Your Ground tissue in plants images are available in this site. Ground tissue in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Ground tissue in plants files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for ground tissue in plants pictures information linked to the ground tissue in plants topic, you have come to the right site. Our site frequently gives you suggestions for seeking the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more informative video content and graphics that match your interests.
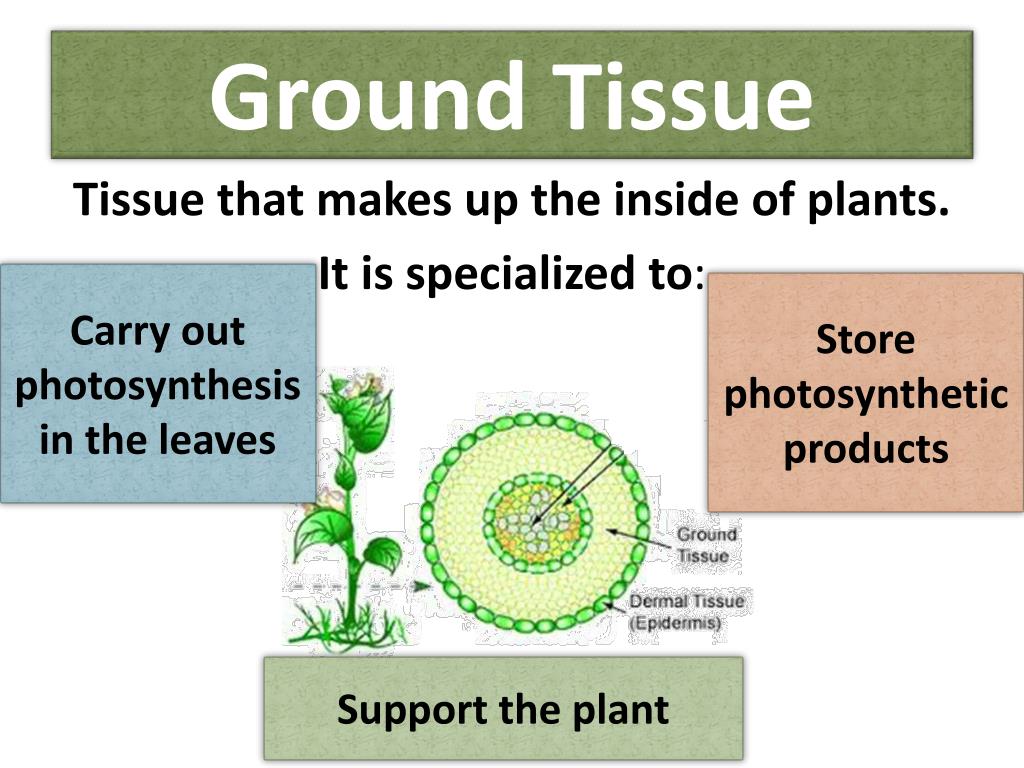
Ground Tissue In Plants. The cortex/endodermis initial cell (cei) generates the two ground tissues, cortex and endodermis, via sequential asymmetric divisions.especially endodermis development has to be under tight control with an evolutionary conserved process, as in nearly all plants it consists of only one cell layer. Ground tissue cells include parenchyma, (photosynthesis in the leaves, and storage in the roots), collenchyma (shoot support in areas of active growth), and schlerenchyma (shoot support in areas where growth has ceased). A ground tissue is a plant tissue other than those of the dermal tissues and the vascular tissues. This tissue type comprises the majority of the plant body.
 Plant Tissue Systems From thoughtco.com
Plant Tissue Systems From thoughtco.com
The ground tissue system consists of The cortex/endodermis initial cell (cei) generates the two ground tissues, cortex and endodermis, via sequential asymmetric divisions.especially endodermis development has to be under tight control with an evolutionary conserved process, as in nearly all plants it consists of only one cell layer. Ground tissue is primarily involved in. They constitute most of the interior parts of the plant; The ground tissue of the vascular plant is responsible for storing the carbohydrates produced by the plant. Parenchymatous cells are usually present in cortex, pericycle, pith and medullary rays, in the primary stems and roots.
