Your How does a plant transport water images are ready in this website. How does a plant transport water are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the How does a plant transport water files here. Download all royalty-free photos.
If you’re looking for how does a plant transport water pictures information linked to the how does a plant transport water interest, you have come to the ideal site. Our website always gives you suggestions for viewing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly search and find more enlightening video articles and images that fit your interests.
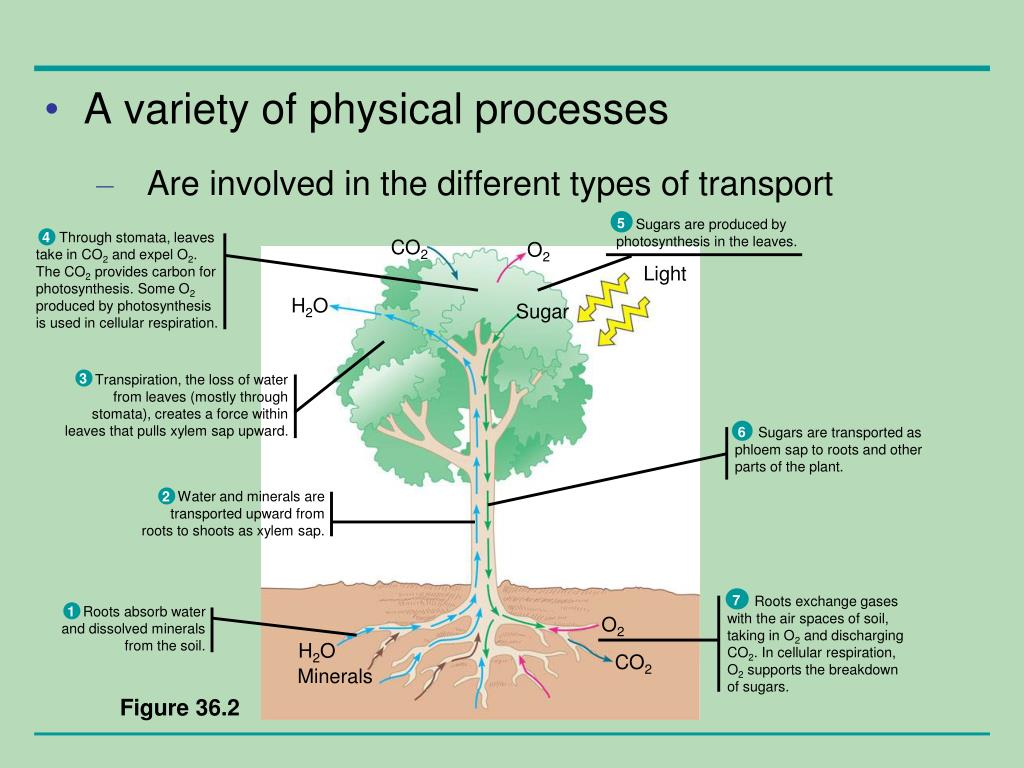
How Does A Plant Transport Water. Vessel elements are wide open tubes, whereas tracheids have more enclosed ends. 15 how is water lost in the plant. Roots absorb water from the soil where the plant is planted. Xylem tissue transports water, mineral ions, and solutes from the roots to the leaves.;
 PPT Transport in Plants II Water Balance of Plants From slideserve.com
PPT Transport in Plants II Water Balance of Plants From slideserve.com
By this process, plants synthesize their food in the leaves. Then, the water travels through the plant to the stem. Roots absorb water from the soil where the plant is planted. Also, tracheids have pits that allow for lateral water transport as. Suitable for teaching 5 to 11s. Plants use water potential to transport water to the leaves so that photosynthesis can take place.
While we have a heart to pump blood around our body, plants have to rely on physics to get water from the ground to their leaves.
Phloem tissue transports nutrients from the leaves to the rest of the plant.; As the plant dries out from the leaves, it brings more water in from the xylem due to some interesting chemical properties. Find out how water travels through a plant from the roots to the leaves.subscribe for more biology clips from bbc teach on mo. Xylem transports water and mineral salts from the roots up to other parts of the plant, while. The internal water potential of a plant cell is more negative than pure water; Only a little amount, of water, is retained in the plant or utilized by it in photosynthesis.
