Your Glycogen in plants images are ready in this website. Glycogen in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Glycogen in plants files here. Get all free photos and vectors.
If you’re searching for glycogen in plants images information linked to the glycogen in plants topic, you have visit the ideal site. Our site frequently provides you with suggestions for seeing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video content and images that fit your interests.
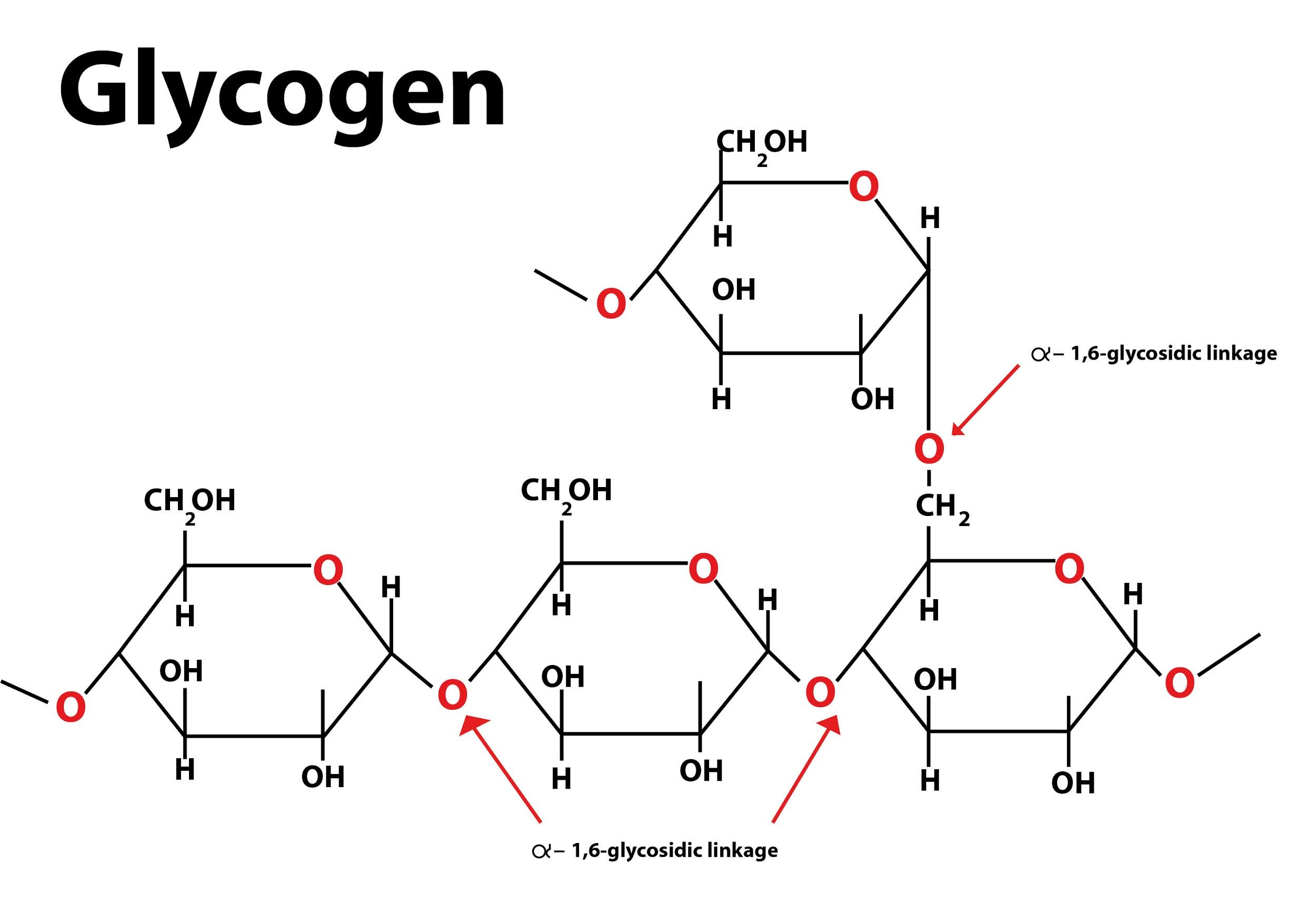
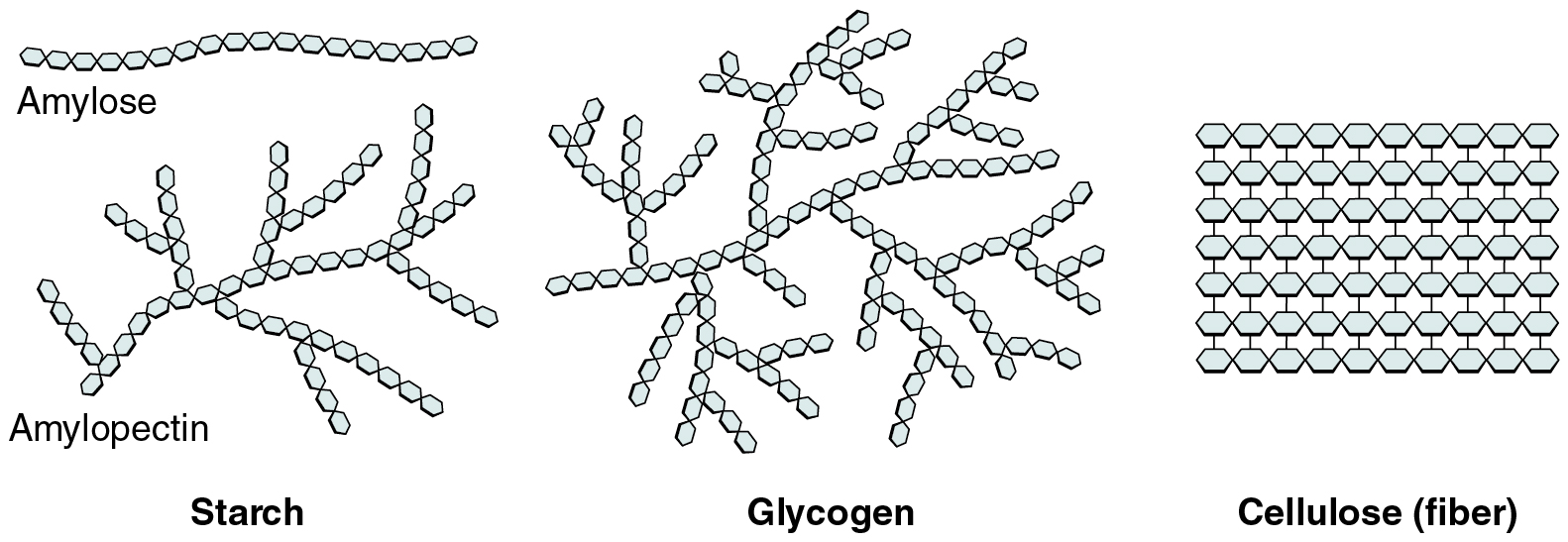
Glycogen In Plants. The main difference between starch, cellulose and glycogen is that starch is the main storage carbohydrate source in plants whereas cellulose is the main structural component of the cell wall of plants and glycogen is the main storage carbohydrate energy source of fungi and animals. This figures shows the structure of glycogen. Each molecule of glycogen is formed by the linkage in branching chains of many thousands of glucose molecules. Glycogen is a glucose polysaccharide occurring in most mammalian and nonmammalian cells, in microorganisms, and even in some plants.
 PPT Starch, Glycogen and Cellulose PowerPoint From slideserve.com
PPT Starch, Glycogen and Cellulose PowerPoint From slideserve.com
It has a similar structure to amylopectin which is a component of starch, more extensively branched and compact than starch. The main difference between starch, cellulose and glycogen is that starch is the main storage carbohydrate source in plants whereas cellulose is the main structural component of the cell wall of plants and glycogen is the main storage carbohydrate energy source of fungi and animals. Both are polysaccharides composed of glucose monomers. Polysaccharides are synthesized by plants, animals, and humans to be stored for food, structural support, or metabolized for energy. Amylopectin is insoluble in water while glycogen is soluble in water. Glycogen, often termed as animal starch, though found in plants that do not contain chlorophyll like yeast, fungi, etc.