This means that ground tissue covers a wide variety of functions.
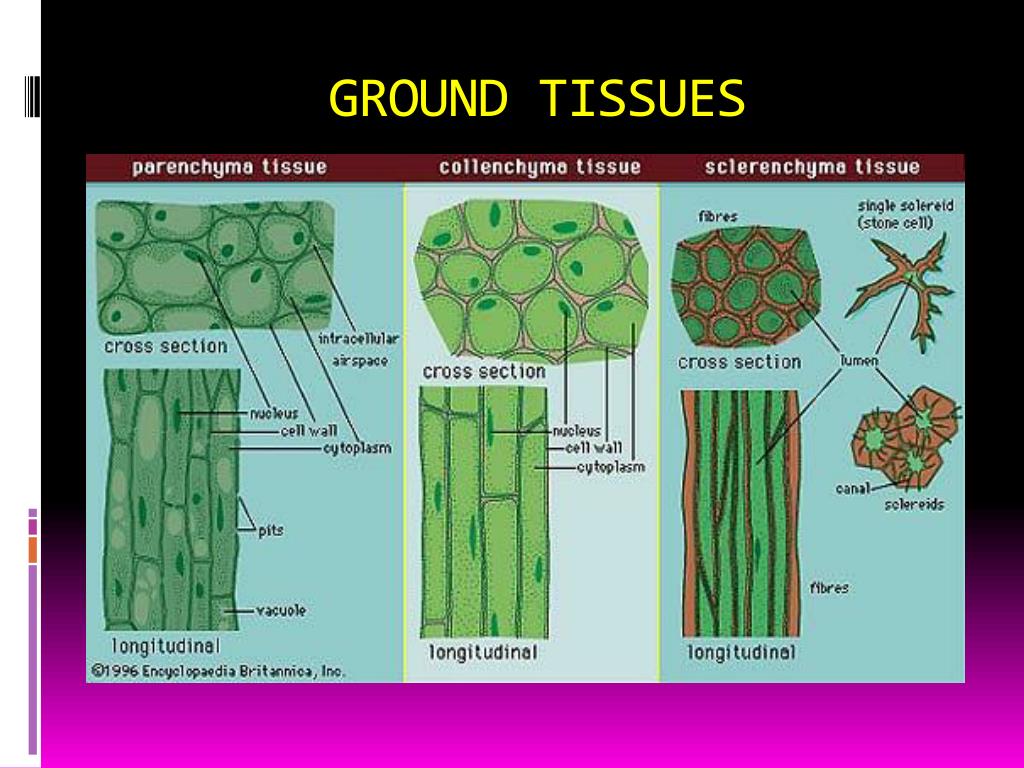
Cordelia bolle, in plant transcription factors, 2016. They are made up of three types of cells: The ground tissue system arises from a ground tissue meristem and consists of three simple tissues: Cordelia bolle, in plant transcription factors, 2016. Generally, they organize into different functional layers in the stem, leaves, roots, and other parts of the cell. Parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma ( figure 5 ).
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Parenchyma have thin walls of cellulose, whereas collenchyma have cell walls with thickened areas of additional cellulose. This tissue includes all plant tissue that is neither vascular nor dermal. Ground tissue is all the other tissue in a plant that isn’t dermal tissue or vascular tissue. They constitute most of the interior parts of the plant; Ground tissue in plants is the filler, separating the dermal tissue layer (outer plant skin so to speak) and the vascular tissues (inner tubes.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
There are two types of. Ground tissue provides support and stores materials in roots and stems. It is produced by the ground meristem. The ground tissue system consists of Where is the ground tissue in plants?
 Source: myriverside.sd43.bc.ca
Source: myriverside.sd43.bc.ca
Is spongy mesophyll ground tissue? Ground tissue is primarily involved in. Is spongy mesophyll ground tissue? The ground tissue of the vascular plant is responsible for storing the carbohydrates produced by the plant. Ground tissue is all the other tissue in a plant that isn’t dermal tissue or vascular tissue.