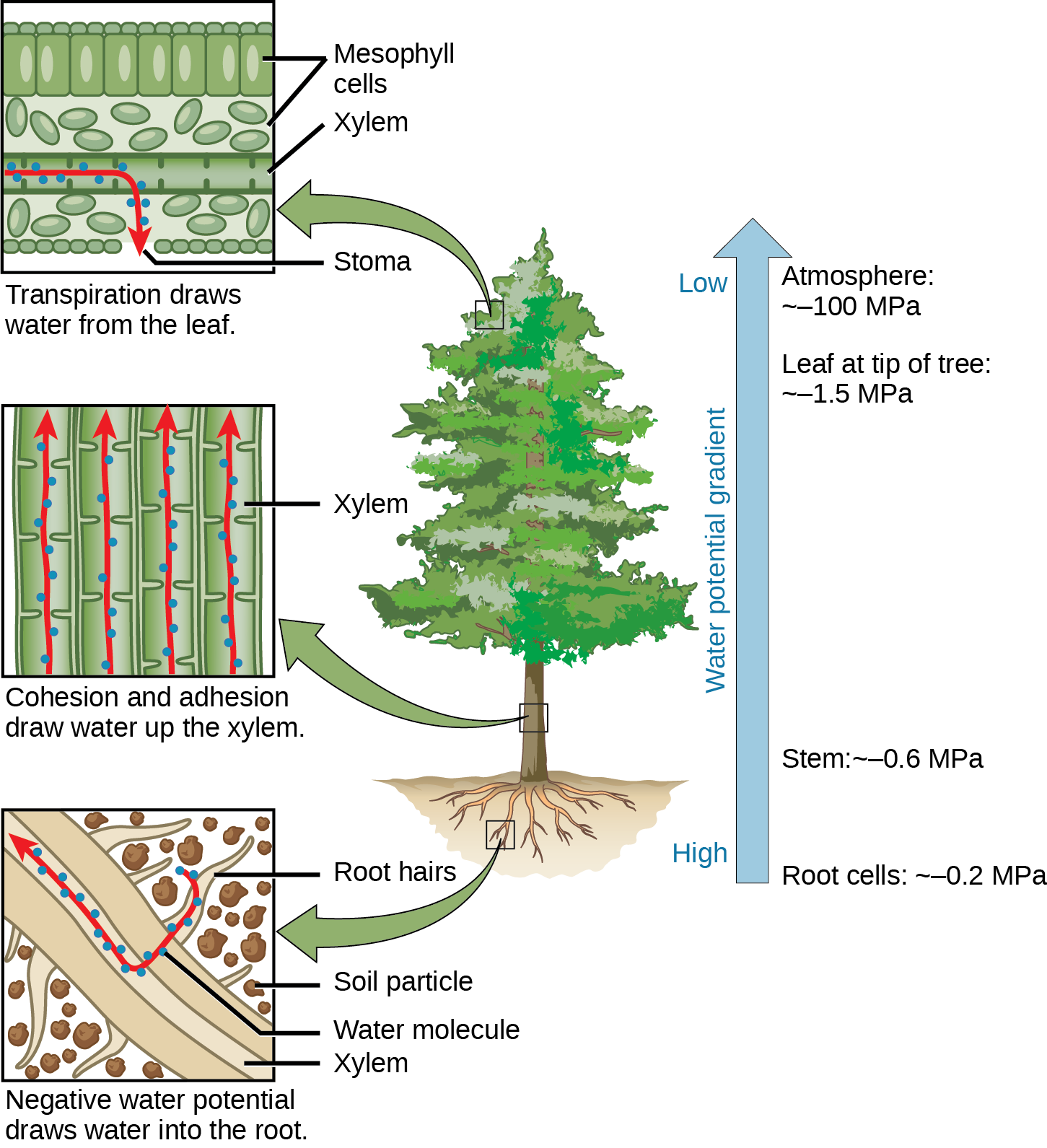 Source: opentextbc.ca
Source: opentextbc.ca
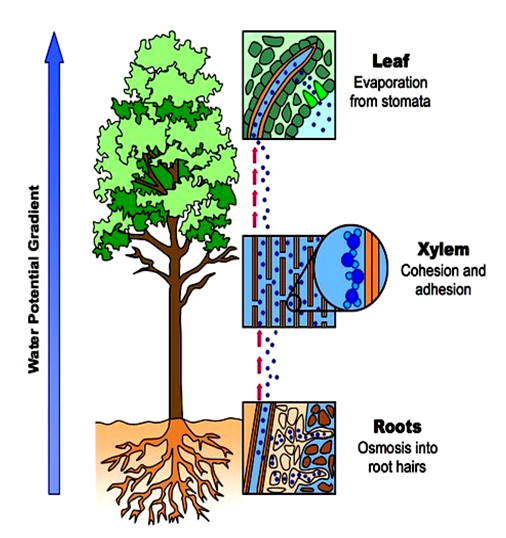
Transpiration is the process of water evaporation through specialized openings in the. The movement of water throughout a plant is driven by the loss of water through it’s leaves, or transpiration. Water is transported to all parts of plants through roots. Water potential is a measure of the potential energy in water as well as the difference between the potential in a given water sample and pure water. Water is sucked up through the stem (just like the way you suck up a drink through a straw!) and then the stem passes water on to the leaves.