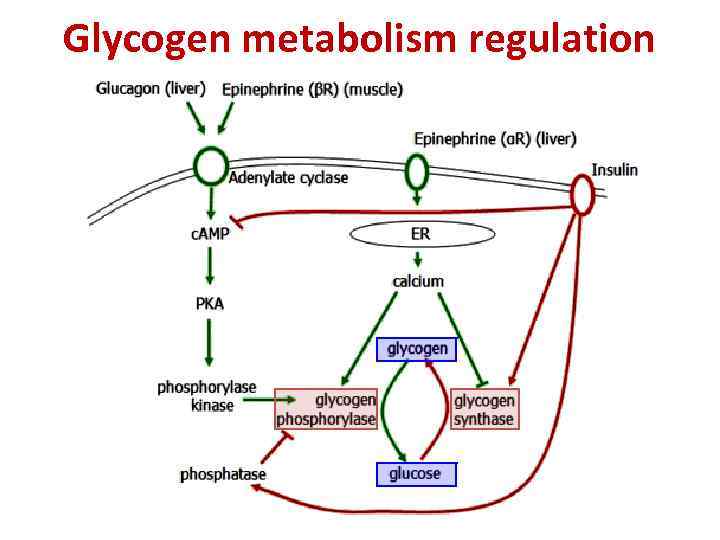
This enzyme has two activities;
Glycogen and starch are a good source of energy aside from the energy that the human body produces. Amylopectin is a type of starch and is one of the storage polysaccharides of plants. Amylopectin is insoluble in water while glycogen is soluble in water. Glycogen is synthesized and stored mainly in the liver and the muscles. Excess starch is converted into glycogen in. The glucose monomer units are held by the strong glycosidic bonds to form the polymer glycogen.
 Source: vedantu.com
Source: vedantu.com
Each molecule of glycogen is formed by the linkage in branching chains of many thousands of glucose molecules. An energy storage polysaccharide formed in the liver of animals. Glycogen is a glucose polysaccharide occurring in most mammalian and nonmammalian cells, in microorganisms, and even in some plants. Glycogen is highly branched compared to amylopectin. Glycogen is also found in seaweeds and plants.
Source: researchgate.net
Excess starch is converted into glycogen in. Hydrolyzed when it is dissolved in water. It has a similar structure to amylopectin which is a component of starch, more extensively branched and compact than starch. Glycogen is also found in seaweeds and plants. Similarly regulated enzymes are required to make glycogen.
 Source: documents.pub
Source: documents.pub
After your body has used the energy it needs, the leftover glucose is stored in little bundles called glycogen in the liver and muscles. Structurally, glycogen is very similar to amylopectin with alpha acetal linkages, however, it has even more branching and more glucose units are present than in amylopectin. Glycogen, white, amorphous, tasteless polysaccharide (c6h1005)n. Glycogen is also stored in muscles and fat cells. The main difference between glycogen and starch is that glycogen is produced in animals and fungi while starch is produced in plants.