 Source: csus.edu
It arises from the ground meristem. A ground tissue is a plant tissue other than those of the dermal tissues and the vascular tissues. This tissue type comprises the majority of the plant body. This means that ground tissue covers a wide variety of functions. It is divided into mainly three types based on the nature of the cell walls, viz., parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Parenchyma, sclerenchyma, and collenchyma cells. Ground tissue is a plant tissue, present between vascular and dermal tissue. Ground tissue in plants is the filler, separating the dermal tissue layer (outer plant skin so to speak) and the vascular tissues (inner tubes. They are made up of three types of cells: It arises from the ground meristem.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
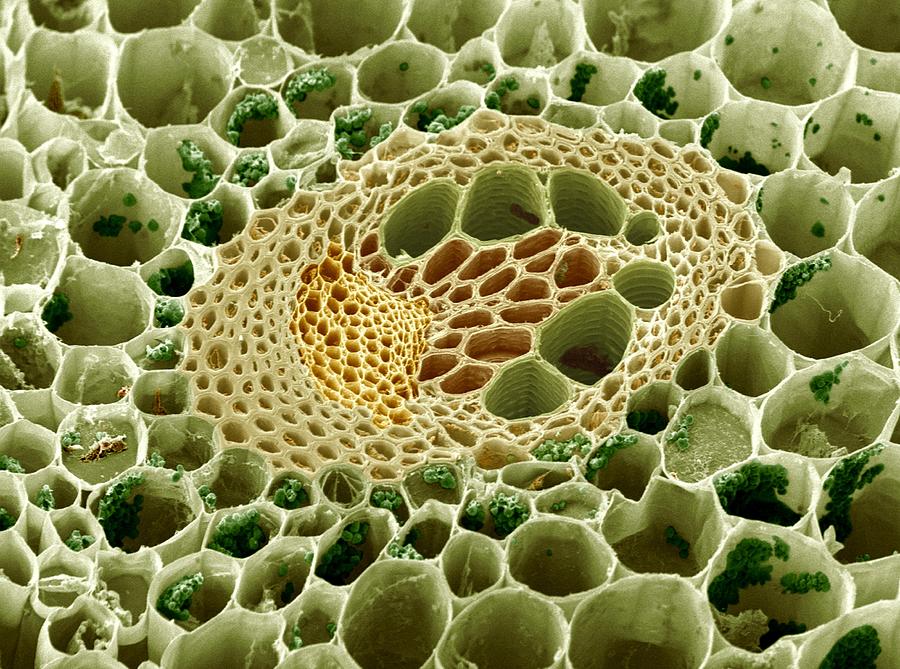
In leaves, ground tissue is packed with chloroplasts, where photosynthesis makes food for the plant. It fills in the plant’s soft components, such as the cortex, pith, pericycle, and so on. Parenchymatous cells are usually present in cortex, pericycle, pith and medullary rays, in the primary stems and roots. Although all tissue types contain parenchyma, certain tissues are predominantly parenchyma, including the cortex and pith in stems and roots, and the mesophyll in leaves. All tissues except epidermis and vascular bundles constitute the ground tissue.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Cortex and pith are types of ground tissue. Ground tissue in plants is the filler, separating the dermal tissue layer (outer plant skin so to speak) and the vascular tissues (inner tubes. Ground tissue provides support and stores materials in roots and stems. Parenchyma parenchyma cells are slightly differentia. Perenchyma is a living ground tissue that makes up the bulk of the primary plant body and takes part in several tasks such as photosynthesis, storage and regeneration.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma ( figure 5 ). Ground tissue cells include parenchyma, (photosynthesis in the leaves, and storage in the roots), collenchyma (shoot support in areas of active growth), and schlerenchyma (shoot support in areas where growth has ceased). The cortex/endodermis initial cell (cei) generates the two ground tissues, cortex and endodermis, via sequential asymmetric divisions.especially endodermis development has to be under tight control with an evolutionary conserved process, as in nearly all plants it consists of only one cell layer. Ground tissue cells include parenchyma, (photosynthesis in the leaves, and storage in the roots), collenchyma (shoot support in areas of active growth), and schlerenchyma (shoot support in areas where growth has ceased). Therefore, given the vital role of this tissue in plants and its function in storing food and water, we can confidently say that a.
