Your Glycolysis in plants images are ready in this website. Glycolysis in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Glycolysis in plants files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos.
If you’re searching for glycolysis in plants pictures information linked to the glycolysis in plants keyword, you have come to the right site. Our website frequently gives you hints for seeking the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more enlightening video content and graphics that fit your interests.
Glycolysis In Plants. During glycolysis, plants convert the simple sugar known as glucose into pyruvic acid and produce energy. Further processing of pyruvate depends on the aerobic or anaerobic nature of an organism. Glycolysis involves breaking down glucose into pyruvate. Discuss history, 10 steps of glycolysis divided into 3 phases (energy spending, splitting and energy conserving phase) , net products of glycolysis, oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetyl coa, site of carbon dioxide production, site of glycolysis.
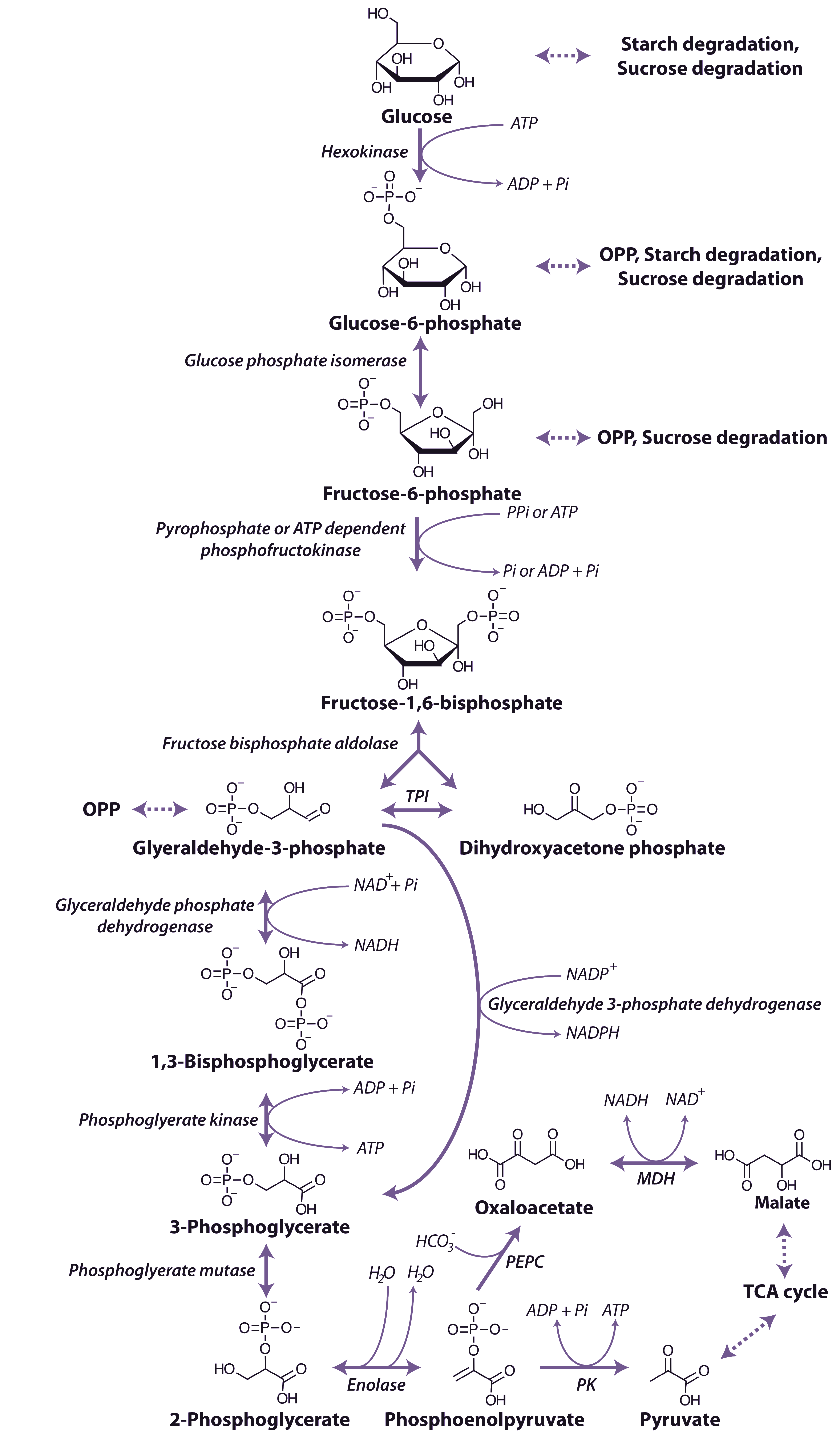 2.4.2 The glycolytic pathway Plants in Action From rseco.org
2.4.2 The glycolytic pathway Plants in Action From rseco.org
One conspicuous feature of plant glycolysis, discovered in the 1970s, is the presence of a complete or nearly complete sequence of glycolytic enzymes in plastids, distinct and spatially separated from the glycolytic enzymes located in the cytosol. Glycolysis (‘splitting of sugar’) is the most common dissimilatory pathway; Glycolysis involves breaking down glucose into pyruvate. Six enzymes are involved in the process. At least six enzymes operate in the metabolic pathway. The simple sugar glucose is generally considered the starting point for looking at glycolysis and fermentation.