 Source: plantphysiol.org
Source: plantphysiol.org
Glycogen is a glucose polysaccharide occurring in most mammalian and nonmammalian cells, in microorganisms, and even in some plants. Glycogen, white, amorphous, tasteless polysaccharide (c6h1005)n. And (ii) the evolution of novel types of. Your body can store enough to fuel you for about a day. The glucose monomer units are held by the strong glycosidic bonds to form the polymer glycogen.
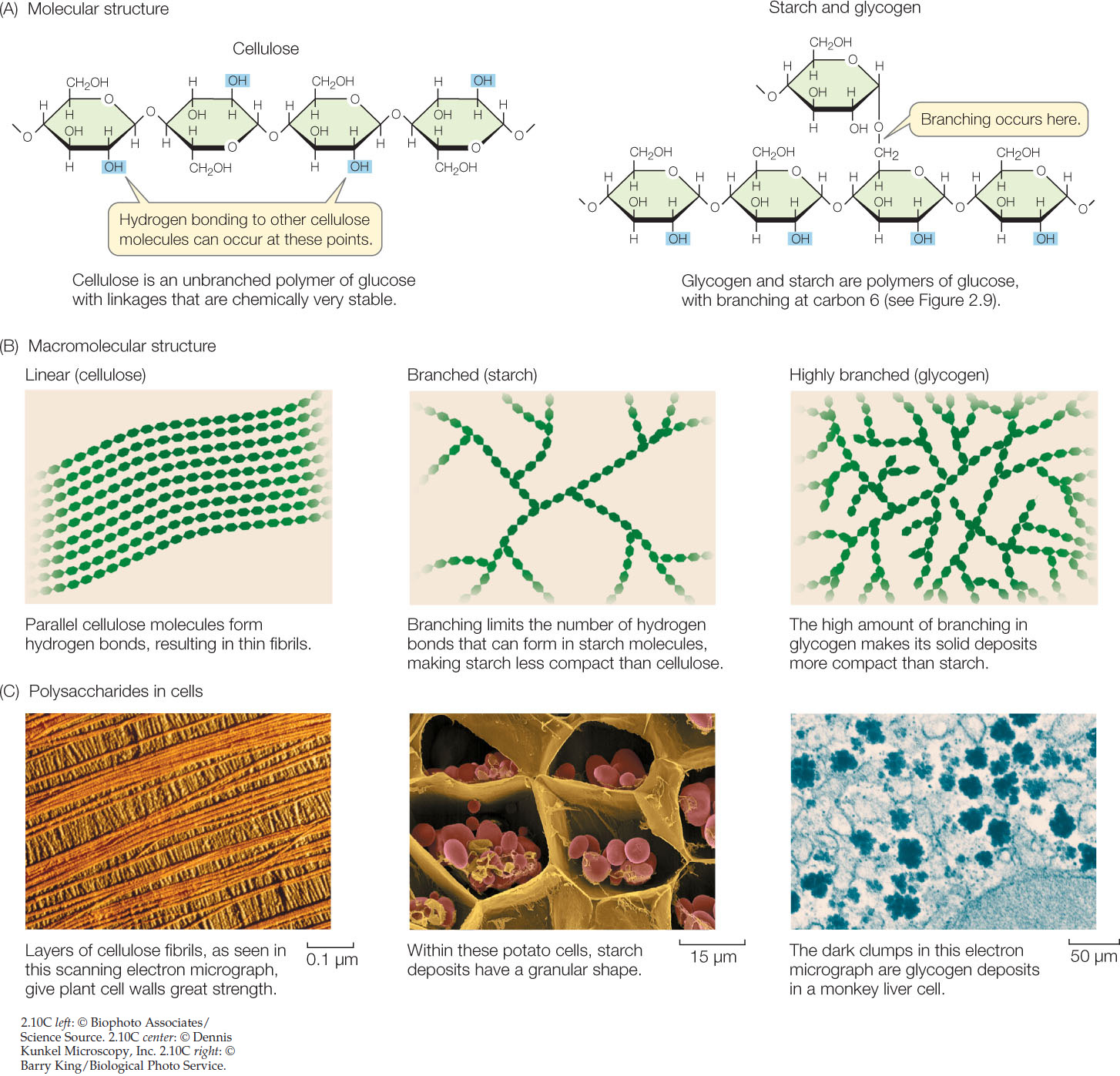 Source: macmillanhighered.com
Source: macmillanhighered.com
The regulation of both sets of enzymes is reciprocal, making sure that you either make glycogen or use. Glycogen is also stored in muscles and fat cells. Amylopectin and glycogen are two types of branched polysaccharides. Glycogen is the form in which carbohydrate is stored in the body. Hydrolyzed when it is dissolved in water.
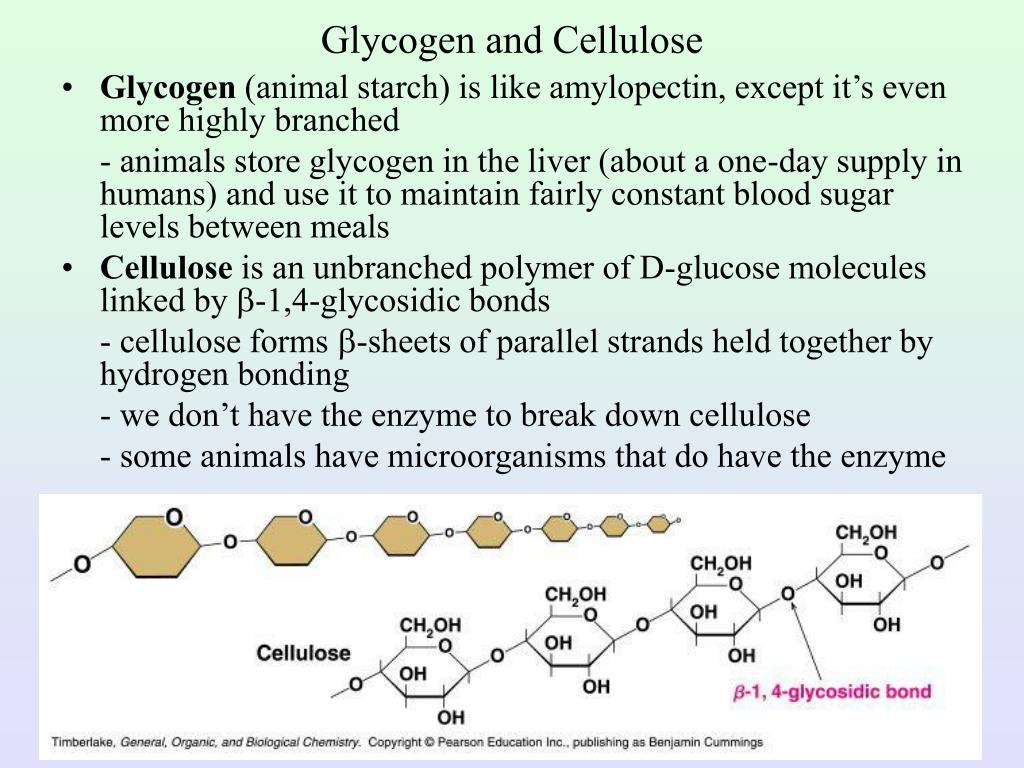 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
It also is found in various species of microorganisms—e.g., bacteria and fungi, including yeasts. It is also the homopolysaccharide having the glycogen bonds or linkages similar to that of the amylopectin, with the more branches. Glycogen is the storage polysaccharide in animals. In this opinion article we propose a scenario detailing how two crucial components have evolved simultaneously to ensure the transition of glycogen to starch in the cytosol of the archaeplastida last common ancestor: Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in animals and humans which is analogous to the starch in plants.