 Source: csus.edu
The ground tissue of plants includes all tissues that are neither dermal nor vascular. They carry out various functions depending on the cell type and location. In brief, dermal, vascular, and ground tissue are three tissue systems of plants. Ground tissue systems are produced by the ground meristems. Perform various roles depending on the type of cells, and plant location, including parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma;
 Source: za.pinterest.com
Source: za.pinterest.com
A ground tissue is a plant tissue other than those of the dermal tissues and the vascular tissues. The ground tissue found beneath the epidermis which surrounds the central cylinder and is delimited from the cylinder by the endodermis is called the cortex. There are three fundamental types of cells that make up a ground tissue, i.e. In some cases, the ground tissue also stores food in the form of starch. It arises from the ground meristem.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
It consists of simple tissues such as parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma. The ground tissue system consists of Thus it is the largest or the most exhaustive system, which begins from the layer next to epidermis and continues right up to the centre of the organs in cylindrical bodies. Ground tissue system dermal tissue surrounds the system of ground tissue, which makes up much of the inside of a plant. Ground tissue is a plant tissue, present between vascular and dermal tissue.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
It arises from the ground meristem. There are three types of ground tissue. The ground tissue of plants includes all tissues that are neither dermal nor vascular. Render supporting matrix for vascular tissues, alongside providing structural assistance to the stem and assisting in storing water and sugars Ground tissue system includes three cell typeys of different functions:
 Source: hortsciences.com
Source: hortsciences.com
Ground tissues are produced by the ground meristems. There are three types of ground tissue. They carry out various functions depending on the cell type and location. It fills in the soft parts of the plants, such as cortex, pith, pericycle, etc. It fills in the soft parts of the plants, such as cortex, pith, pericycle, etc.
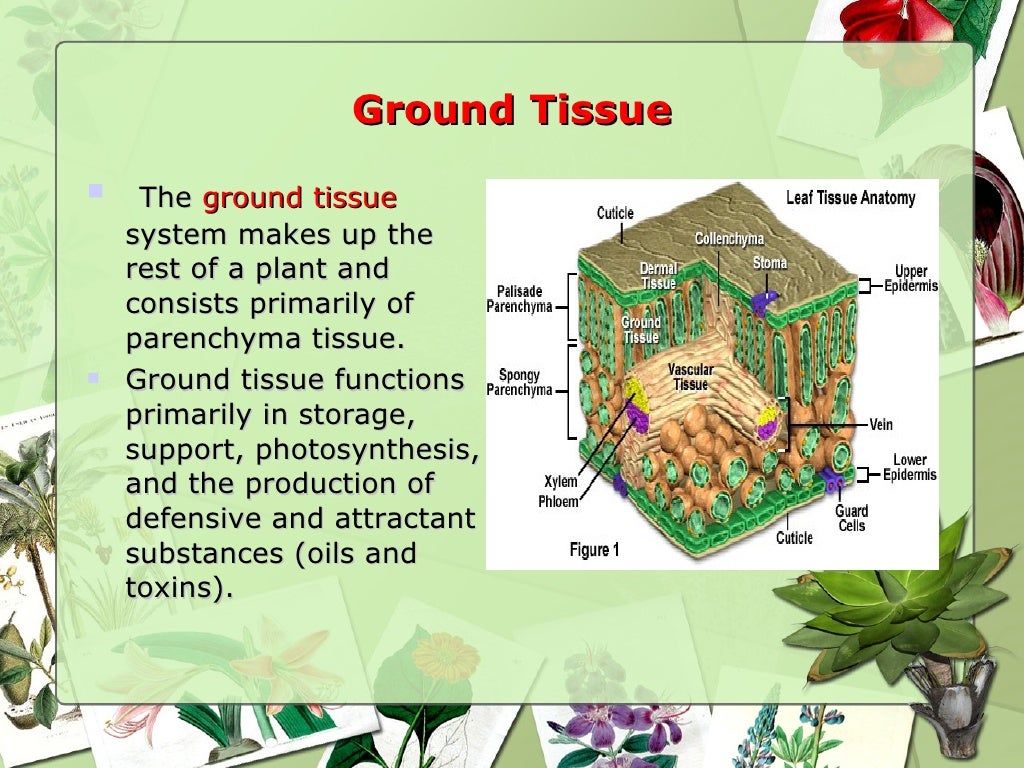 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Ground tissue systems are produced by the ground meristems. They are a type of ground tissue that is actually found as two distinct types in the leaves. The ground tissue of plants includes all tissues that are neither dermal nor vascular. The ground tissue of the vascular plant is responsible for storing the carbohydrates produced by the plant. Parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma ( figure 5 ).
