new plant species. Early history of genome editing 1. Tid lacks the cas3 nuclease domain; Therefore, it is easily speculated that a majority of the genomic content in plastid genomes was utilized for photosynthesis [168,169].
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Over the last decade, genome editing platforms. Commission is expected to publish a. These diverse sizes of plastid genome can provide valuable importance for genome editing in plants. Therefore, it is easily speculated that a majority of the genomic content in plastid genomes was utilized for photosynthesis [168,169]. Instead, cas10d is the functional nuclease in vivo.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
These diverse sizes of plastid genome can provide valuable importance for genome editing in plants. Genome editing holds the potential for rapid crop improvement to meet the challenge of feeding the planet in a changing climate. Recently, genome editing technologies have shown great potential in plants. Virulence or disease resistance why to modify the genome??? In the past decade, genome editing technology has quickly developed through not only the study of gene function but also its wide use toward plant improvement.
 Source: geneticliteracyproject.org
Source: geneticliteracyproject.org
Precise plant genome editing technologies have provided new opportunities to accelerate crop improvement and develop more sustainable agricultural systems. Currently, genome editing tools, particularly crispr/cas, have been widely adopted in many plant species, and many elite plant germplasms have been created using different genome editing tools. The delivery of gene editing reagents into the plant cells has been dominated by plasmid vectors. Early history of genome editing 1. Over the last decade, genome editing platforms.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
Plastids are primarily involved in photosynthesis. To understand biological functions 2. This project has been formulated based on leads obtained in 12th fyp project and expertise developed by the group. Tid lacks the cas3 nuclease domain; Genome editing is a method that lets scientists change the dna of many organisms, including plants, bacteria, and animals.
 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Tid was active in targeted. Genome editing in plants with crispr/cas9 1. Plastids are primarily involved in photosynthesis. The domestication of crop plants began approximately 10,000 years ago by selecting for increased seeds per inflorescence, increased seedling vigor, reduced seed dormancy and dispersal/shatter, and altered plant architecture such as compact/dwarf growth and reduced branching/tillering. To understand biological functions 2.
 Source: blogs.biomedcentral.com
Source: blogs.biomedcentral.com
( 2021) in their article “genome editing for resistance against plant pests and pathogens”, discuss recent reports on the editing of plant susceptibility genes and pathogen virulence factors. In addition, these techniques have been adapted for other purposes, such as the visualization of transcripts or the activation/repression of gene expression. Currently, powerful systems are available for genome editing in plants. Genome editing can also be used to protect plants against pests and diseases. Plant research and breeding are very important in meeting this challenge.
 Source: kurzweilai.net
Source: kurzweilai.net
Genome editing holds the potential for rapid crop improvement to meet the challenge of feeding the planet in a changing climate. In addition to photosynthetic genes, plastid genomes also contain. Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (crispr)/crispr. In addition, these techniques have been adapted for other purposes, such as the visualization of transcripts or the activation/repression of gene expression. Genome editing in plants with crispr/cas9 1.
 Source: plantae.org
Source: plantae.org
Genome editing can also be used to protect plants against pests and diseases. Building on scientific progress, a number of genome editing techniques have been developed over the past two decades allowing an unprecedented level of precision in our control over genetic material and its corresponding traits. Genotype forward genetics reverse genetics phenotype 1. Plant research and breeding are very important in meeting this challenge. Therefore, it is easily speculated that a majority of the genomic content in plastid genomes was utilized for photosynthesis [168,169].
 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
New genome editing techniques are still being developed and improved for new plant species. Genotype forward genetics reverse genetics phenotype 1. Genome editing in plants with crispr/cas9 1. Recently, genome editing technologies have shown great potential in plants. In addition to photosynthetic genes, plastid genomes also contain.