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Cellulose, however, is only found in plant cells. The main difference between starch, cellulose and glycogen is that starch is the main storage carbohydrate source in plants whereas cellulose is the main structural component of the cell wall of plants and glycogen is the main storage carbohydrate energy source of fungi and animals. The main difference between glycogen and starch is that glycogen is produced in animals and fungi while starch is produced in plants. In this opinion article we propose a scenario detailing how two crucial components have evolved simultaneously to ensure the transition of glycogen to starch in the cytosol of the archaeplastida last common ancestor: Glycogen serves as an energy reservoir, being broken down to glucose when needed.
 Source: keto-vegan.com
Source: keto-vegan.com
The main difference between glycogen and starch is that glycogen is produced in animals and fungi while starch is produced in plants. Such a molecule is found in plants and is called amylose. Amylopectin and glycogen are two forms of starch found in plants and animals respectively. Glycogen is synthesized and stored mainly in the liver and the muscles. Amylopectin is a type of starch and is one of the storage polysaccharides of plants.
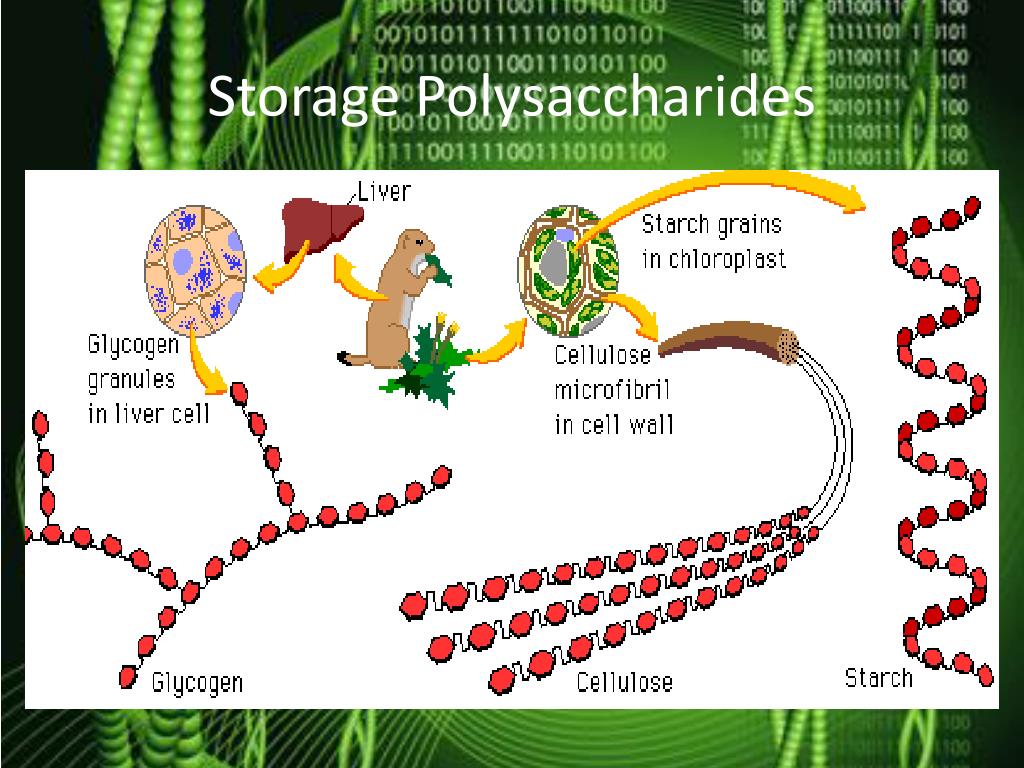 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Each molecule of glycogen is formed by the linkage in branching chains of many thousands of glucose molecules. This enzyme has two activities; The main difference between glycogen and starch is that glycogen is produced in animals and fungi while starch is produced in plants. Such a molecule is found in plants and is called amylose. Excess starch is converted into glycogen in.
