Your Guard cells in plants images are available in this site. Guard cells in plants are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Guard cells in plants files here. Find and Download all free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for guard cells in plants pictures information related to the guard cells in plants keyword, you have come to the ideal site. Our website always gives you suggestions for seeking the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and locate more enlightening video content and images that fit your interests.
Guard Cells In Plants. How do stomata and guard cells regulate water loss in a plant? However, the function of these organelles in stomatal responses has been a subject of debate. Chloroplasts are a key feature of most guard cells; That the ventral wall of the guard cell to the outside of the pore is an area of major water loss.
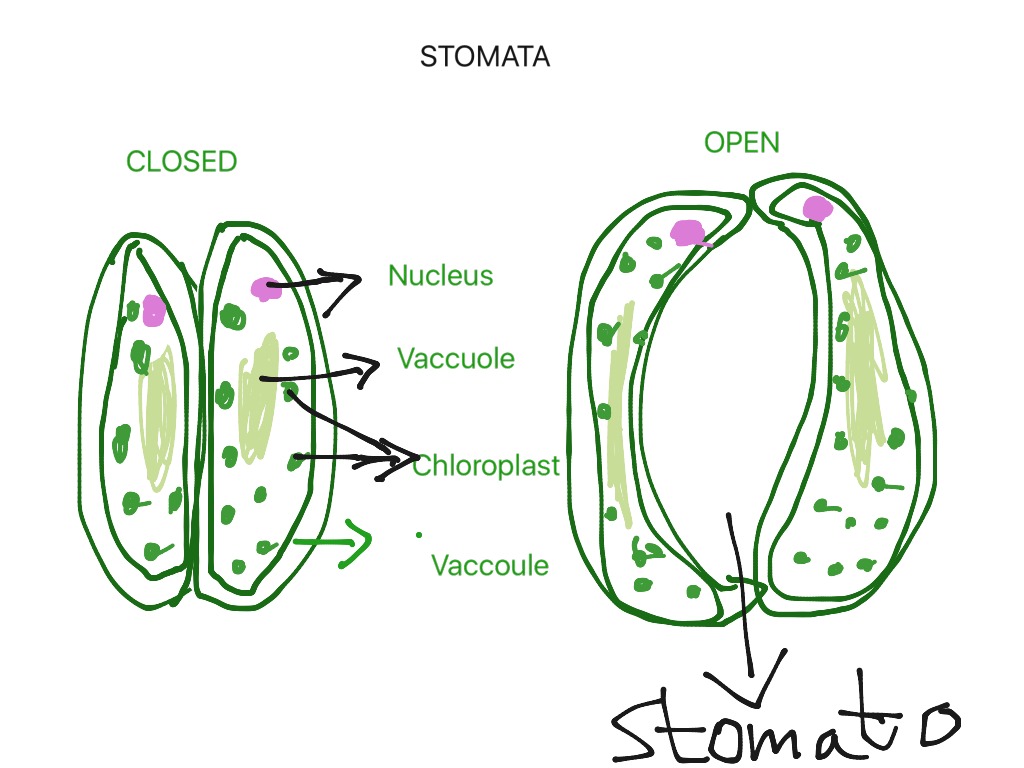 STRUCTURE OF GUARD CELLS (stomata) Science, Biology From showme.com
STRUCTURE OF GUARD CELLS (stomata) Science, Biology From showme.com
These control both the influx of co2 as a raw material for photosynthesis and water loss from plants. When the guard cells are flaccid, because of low water content, they are nearly straight and lie with their inner walls touching each other, so that the stomatal pore is closed. Guard cells help in transpiration. Guard cells allow land plants to survive under restricted or fluctuating water availability. However, for plants in hotter/dry areas, these cells are located on the lower surface of the leaf and tend to be fewer in number. Guard cells are specialized cells found in the epidermis of leaves and stems of plants.
Several environmental factors induce opening of stomata, including blue light, high humidity, and low co2.