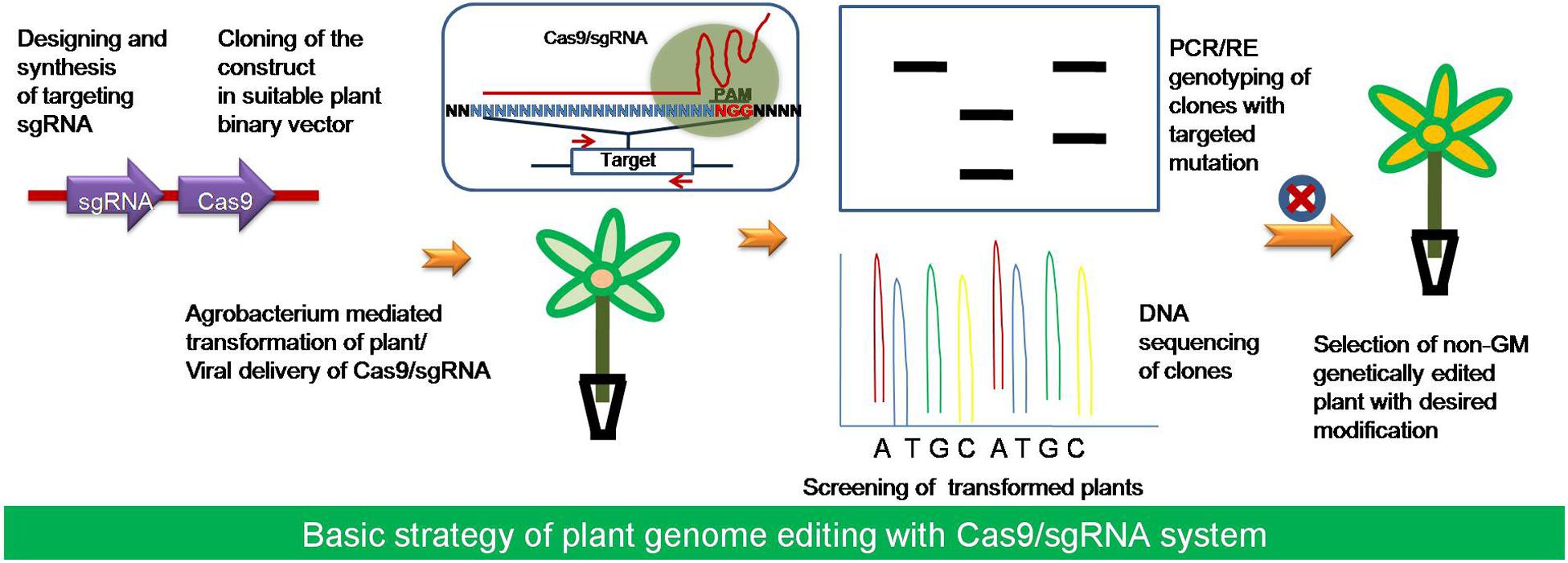 Source: journal.frontiersin.org
Source: journal.frontiersin.org
The domestication of crop plants began approximately 10,000 years ago by selecting for increased seeds per inflorescence, increased seedling vigor, reduced seed dormancy and dispersal/shatter, and altered plant architecture such as compact/dwarf growth and reduced branching/tillering. Building on scientific progress, a number of genome editing techniques have been developed over the past two decades allowing an unprecedented level of precision in our control over genetic material and its corresponding traits. • targeted interventions • alter the structural or functional characteristics like colour or number of blooms in flowering plants some disease traits in animals and plants Editing dna can lead to changes in physical traits, like eye color, and disease risk. Shalu jain department of plant pathology ndsu 2.