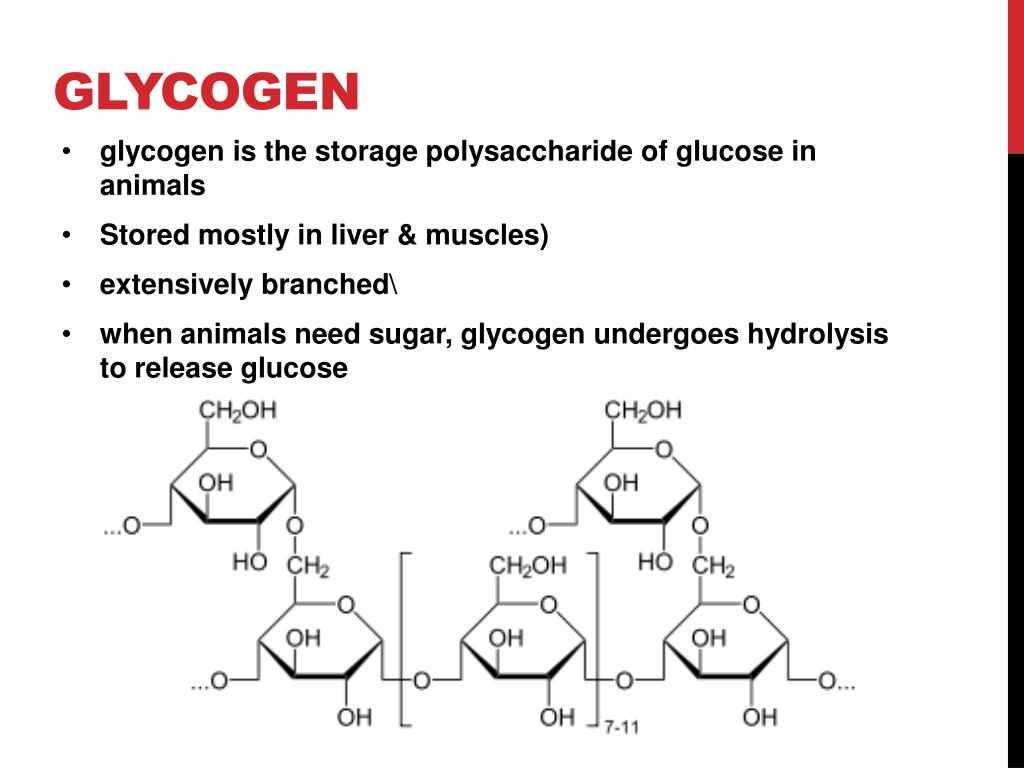 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Glycogen is the energy storage carbohydrate that is found only in animals and plants. Glycogen is the form in which carbohydrate is stored in the body. Similarly regulated enzymes are required to make glycogen. This figures shows the structure of glycogen. Thus, glycogen is a natural polymer, a polysaccharide, which has a similar structure to the starch which is found in plants.