The opening and closing of the stomatal pore are regulated by the turgidity of the guard cells. They promote the gas exchange of plants with the external environment, forming a stoma. The opening and closing of the stomatal pore are regulated by the water potential inside guard cells. The primary site of cellular respiration in plants microtubules: It has been reported that a guard cell in a c4 plant contains both pepc and rubisco. When the plant is filled with moisture, the guard cells become filled with fluid, causing the stoma to open.
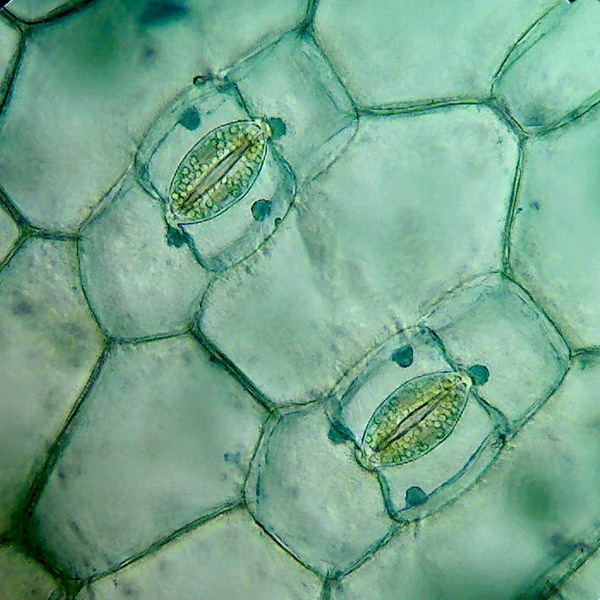 Source: microscopy-uk.org.uk
Source: microscopy-uk.org.uk
Guard cells allow land plants to survive under restricted or fluctuating water availability. Guard cells are part of the system that maintains drought resistance in plants. Nicotiana glauca (graham), tree tobacco, and beta vulgaris, sugar. Would guard cells close stomata? Optogenetic control of stomatal guard cells could help prevent transpiration in plants.
 Source: asknature.org
Source: asknature.org
Plants also utilize stomata to prevent water loss and withering away during drought. Guard cells are specialized cells found in the epidermis of leaves and stems of plants. Guard cell photosynthesis and stomatal function Thick cell walls facing the air outside the leaf and the stoma thin cell walls facing adjacent epidermal cells cellulose microfibrils arranged in bands around the cell cell walls have no plasmodesmata Guard cells help in transpiration.
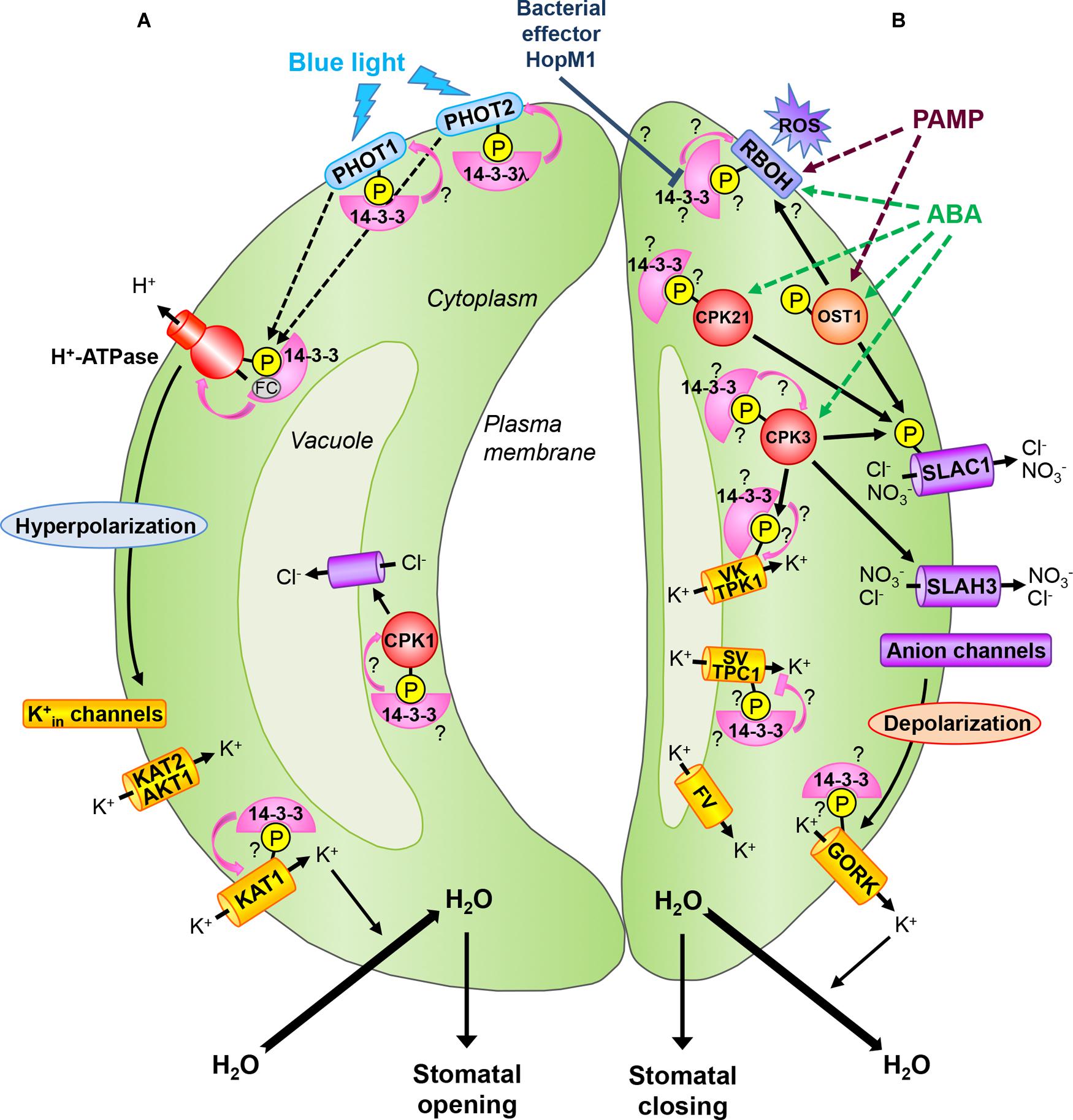 Source: journal.frontiersin.org
Source: journal.frontiersin.org