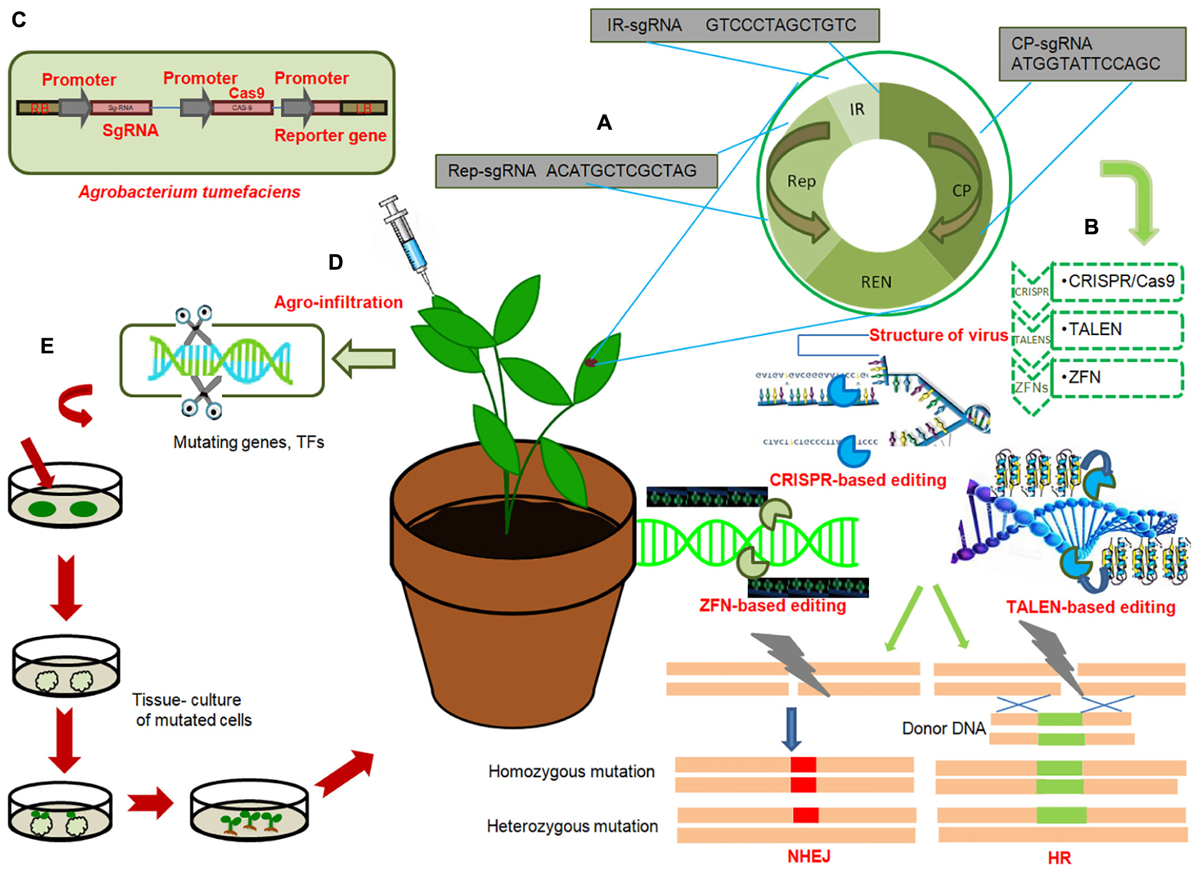 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Precise plant genome editing technologies have provided new opportunities to accelerate crop improvement and develop more sustainable agricultural systems. Commission is expected to publish a. • targeted interventions • alter the structural or functional characteristics like colour or number of blooms in flowering plants some disease traits in animals and plants Genome editing holds the potential for rapid crop improvement to meet the challenge of feeding the planet in a changing climate. Genotype forward genetics reverse genetics phenotype 1.