Glycolysis is the process in which glucose, derived from sucrose, undergoes partial oxidation to form two molecules of pyruvic acid.
The final step of glycolysis. It is a linear pathway of metabolic reactions. Respiration in plants glycolysis (emp pathway) it is the partial oxidation (breakdown) of glucose to 2 molecules of pyruvic acid (c 3 h 4 o 3 ) in the absence of o 2. Glucose and fructose are phosphorylated to give rise to glucose. In this process, glucose undergoes partial oxidation to form two molecules of pyruvic acid. The process entails the oxidation of glucose molecules, the single most crucial organic fuel in plants, microbes, and animals.

Glycolysis is the process in which glucose, derived from sucrose, undergoes partial oxidation to form two molecules of pyruvic acid. This is common in all living beings. The majority of microbes utilise the glycolytic pathway for the catabolism of. Glycolysis is the process in which one glucose molecule is broken down to form two molecules of pyruvic acid (also called pyruvate). Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and is present in all living organisms.
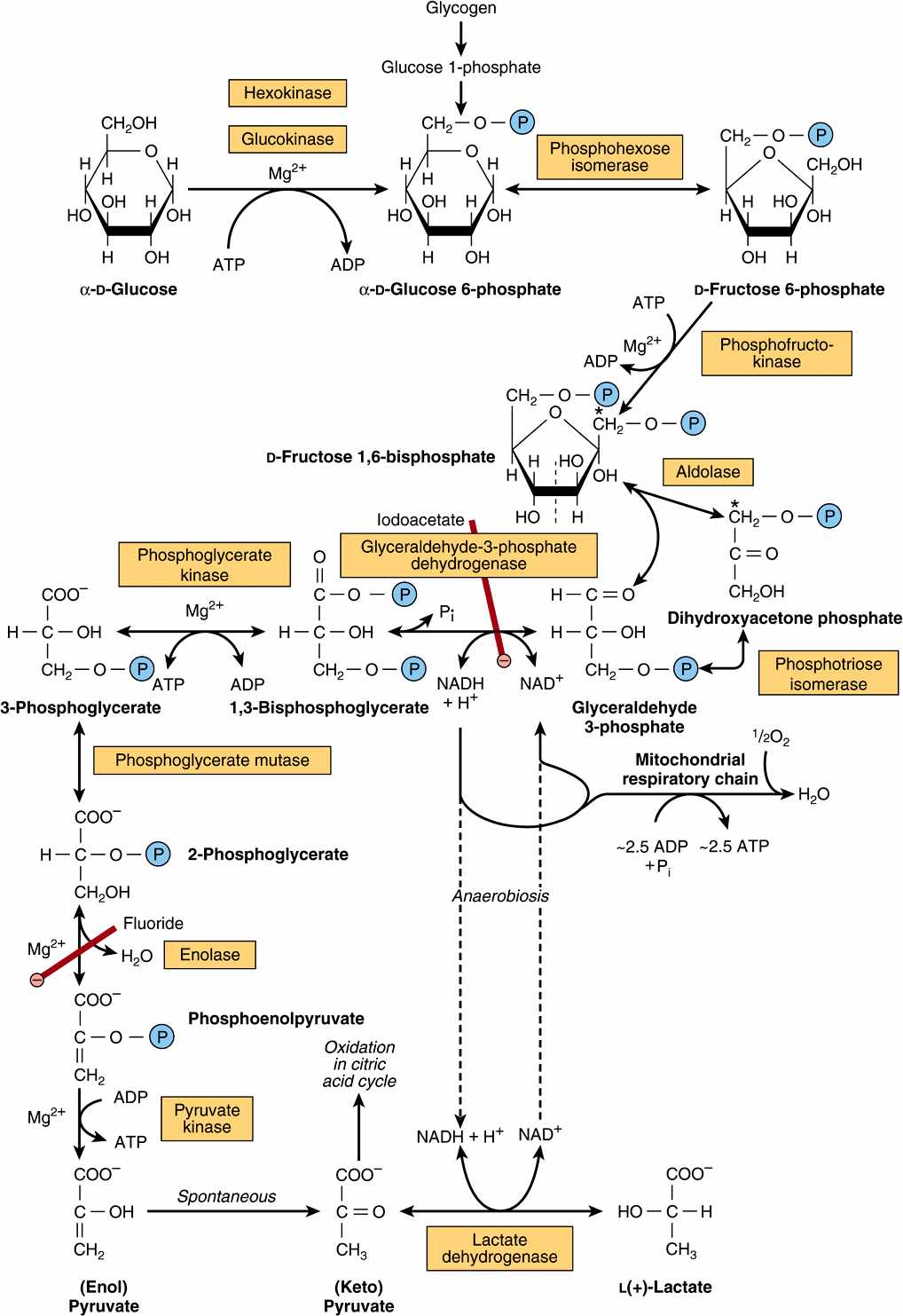 Source: basicmedicalkey.com
Source: basicmedicalkey.com
Glycolysis is the partial oxidation of glucose or similar hexose sugar into two molecules of pyruvic acid through a series of enzyme mediated reactions releasing some atp and nadh2. Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes. Parnas and gustav were the first ones to give the scheme of glycolysis. Glycolysis is the beginning of the process of extracting usable energy from food. The functions of glycolysis glycolysis evolved as a catabolic anaerobic pathway to fulfil two fundamental roles.
Source: regulation.mojok.my.id
Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis glucose occupies a central position in the metabolism of plants, animals and many microorganisms. Here, the plants carry out the partial oxidation of glucose. During glycolysis, plants convert the simple sugar known as glucose into pyruvic acid and produce energy. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and is present in all living organisms. Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Many scientists, like louis pasteur and eduard buchner, uncovered some of the steps in glycolysis but never connected those steps with the entire pathway. Two alternate cytosolic reactions enhance the pathway�s atp yield through the use of pyrophosphate in place of atp. It is a linear pathway of metabolic reactions. The simple sugar glucose is generally considered the starting point for looking at glycolysis and fermentation. Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
A glucose molecule is partially oxidized to two molecules of pyruvic acid. The organisms that do not have access to glucose from other sources must make it. Further processing of pyruvate depends on the aerobic or anaerobic nature of an organism. The majority of microbes utilise the glycolytic pathway for the catabolism of. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of the cells.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The upcoming discussion will update you about the differences between glycolysis and krebs’ cycle. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of the cells. The functions of glycolysis glycolysis evolved as a catabolic anaerobic pathway to fulfil two fundamental roles. Glycolysis is the process in which one glucose molecule is broken down to form two molecules of pyruvic acid (also called pyruvate). The simple sugar glucose is generally considered the starting point for looking at glycolysis and fermentation.