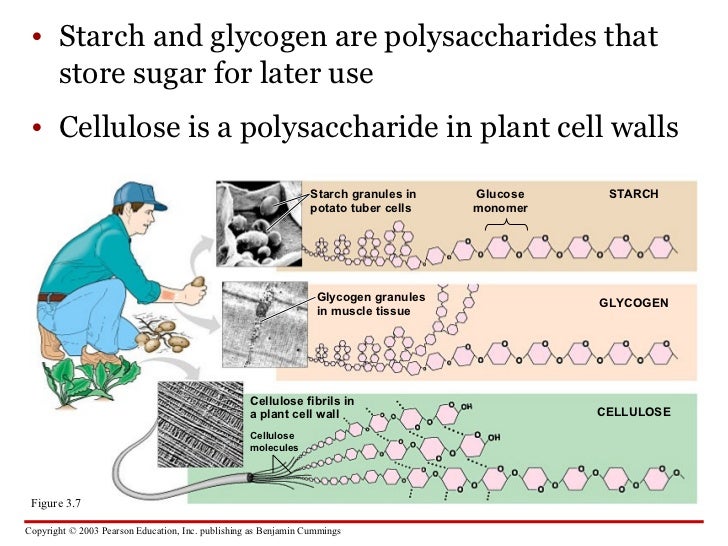 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
It has the same structure as amylopectin which is a starch, more widely branched and compacted than starch. Same as in all life. Plants are able to synthesize glucose, and the excess glucose is stored as starch in different plant parts, including roots and seeds. Glycogen is synthesized and stored mainly in the liver and the muscles. Glycogen is the analog of starch i.e., glucose polymer, in plants, it acts as energy storage.
 Source: present5.com
Source: present5.com
In this opinion article we propose a scenario detailing how two crucial components have evolved simultaneously to ensure the transition of glycogen to starch in the cytosol of the archaeplastida last common ancestor: In vertebrates it is stored mainly in the liver as a reserve of glucose for other tissues. Glycogen, often termed as animal starch, though found in plants that do not contain chlorophyll like yeast, fungi, etc. And (ii) the evolution of novel types of. Glycogen is a glucose polysaccharide occurring in most mammalian and nonmammalian cells, in microorganisms, and even in some plants.
 Source: cell.com
Source: cell.com
It has the same structure as amylopectin which is a starch, more widely branched and compacted than starch. Starch can usually be found in staple foods like rice, barley, oats and potatoes. Plants store energy in starches essentially because they lack the enzymes to break down fats for energy. Glycogen is a complex carbohydrate found only animals. Glycogen is synthesized and stored mainly in the liver and the muscles.
 Source: opentextbc.ca
Source: opentextbc.ca
Starch can usually be found in staple foods like rice, barley, oats and potatoes. Amylopectin and glycogen are two forms of starch found in plants and animals respectively. Cellulose, however, is only found in plant cells. Hydrolyzed when it is dissolved in water. Glycogen and starch are carbohydrate polymers that are of great importance both in plants and animal cells.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Each molecule of glycogen is formed by the linkage in branching chains of many thousands of glucose molecules. Glycogen serves as an energy reservoir, being broken down to glucose when needed. It also is found in various species of microorganisms—e.g., bacteria and fungi, including yeasts. It has a similar structure to amylopectin which is a component of starch, more extensively branched and compact than starch. The glucose monomer units are held by the strong glycosidic bonds to form the polymer glycogen.
 Source: phbuom.50webs.com
Difference between glycogen and starch. Glycogen is a glucose polysaccharide occurring in most mammalian and nonmammalian cells, in microorganisms, and even in some plants. Glycogen is an analogue of starch, which is the main form of glucose storage in most plants, but starch has fewer branches and is less compact than glycogen. Starch, the same with glycogen, is another source of energy that can be found in plants only. This enzyme has two activities;
 Source: legacy.hopkinsville.kctcs.edu
Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in animals and humans which is analogous to the starch in plants. Plants store energy in starches essentially because they lack the enzymes to break down fats for energy. Excess starch is converted into glycogen in. Structurally, glycogen is very similar to amylopectin with alpha acetal linkages, however, it has even more branching and more glucose units are present than in amylopectin. Glycogen is synthesized and stored mainly in the liver and the muscles.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in animals and humans which is analogous to the starch in plants. An energy storage polysaccharide formed in the liver of animals. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in animals and humans which is analogous to the starch in plants. Glycogen serves as an energy reservoir, being broken down to glucose when needed. It stores energy and found in the muscles and liver.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title glycogen in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.