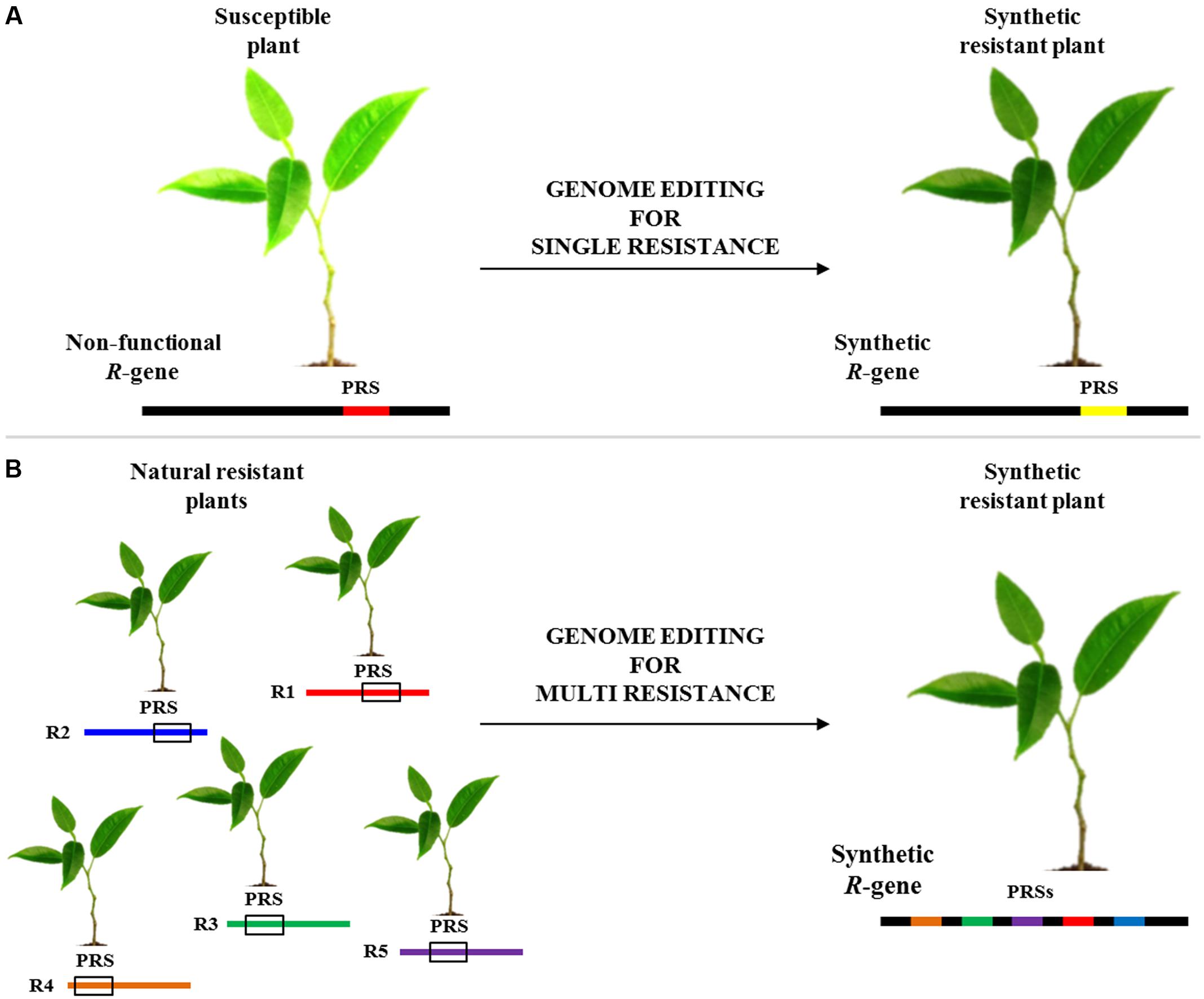 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Genome editing is a method that lets scientists change the dna of many organisms, including plants, bacteria, and animals. Editing dna can lead to changes in physical traits, like eye color, and disease risk. Currently, powerful systems are available for genome editing in plants. Genome editing holds the potential for rapid crop improvement to meet the challenge of feeding the planet in a changing climate. Therefore, it is easily speculated that a majority of the genomic content in plastid genomes was utilized for photosynthesis [168,169].