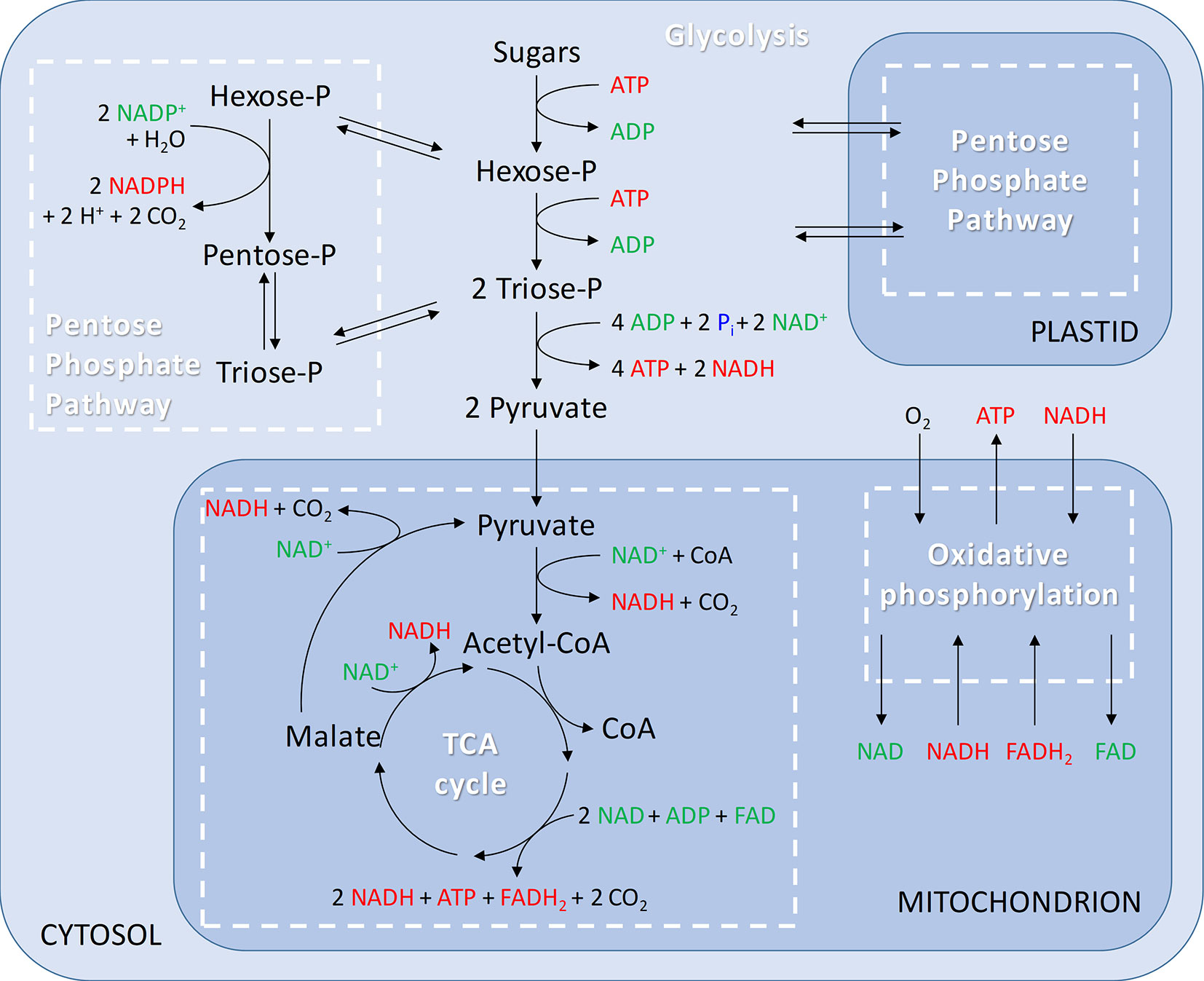 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Here, the plants carry out the partial oxidation of glucose. Parnas and gustav were the first ones to give the scheme of glycolysis. It occurs in the cytosol of all cells and this is thought to indicate that it is one of the most ancient pathways of carbon metabolism. Glycolysis takes place in both aerobic and anaerobic organisms and is the first step towards the metabolism of glucose. The process takes place in the cytoplasm of plant and animal cells.