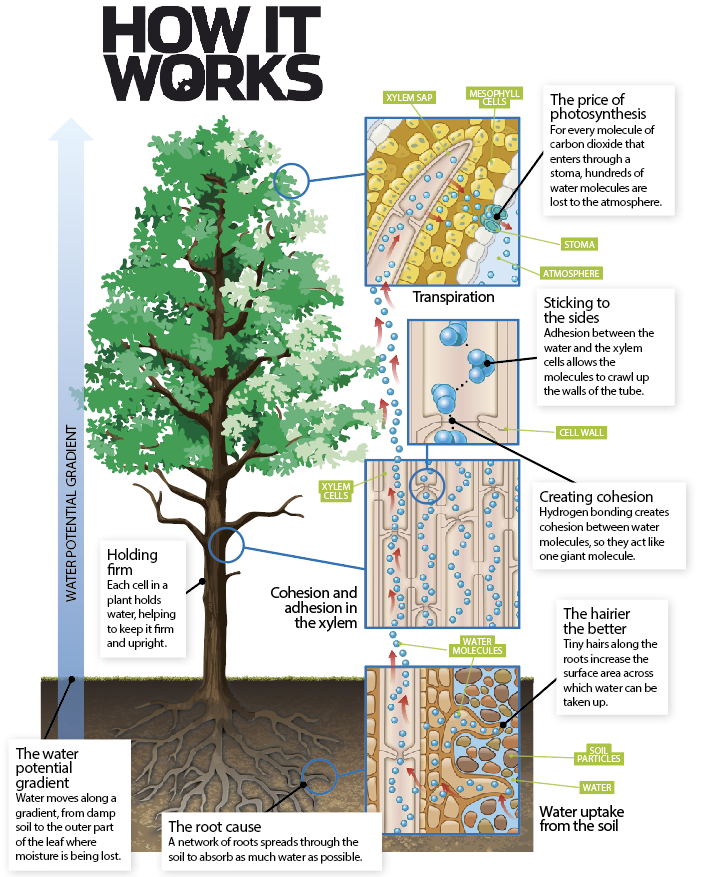 Source: howitworksdaily.com
Source: howitworksdaily.com
The main driving factor is the difference in water potential between the soil. Water moves from an area of higher total water potential (higher gibbs free energy) to an area of lower total water potential. 13 how is food transported in plants brainly? You don�t always need roots. As more water evaporates, the plant pulls up more and more water.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
This process allows plants to move water to tree canopies more than to 100 meters above the soil surface! 9 how do plants feed themselves? 3 or 4 fresh white carnations; This is expressed as δψ. Also, tracheids have pits that allow for lateral water transport as.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Transpiration is the loss of. How to prove that water moves up a plants stem. 9 how do plants feed themselves? You need to be able to recognize the xylem & phloem in three different parts of the. Plants need to transport water from the roots to the leaves.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Xylem tissue transports water, mineral ions, and solutes from the roots to the leaves.; 11 how translocation of water and foods happens inside the plant body? The three main steps of water transport in plants. 12 how is food transported? You don�t always need roots.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The main driving factor is the difference in water potential between the soil. In plants, water always moves from an area of higher water potential to an area of lower water potential. Water evaporates from the leaves into the atmosphere. Keep in mind that one requires energy and one does not. By this process, plants synthesize their food in the leaves.
 Source: oercommons.org
Source: oercommons.org
The main driving factor is the difference in water potential between the soil. The adhesion helps the transportation of sticking in the stems, while cohesion pulls the water down into the roots. 12 how is food transported? Water transport also occurs at the cellular level, as individual cells absorb and release water, and pass it along to neighboring cells. From the soil into the plant.
![Water Transport in a Plant [PPT Powerpoint] Water Transport in a Plant [PPT Powerpoint]](https://reader011.documents.pub/reader011/slide/20190125/568137e3550346895d9f8f49/document-10.png?t=1606852641) Source: documents.pub
Source: documents.pub
Water transport also occurs at the cellular level, as individual cells absorb and release water, and pass it along to neighboring cells. Water potential is represented by the equation ψ system = ψ total = ψ s + ψ p + ψ g + ψ m. Keep in mind that one requires energy and one does not. In plants, this transport includes moving sugars from the photosynthetic parts of a plant (the leaves ) to non. The plant then sucks up more.