How do stomata and guard cells regulate water loss in a plant? The opening and closing of the stomatal pore are regulated by the water potential inside guard cells. Guard cells use osmotic pressure to open and close stomata, allowing plants to regulate the amount of water and solutes within them.over 95% of a plant’s water loss occurs through the stoma via water vapor. Optogenetic control of stomatal guard cells could help prevent transpiration in plants. Contains the hereditary material, or dna, of the cell mitochondria:
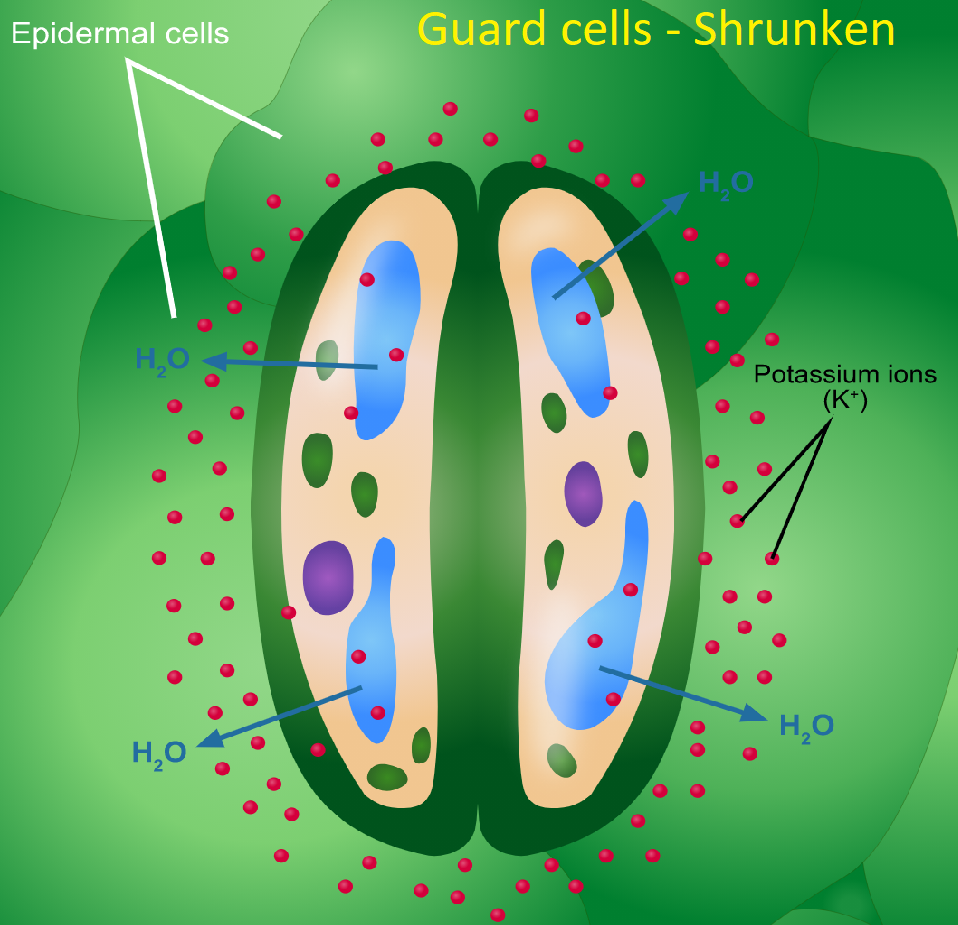 Source: vedantu.com
Source: vedantu.com
Each pair of guard cells and the regulated pore they enclose, known as a stoma or stomate, provides a conduit for atmospheric photosynthetic gas exchange (co 2 uptake and o 2 release) and transpirational release of water (h 2 o) in terrestrial plants, in addition to defense against pathogenic invasion. In low light the guard cells lose water and become flaccid , causing the. However, for plants in hotter/dry areas, these cells are located on the lower surface of the leaf and tend to be fewer in number. Again, however, stomatal closure would effectively close off this pathway of water loss although Plants also utilize stomata to prevent water loss and withering away during drought.
 Source: sciencefacts.net
Source: sciencefacts.net
Guard cells are specialized cells found in the epidermis of leaves and stems of plants. Contains the hereditary material, or dna, of the cell mitochondria: They are specialized parenchyma cells, which are the only photosynthesizing cells found in the plant epidermis. Guard cells help in transpiration. Stomata are tiny holes found in the underside of leaves.