 Source: pnas.org
Source: pnas.org
In plants, this glucose is derived from sucrose, which is the end product. Glycolysis glycolysis is the first part of respiration. The upcoming discussion will update you about the differences between glycolysis and krebs’ cycle. Glycolysis is the process in which one glucose molecule is broken down to form two molecules of pyruvic acid (also called pyruvate). If you�re seeing this message, it means we�re having trouble loading external resources on our website.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The ultimate carbohydrate source in plants is most commonly sucrose as that is the form of carbohydrate that normally shuttles reduced carbon either in time or in space between photosynthetic and respiratory pathways. If you�re seeing this message, it means we�re having trouble loading external resources on our website. Six enzymes are involved in the process. Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose c 6 h 12 o 6, into pyruvic acid, ch 3 cocooh. The rate of respiration in plants is much lower than in animals.
 Source: studiousguy.com
Source: studiousguy.com
Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and is present in all living organisms. The end products of the reaction include 2 pyruvate, 2 atp and 2 nadh molecules. Plants make glucose by photosynthesis. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of the cells. Glycolysis is the beginning of the process of extracting usable energy from food.
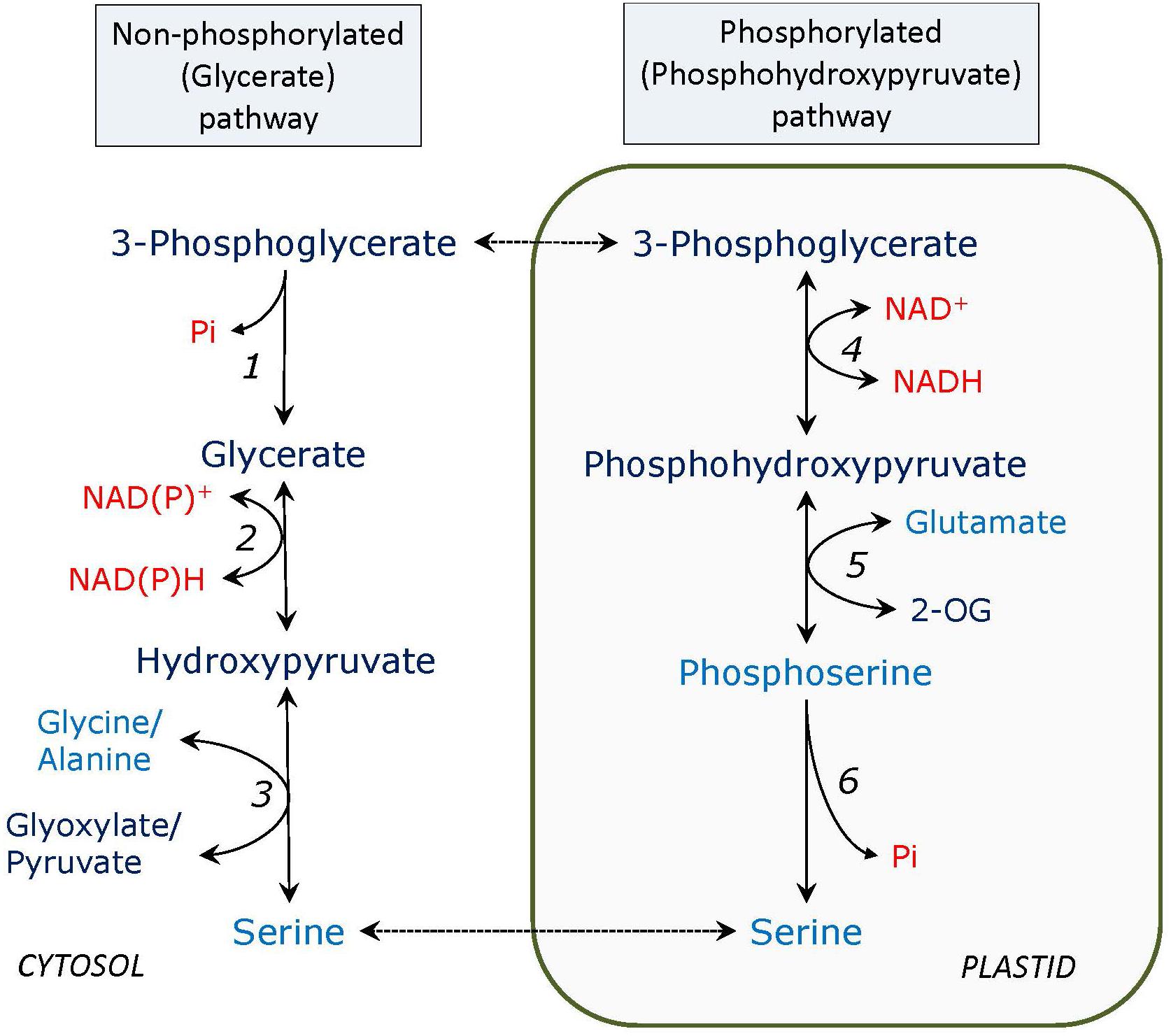 Source: frontiersin.org
Source: frontiersin.org
Parnas and gustav were the first ones to give the scheme of glycolysis. Glycolysis is the partial oxidation of glucose or similar hexose sugar into two molecules of pyruvic acid through a series of enzyme mediated reactions releasing some atp and nadh2. The rate of respiration in plants is much lower than in animals. Plants do not have great demands for gaseous exchange. Glucose and fructose are phosphorylated to give rise to glucose.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
In anaerobic respiration, pyruvate is. Learn the concepts of class 11 biology respiration in plants with videos and stories. The ultimate carbohydrate source in plants is most commonly sucrose as that is the form of carbohydrate that normally shuttles reduced carbon either in time or in space between photosynthetic and respiratory pathways. Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis glucose occupies a central position in the metabolism of plants, animals and many microorganisms. Parnas and gustav were the first ones to give the scheme of glycolysis.
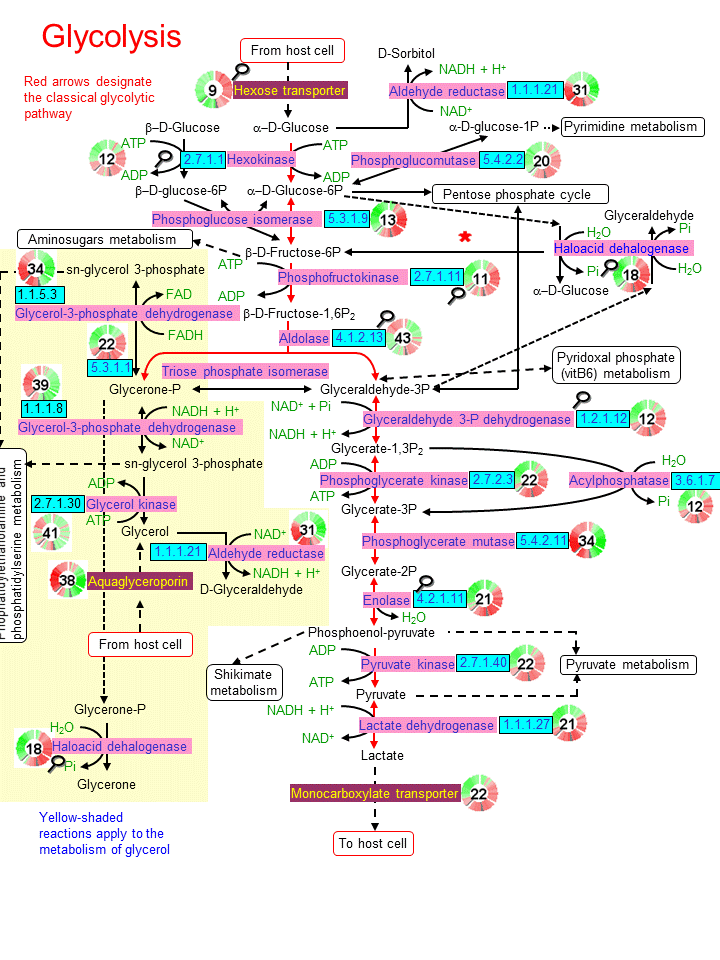 Source: mpmp.huji.ac.il
Source: mpmp.huji.ac.il
This is common in all living beings. The majority of microbes utilise the glycolytic pathway for the catabolism of. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of the cells. The final step of glycolysis. Six enzymes are involved in the process.