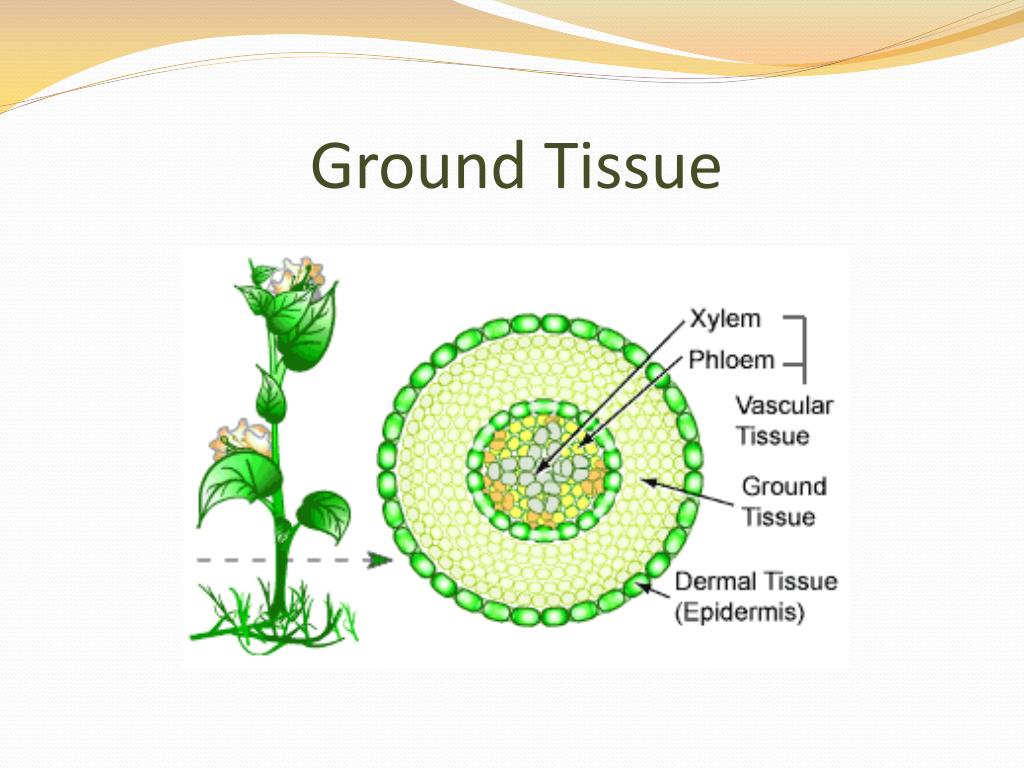 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Generally, they organize into different functional layers in the stem, leaves, roots, and other parts of the cell. All tissues except epidermis and vascular bundles constitute the ground tissue. Parenchyma have thin walls of cellulose, whereas collenchyma have cell walls with thickened areas of additional cellulose. Parenchyma parenchyma cells are slightly differentia. This means that ground tissue covers a wide variety of functions.