 Source: hubpages.com
Source: hubpages.com
Stomata, the openings formed by pairs of specialized epidermal guard cells, regulate gas exchange in plants. They control water loss and gas exchange by opening and closing. In bright light the guard cells take in water by osmosis and become plump and turgid. Stomatal aperture is actively regulated by reversible changes in guard cell osmolyte content. How do stomata and guard cells regulate water loss in a plant?
 Source: pulpbits.net
Source: pulpbits.net
Guard cells help in transpiration. Guard cells are found in the epidermis of leaves and stems of plants. Because of their small size guard cells are rapidly influenced by turgor change and thus regulate the opening and closing of stomata. The opening and closing of the stomatal pore are regulated by the water potential inside guard cells. Contains the hereditary material, or dna, of the cell mitochondria:
 Source: botany.one
Source: botany.one
Each pair of guard cells and the regulated pore they enclose, known as a stoma or stomate, provides a conduit for atmospheric photosynthetic gas exchange (co 2 uptake and o 2 release) and transpirational release of water (h 2 o) in terrestrial plants, in addition to defense against pathogenic invasion. Do single guard cells in c4 plants actually perform full photosynthesis?. Guard cells of mutant plants (appendix fig s1). Guard cells in biology or guard cells in botany are specialized cells that are located in the epidermis of the leaf of a plant. Guard cells help in transpiration.