 Source: brainkart.com
Source: brainkart.com
It is a very ancient pathway and is the first stage of cellular respiration. The rate of respiration in plants is much lower than in animals. The simple sugar glucose is generally considered the starting point for looking at glycolysis and fermentation. Further processing of pyruvate depends on the aerobic or anaerobic nature of an organism. Respiration in plants glycolysis (emp pathway) it is the partial oxidation (breakdown) of glucose to 2 molecules of pyruvic acid (c 3 h 4 o 3 ) in the absence of o 2.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
It occurs in the cytoplasm. Discuss history, 10 steps of glycolysis divided into 3 phases (energy spending, splitting and energy conserving phase) , net products of glycolysis, oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetyl coa, site of carbon dioxide production, site of glycolysis. Parnas and gustav were the first ones to give the scheme of glycolysis. The organisms that do not have access to glucose from other sources must make it. The majority of microbes utilise the glycolytic pathway for the catabolism of.
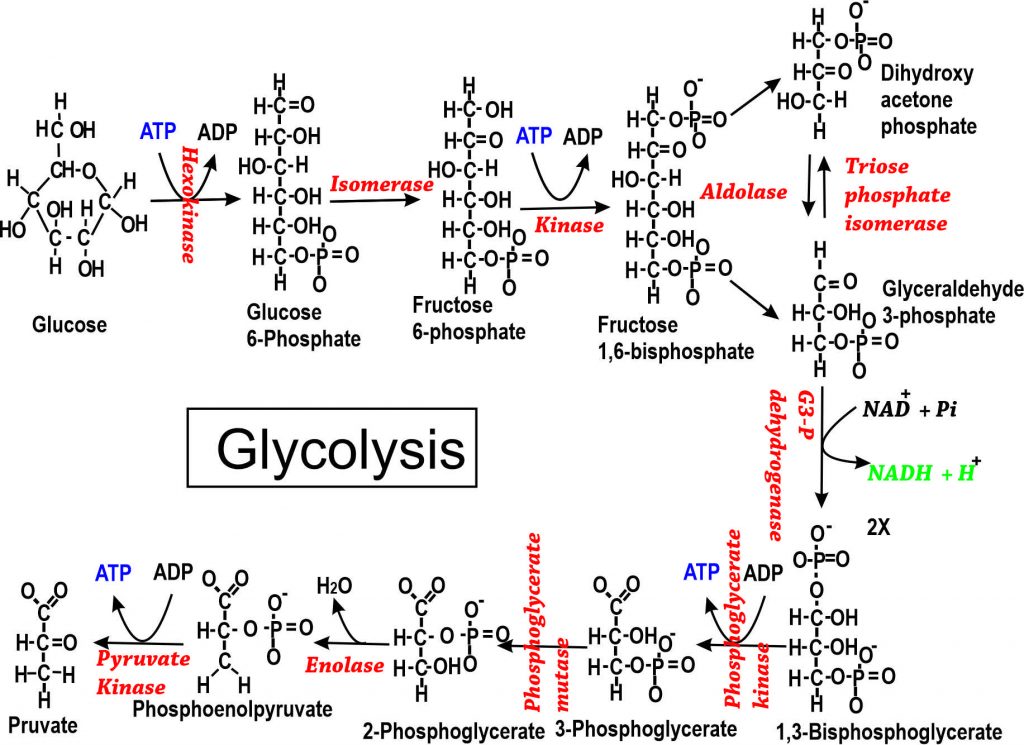 Source: istudy.pk
Source: istudy.pk