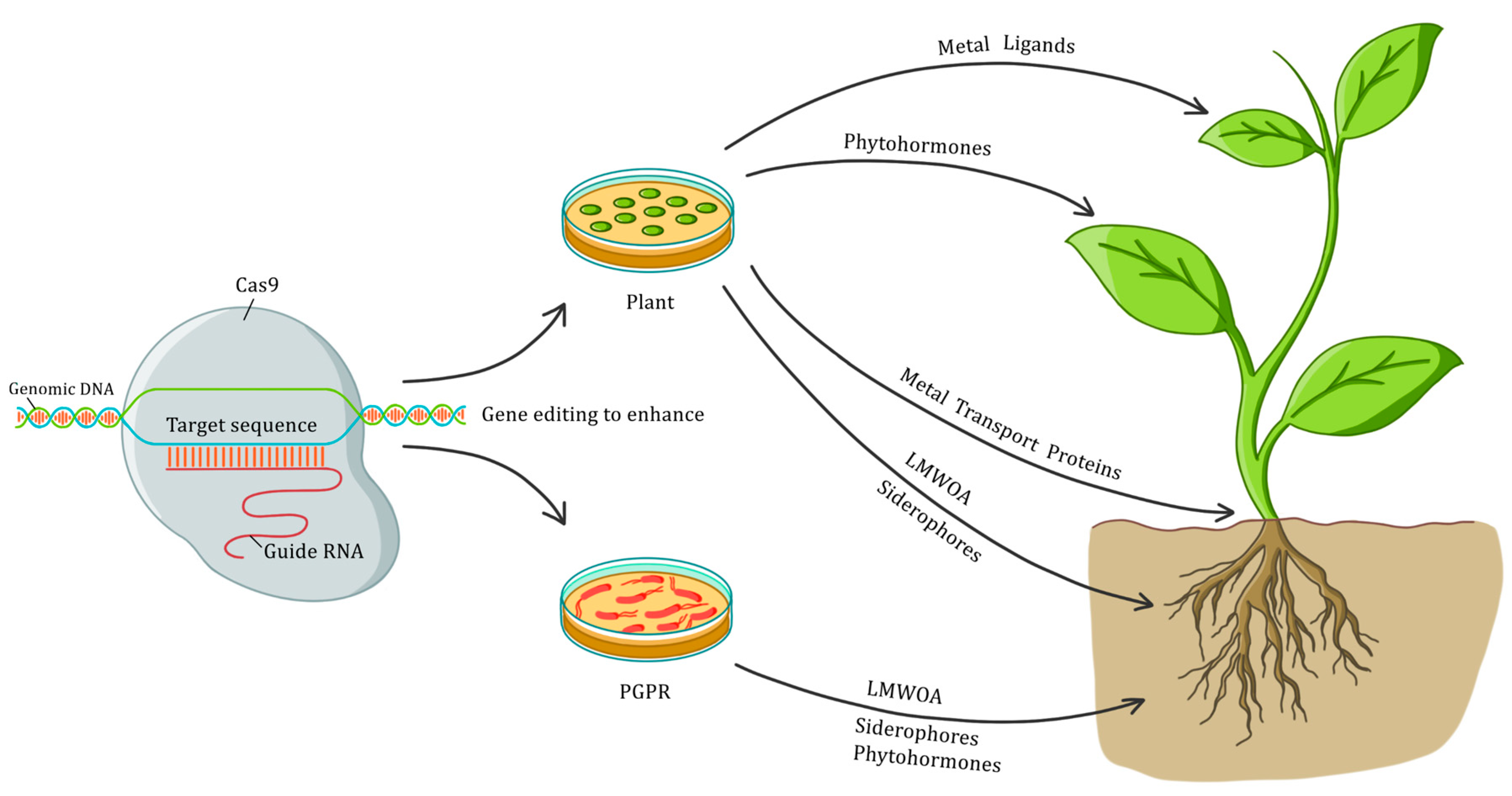 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Virulence or disease resistance why to modify the genome??? Editing dna can lead to changes in physical traits, like eye color, and disease risk. The emergence of genome editing methods promises a real revolution in genetic engineering. ( 2021) in their article “genome editing for resistance against plant pests and pathogens”, discuss recent reports on the editing of plant susceptibility genes and pathogen virulence factors. • targeted interventions • alter the structural or functional characteristics like colour or number of blooms in flowering plants some disease traits in animals and plants
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Principles and applications addresses the information of genome editing starting from principles and historical aspects to the latest advancements in the field. Genotype forward genetics reverse genetics phenotype 1. Currently, powerful systems are available for genome editing in plants. Genome editing holds the potential for rapid crop improvement to meet the challenge of feeding the planet in a changing climate. Plastids are primarily involved in photosynthesis.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The domestication of crop plants began approximately 10,000 years ago by selecting for increased seeds per inflorescence, increased seedling vigor, reduced seed dormancy and dispersal/shatter, and altered plant architecture such as compact/dwarf growth and reduced branching/tillering. Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (crispr)/crispr. Early history of genome editing 1. Tid was active in targeted. The emergence of genome editing methods promises a real revolution in genetic engineering.