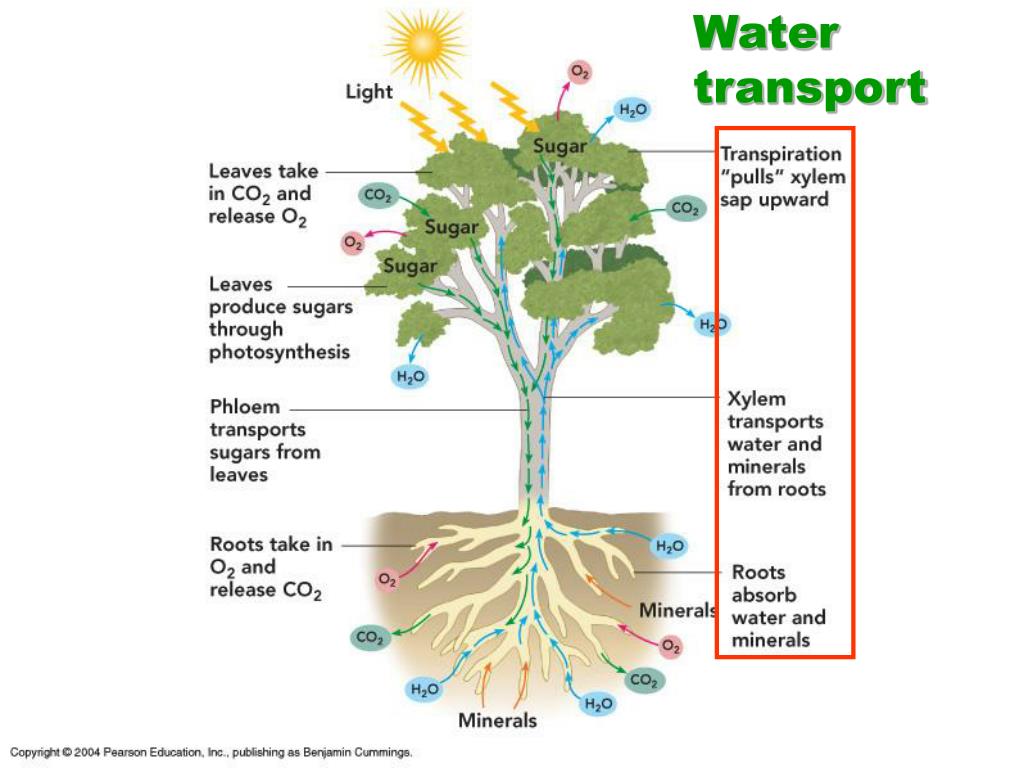 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Plants have tissues to transport water, nutrients and minerals. While we have a heart to pump blood around our body, plants have to rely on physics to get water from the ground to their leaves. This is called capillary action and this process helps plants collect the necessary nutrients from water as it transports down the stem. The transport system in plants is mainly made of the xylem and phloem tissue. This process is called transpiration.
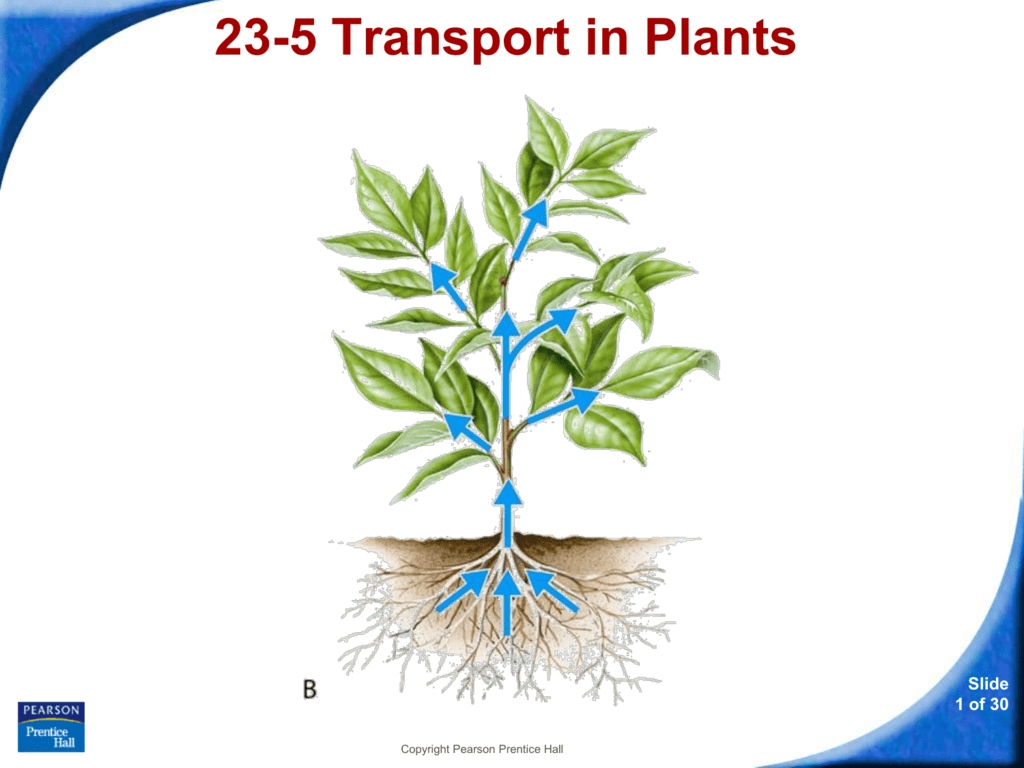 Source: studylib.net
Source: studylib.net
As more water evaporates, the plant pulls up more and more water. View in classroom curriculum download (pdf) core content. Suitable for teaching 5 to 11s. Water potential is a measure of the potential energy in water as well as the difference between the potential in a given water sample and pure water. Water potential is represented by the equation ψ system = ψ total = ψ s + ψ p + ψ g + ψ m.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Essentially all of the water used by land plants is absorbed from the soil by roots. Keep in mind that one requires energy and one does not. View in classroom curriculum download (pdf) core content. Only a little amount, of water, is retained in the plant or utilized by it in photosynthesis. Plants need to transport water from the roots to the leaves.
 Source: efcl.postech.ac.kr
Source: efcl.postech.ac.kr
A root system consists of a complex network of individual roots that vary in age. Water potential is represented by the equation ψ system = ψ total = ψ s + ψ p + ψ g + ψ m. Water also diffuses out of the stomata at the same time, drying out the inside of the leaf ever so slightly. The tension created by transpiration “pulls” water in the plant xylem, drawing the water upward in much the same way that you draw water upward when you suck on a straw. In plants, water always moves from an area of higher water potential to an area of lower water potential.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Water moves from an area of higher total water potential (higher gibbs free energy) to an area of lower total water potential. Also, tracheids have pits that allow for lateral water transport as. Water potential is represented by the equation ψ system = ψ total = ψ s + ψ p + ψ g + ψ m. How is water transported in plants? 3 or 4 fresh white carnations;