 Source: hubpages.com
Source: hubpages.com
Nicotiana glauca (graham), tree tobacco, and beta vulgaris, sugar. Each stomatal opening is surrounded by two specialized epidermal cells, called guard cells. They promote the gas exchange of plants with the external environment, forming a stoma. Guard cells are part of the system that maintains drought resistance in plants. Thick cell walls facing the air outside the leaf and the stoma thin cell walls facing adjacent epidermal cells cellulose microfibrils arranged in bands around the cell cell walls have no plasmodesmata
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Plants also utilize stomata to prevent water loss and withering away during drought. Plants have been regenerated from cultured guard cell protoplasts of two species: The opening and closing of the stomatal pore are regulated by the turgidity of the guard cells. Optogenetic control of stomatal guard cells could help prevent transpiration in plants. Guard cells help in transpiration.
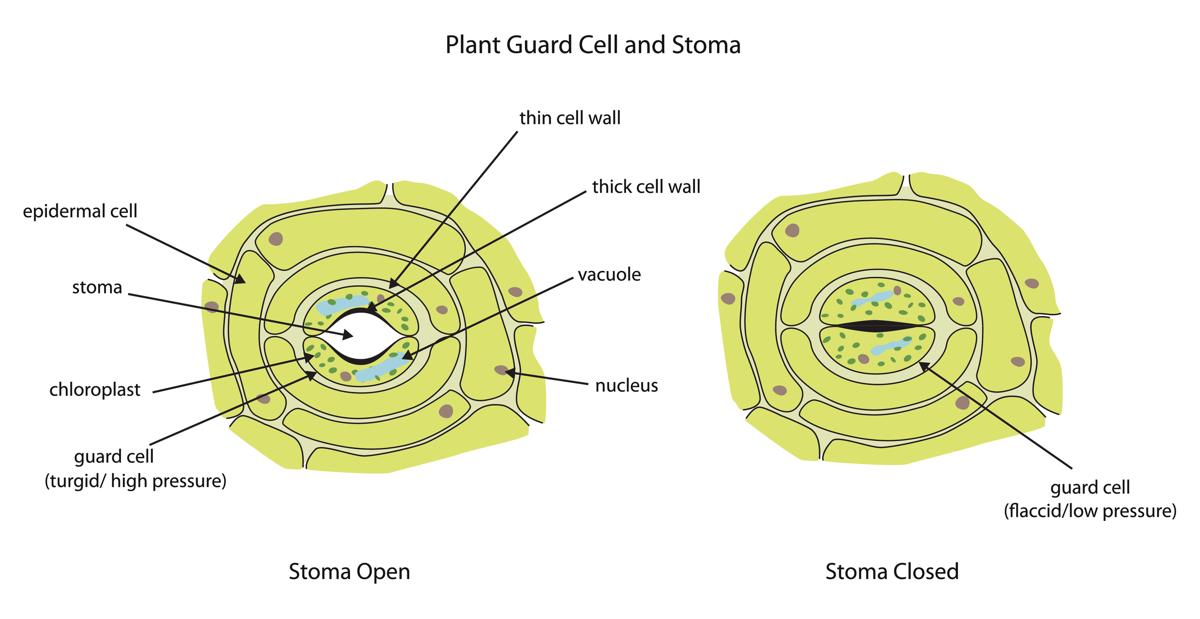 Source: biologywise.com
Source: biologywise.com
They control the exchange of gases between the external environment and the interior of the plant by regulating the aperture of stomatal pores in response to environmental stimuli such as light intensity, and are important regulators of plant productivity. When the plant loses enough moisture, the stomata wither and draw closed automatically. Stomata, the openings formed by pairs of specialized epidermal guard cells, regulate gas exchange in plants. They control water loss and gas exchange by opening and closing. The opening and closing of the stomatal pore are regulated by the turgidity of the guard cells.