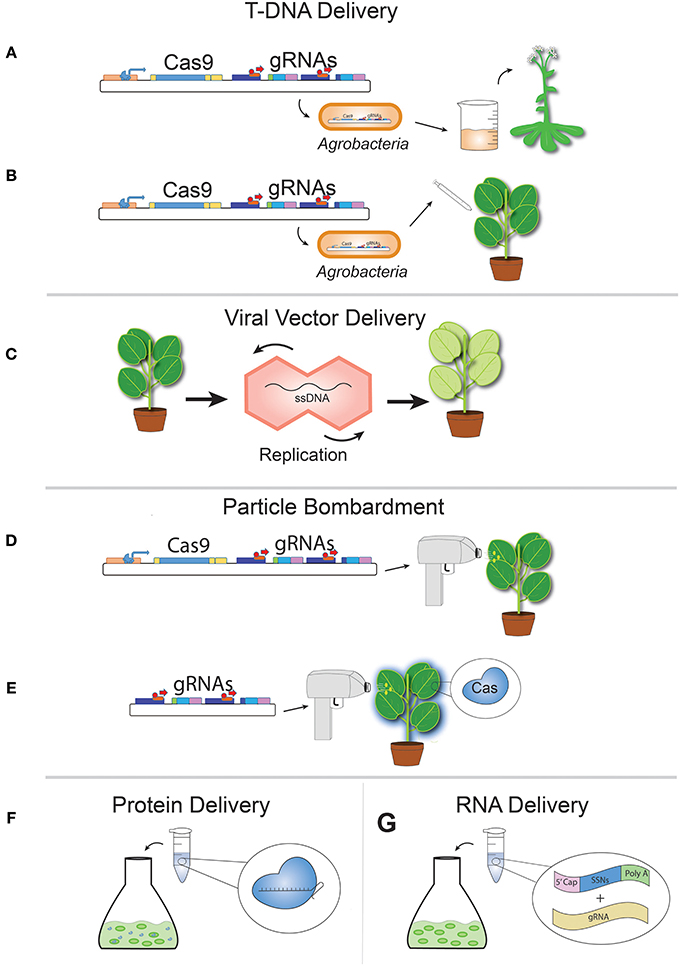 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Genome editing is a method that lets scientists change the dna of many organisms, including plants, bacteria, and animals. Genome editing in plants with crispr/cas9 1. The domestication of crop plants began approximately 10,000 years ago by selecting for increased seeds per inflorescence, increased seedling vigor, reduced seed dormancy and dispersal/shatter, and altered plant architecture such as compact/dwarf growth and reduced branching/tillering. Genotype forward genetics reverse genetics phenotype 1. Commission is expected to publish a.