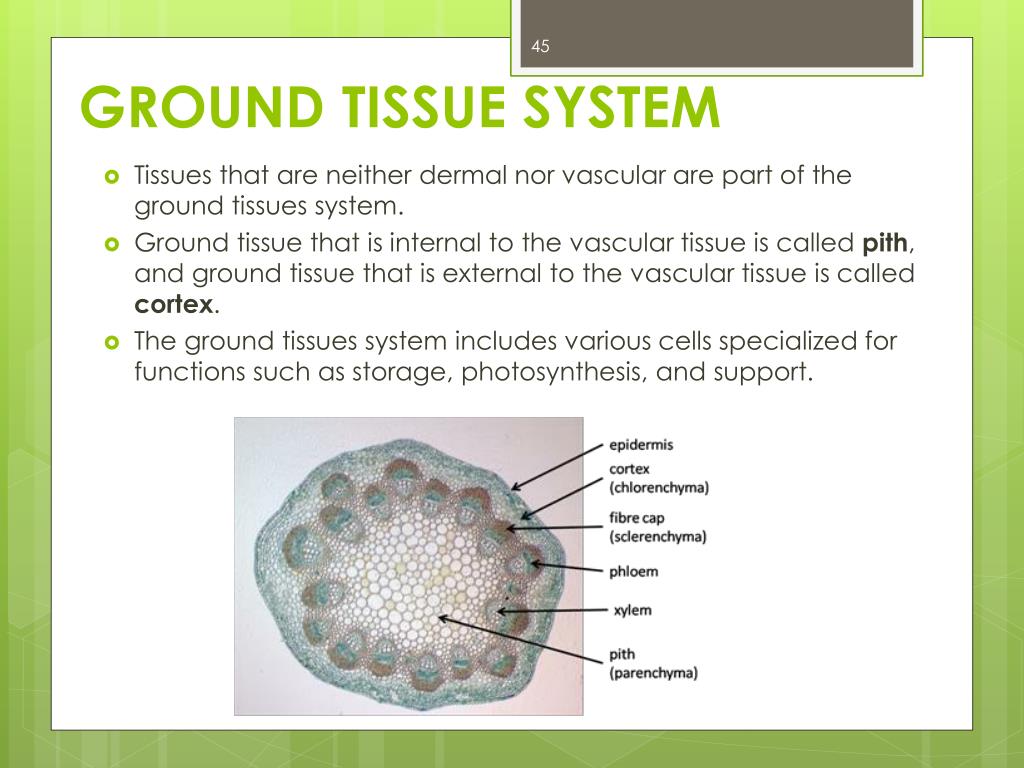 Source: mpcourseworkfxky.rotherhamonline.info
Source: mpcourseworkfxky.rotherhamonline.info
Parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma ( figure 5 ). American heritage® dictionary of the english language, fifth edition. Ground tissues synthesize organic compounds and provide support to the plant. The spongy mesophyll also allows the plant to bend and move in the wind, which itself helps move gases around the leaf’s cells. Ground tissue provides support and stores materials in roots and stems.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
Generally, they organize into different functional layers in the stem, leaves, roots, and other parts of the cell. Ground tissues synthesize organic compounds and provide support to the plant. Parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma ( figure 5 ). Parenchyma, sclerenchyma, and collenchyma cells. There are two types of.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
Perenchyma is a living ground tissue that makes up the bulk of the primary plant body and takes part in several tasks such as photosynthesis, storage and regeneration. Although all tissue types contain parenchyma, certain tissues are predominantly parenchyma, including the cortex and pith in stems and roots, and the mesophyll in leaves. The most basic cell type, which makes up the ground tissue in plants, is the parenchyma cell (fig. It stores nutrients, carbohydrates and water. This tissue type comprises the majority of the plant body.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title ground tissue in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.