 Source: showme.com
Source: showme.com
Several environmental factors induce opening of stomata, including blue light, high humidity, and low co2. However, for plants in hotter/dry areas, these cells are located on the lower surface of the leaf and tend to be fewer in number. Guard cells are part of the system that maintains drought resistance in plants. In most aquatic plants, guard cells, and thus the stomata, are located on the upper surface of the leaf which allows for more water to be released into the environment. Contains the hereditary material, or dna, of the cell mitochondria:
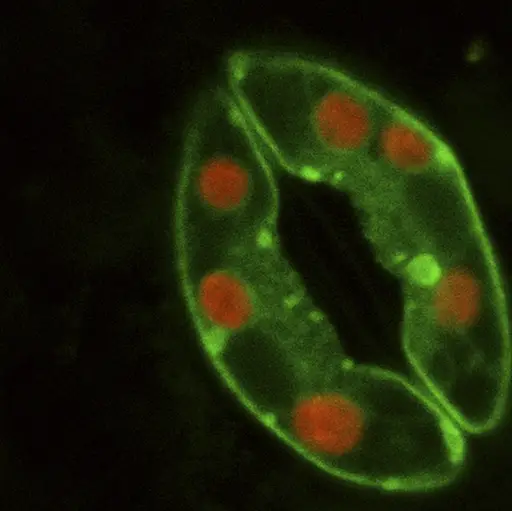 Source: microscopemaster.com
Source: microscopemaster.com
It has been reported that a guard cell in a c4 plant contains both pepc and rubisco. Plants have been regenerated from cultured guard cell protoplasts of two species: The opening and closing of the stomatal pore are regulated by the water potential inside guard cells. In bright light the guard cells take in water by osmosis and become plump and turgid. Would guard cells close stomata?

That the ventral wall of the guard cell to the outside of the pore is an area of major water loss. Guard cells are part of the system that maintains drought resistance in plants. Plants have been regenerated from cultured guard cell protoplasts of two species: When the plant is filled with moisture, the guard cells become filled with fluid, causing the stoma to open. In low light the guard cells lose water and become flaccid , causing the.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
They promote the gas exchange of plants with the external environment, forming a stoma. They control water loss and gas exchange by opening and closing. These control both the influx of co2 as a raw material for photosynthesis and water loss from plants. It has been reported that a guard cell in a c4 plant contains both pepc and rubisco. The guard cells contain abundant starch grains ;
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
Guard cells allow land plants to survive under restricted or fluctuating water availability. Guard cells are specialized cells found in the epidermis of leaves and stems of plants. Guard cell photosynthesis and stomatal function Plants have been regenerated from cultured guard cell protoplasts of two species: Plants also utilize stomata to prevent water loss and withering away during drought.