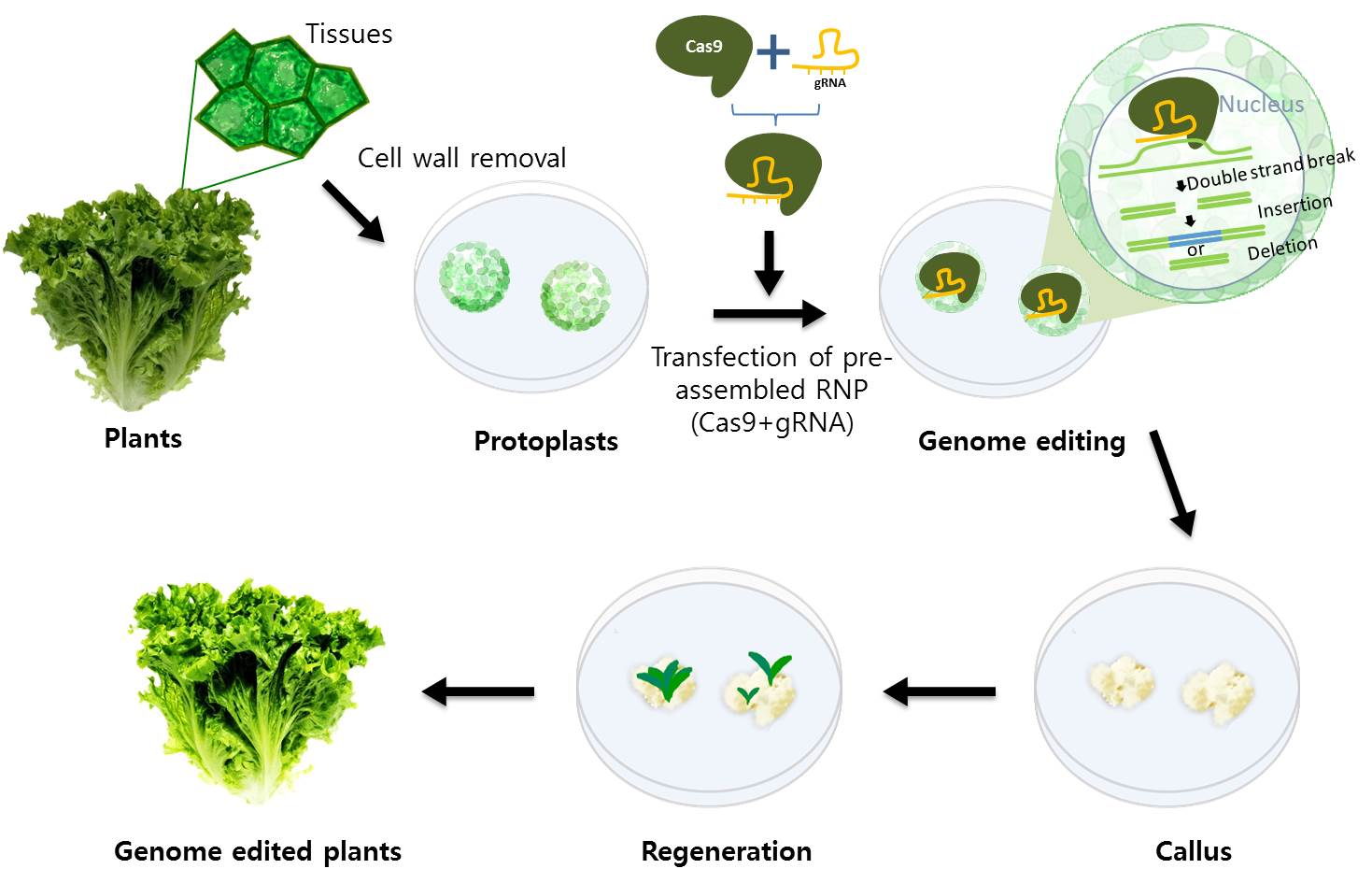 Source: naturegenic.com
Source: naturegenic.com
Commission is expected to publish a. Therefore, it is easily speculated that a majority of the genomic content in plastid genomes was utilized for photosynthesis [168,169]. Tid lacks the cas3 nuclease domain; Genome editing • the concept of genome editing is not limited to genes. To understand biological functions 2.
 Source: genomebiology.biomedcentral.com
Source: genomebiology.biomedcentral.com
Genome editing is a method that lets scientists change the dna of many organisms, including plants, bacteria, and animals. The delivery of gene editing reagents into the plant cells has been dominated by plasmid vectors. Currently, powerful systems are available for genome editing in plants. Shalu jain department of plant pathology ndsu 2. These diverse sizes of plastid genome can provide valuable importance for genome editing in plants.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title genome editing in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