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
10 what helps in transportation of water in plants? The adhesion helps the transportation of sticking in the stems, while cohesion pulls the water down into the roots. Vessel elements are wide open tubes, whereas tracheids have more enclosed ends. As openings on the leaves (known as stomata) open to allow carbon dioxide in, water evaporates through transpiration. As a result, the combined cohesion and adhesion forces create a constant chain of water molecules moving up the plant.
 Source: dreamstime.com
Source: dreamstime.com
It is driven by capillary action and in some plants by root pressure. 13 how is food transported in plants brainly? 3 or 4 fresh white carnations; 11 how translocation of water and foods happens inside the plant body? Transpiration is the process of water evaporation through specialized openings in the.
 Source: vdocuments.mx
Source: vdocuments.mx
The transport system in plants is mainly made of the xylem and phloem tissue. Solutes, pressure, gravity, and matric potential are all important for the transport of water in plants. 11 how translocation of water and foods happens inside the plant body? The main driving force of water uptake and transport into a plant is transpiration of water from leaves. Only a little amount, of water, is retained in the plant or utilized by it in photosynthesis.
 Source: ombiology4u.blogspot.com
Source: ombiology4u.blogspot.com
You need to be able to recognize the xylem & phloem in three different parts of the. Suitable for teaching 5 to 11s. Water enters and leaves cells through osmosis, the passive diffusion of water across a membrane. Transpiration is the process of water evaporation through specialized openings in the. By this process, plants synthesize their food in the leaves.
 Source: ussromantics.com
Source: ussromantics.com
The plant then sucks up more. How does a plant transport water? This is called capillary action and this process helps plants collect the necessary nutrients from water as it transports down the stem. Water potential is a measure of the potential energy in water as well as the difference between the potential in a given water sample and pure water. This is expressed as δψ.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title how does a plant transport water by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