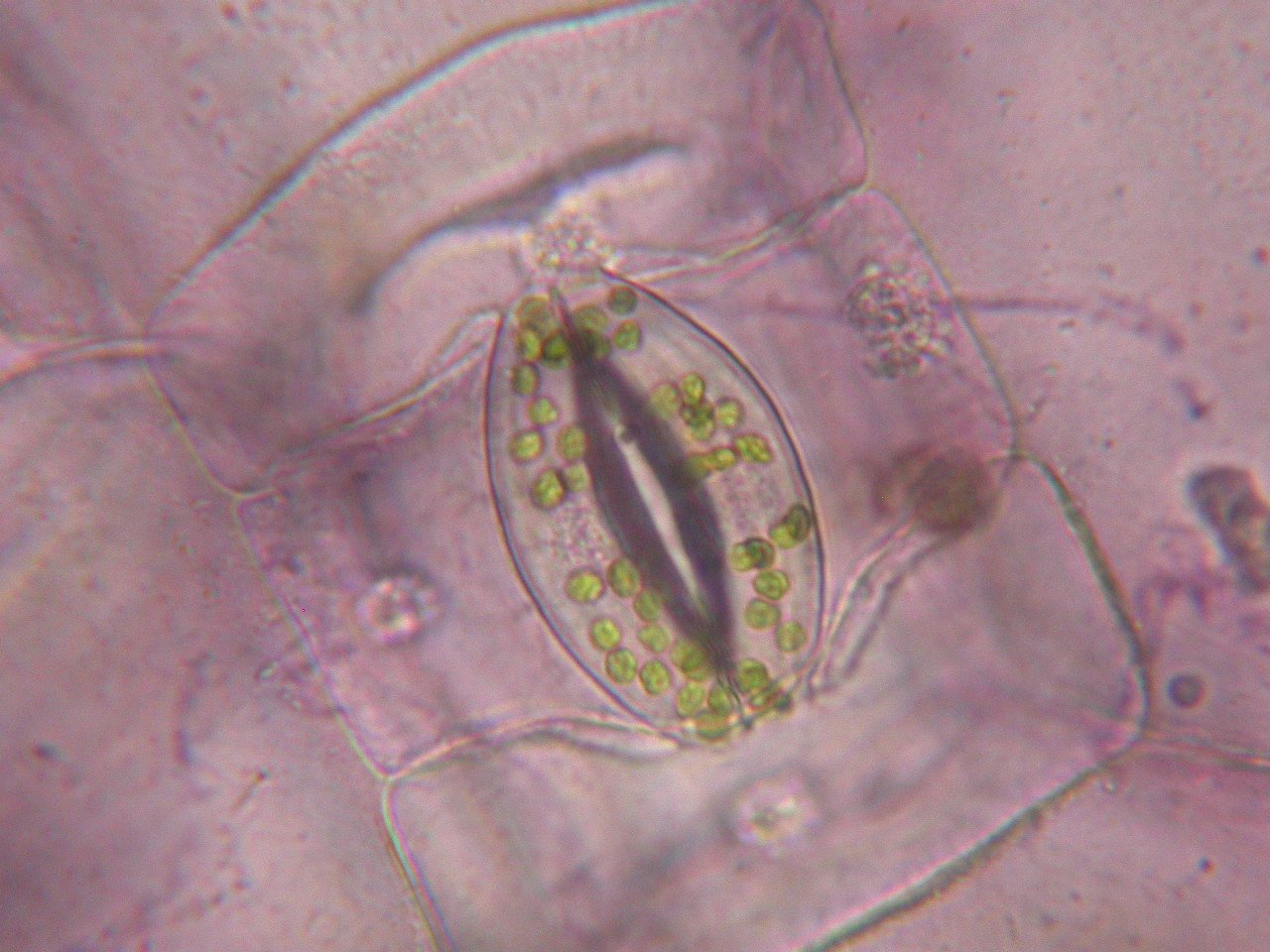 Source: employees.csbsju.edu
Source: employees.csbsju.edu
Stomatal apertures affect photosynthesis, water use efficiency, and hence crop yields. That the ventral wall of the guard cell to the outside of the pore is an area of major water loss. Guard cells allow land plants to survive under restricted or fluctuating water availability. However, for plants in hotter/dry areas, these cells are located on the lower surface of the leaf and tend to be fewer in number. Guard cells are part of the system that maintains drought resistance in plants.
 Source: biology4alevel.blogspot.com
Source: biology4alevel.blogspot.com
Stomata, the openings formed by pairs of specialized epidermal guard cells, regulate gas exchange in plants. Guard cells of mutant plants (appendix fig s1). Would guard cells close stomata? Do single guard cells in c4 plants actually perform full photosynthesis?. Guard cells allow land plants to survive under restricted or fluctuating water availability.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title guard cells in plants by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.