It occurs in the cytoplasm. Glycolysis is the beginning of the process of extracting usable energy from food. In animals, glucose has four major fates as shown in figure 1. In glycolysis, 2 atp molecules are consumed, producing 4 atp, 2 nadh, and 2 pyruvates per glucose molecule. Glycolysis occurs in plant, animal, and microbe cells:
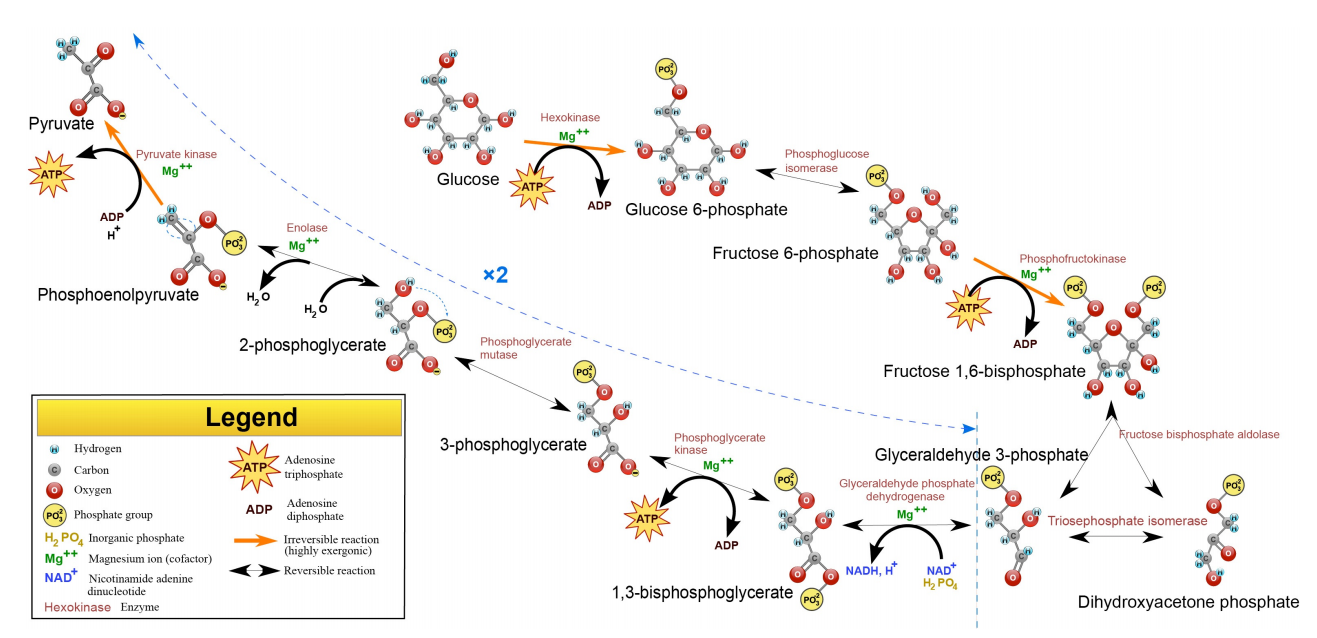 Source: bio.libretexts.org
Source: bio.libretexts.org
Two alternate cytosolic reactions enhance the pathway�s atp yield through the use of pyrophosphate in place of atp. Plants do not have great demands for gaseous exchange. A detailed schematic diagram of glycolysis is shown in figure 11.3 of your text. Glycolysis involves the conversion of carbohydrates into organic acids (figure 2 ). It is the process in which a glucose molecule is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate.
 Source: rseco.org
Source: rseco.org
Glycolysis is a sequence of ten reactions catalyzed by enzymes. It occurs widely and is found in animal and plant cells as well as in microorganisms. If you�re seeing this message, it means we�re having trouble loading external resources on our website. Glycolysis is the process in which glucose, derived from sucrose, undergoes partial oxidation to form two molecules of pyruvic acid. Parnas and gustav were the first ones to give the scheme of glycolysis.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title glycolysis in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







